Summary
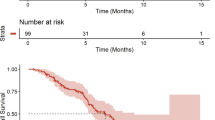
Purpose The oral PI3K inhibitor BKM120 has been reported as safe and well tolerated in early phase clinical trials of advanced cancer patients. We performed a phase I trial of BKM120 plus mFOLFOX6 (5-FU/LV + oxaliplatin), a common chemotherapeutic backbone in GI malignancies, to establish the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and characterize the safety and tolerability of the combination. Methods Patients with advanced solid tumors received oral BKM120 daily combined with standard doses of mFOLFOX6 every 2 weeks of a 28 day cycle. The study utilized a standard 3 + 3 dose escalation schema. Results A total of 17 patients received treatment with BKM120, 13 of which were evaluate for dose limited toxicity (DLT). The most common tumor types were colorectal cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. DLT included grade 3 hyperglycemia, grade 3 AST/ALT elevation, grade 4 neutropenia and grade 4 thrombocytopenia. A total of 76 % of patients experienced treatment related grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs), the most common of which were neutropenia, fatigue, leukopenia, hyperglycemia and thrombocytopenia. One patient demonstrated an unconfirmed partial response and three patients had stable disease. Discussion The MTD of BKM120 in combination with standard doses of mFOLFOX6 was 40 mg daily, which is well below the 100 mg daily dose proven effective and tolerable both as a single agent and in combination with other chemotherapeutics. In addition, the regimen of BKM120 with mFOLFOX6 in patients with refractory solid tumors resulted in increased toxicity than would be expected from either the PI3K inhibitor or the chemotherapy backbone alone.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown KK, Toker A (2015) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway and therapy resistance in cancer. F1000Prime Rep 7:13
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(7):489–501
Cai X et al. (2015) Synergistic inhibition of colon carcinoma cell growth by Hedgehog-Gli1 inhibitor arsenic trioxide and phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002. Onco Targets Ther 8:877–883
Cheng HB et al. (2015) Longikaurin E induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via modulation of the p38 and PI3K/AKT pathways by ROS. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388(6):623–634
Simioni C et al. (2015) The novel dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 displays cytotoxic activity in both normoxic and hypoxic hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 6:17147–17160
Zheng YB et al. (2015) Paeoniflorin inhibits human gastric carcinoma cell proliferation through up-regulation of microRNA-124 and suppression of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling. World J Gastroenterol 21(23):7197–7207
Horiguchi H et al. (2014) Angiopoietin-like protein 2 renders colorectal cancer cells resistant to chemotherapy by activating spleen tyrosine kinase-phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent anti-apoptotic signaling. Cancer Sci 105(12):1550–1559
Li B et al. (2014) Suppression of esophageal tumor growth and chemoresistance by directly targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 5(22):11576–11587
Ng SSW et al. (2000) Inhibition of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 60(19):5451–5455
Bendell JC et al. (2012) Phase I, dose-escalation study of BKM120, an oral pan-Class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 30(3):282–290
Hyman DM et al. (2015) Parallel phase Ib studies of two schedules of buparlisib (BKM120) plus carboplatin and paclitaxel (q21 days or q28 days) for patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75(4):747–755
Mayer IA et al. (2014) Stand up to cancer phase Ib study of pan-phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor buparlisib with letrozole in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 32(12):1202–1209
Zambrano CC, Schuler MH, Machiels J-PH, Hess D, Paz-Ares L, Awada A, von Moos R, Steeghs N, Ahnert JR, De Mesmaeker P, Richly H, Herremans C, Joerger M, Jaime JC, Alsina M, Baffert F, Demanse D, Duval V, Morozov A, Dirix L (2014) Phase lb study of buparlisib (BKM120) plus either paclitaxel (PTX) in advanced solid tumors (aST) or PTX plus trastuzumab (TZ) in HER2+ breast cancer (BC). J Clin Oncol 32(5s):abstract 627
Goldberg RM et al. (2004) A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(1):23–30
Tournigand C et al. (2004) FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 22(2):229–237
Feng JP et al. (2013) Secondary diabetes associated with 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy regimens in non-diabetic patients with colorectal cancer: results from a single-centre cohort study. Color Dis 15(1):27–33
Feng JP et al. (2010) Impact of 5-fluorouracil on glucose metabolism and pancreatic pathology in rats. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 13(12):935–938
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge grant funding support for this project. Dr. McRee receives support from the UNC Calabresi K12 Career Development Grant 2K12CA120780-06. Dr. Sanoff receives support from the National Cancer Institute K07CA160722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Hanna Sanoff has received research funding from Novartis. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McRee, A.J., Sanoff, H.K., Carlson, C. et al. A phase I trial of mFOLFOX6 combined with the oral PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 33, 1225–1231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0298-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0298-3