Summary
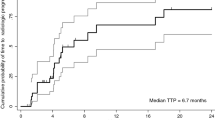
Background Ganetespib (STA-9090) is an Hsp90 inhibitor that downregulates VEGFR, c-MET, HER2, IGF-IR, EGFR, and other Hsp90 client proteins involved in hepatocarcinogenesis, thereby making it an attractive therapy for HCC. This Phase I study was performed to establish the safety, tolerability, recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D), and preliminary clinical activity of ganetespib in previously treated patients with advanced HCC. Methods Patients with advanced HCC, Child-Pugh A cirrhosis, progression on or intolerance to sorafenib, and ECOG PS ≤ 1 were enrolled in a standard 3x3 dose escalation study at doses of 100 mg/m2, 150 mg/m2, and 200 mg/m2 IV given on days 1, 8, and 15 of each 28-day cycle. Objective response by RECIST version 1.1 criteria was evaluated by CT/MRI every 8 weeks. Results Fourteen patients were enrolled in this trial and received at least one dose of the study drug. Of the 14 patients: median age, 57 years old; male 71 %; Asian 36 %; HCC etiology (HBV 36 %, HCV 43 %, Hemachromatosis 7 %, unknown 21 %); Child Pugh Class (A 93 %, B 7 %); median number of prior treatments 2; median baseline AFP 70.1 ng/mL. The RP2D was determined to be 200 mg/m2. The most commonly seen AEs were diarrhea (93 %), fatigue (71 %), AST elevation (64 %), and hyperglycemia (64 %). The most common Gr 3/4 AEs were hyperglycemia (21 %) and lipasemia (21 %). One (7 %) patient had a fatal AE, septic shock, within 30 days of receiving the study drug. One dose-limiting toxicity, grade 3 lipasemia, was observed at the 100 mg/m2 dose. Pharmacokinetics studies showed a t1/2, CL, Tmax, and Vss of 6.45 h, 48.28 L/h (25.56 L/h/m2), 0.76 h, and 191 L (100.4 L/m2), respectively. No objective responses were seen; one patient (7 %) had stable disease at 16 weeks. Median time to progression was 1.8 months, and median overall survival was 7.2 months. Conclusion Ganetespib had a manageable safety profile in patients with advanced HCC who had progressed on at least one line of systemic therapy. The pharmacokinetic profile showed that ganetespib exposure in patients with mild hepatic dysfunction is similar to that seen in patients with normal liver function. Ganetespib showed limited clinical benefit in patients with advanced HCC in this phase I trial.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay, J., GLOBOCAN 2008 v1.2, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase [Internet]. International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, <country-region > </country-region > France, 2010; Vol. No. 10
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Häussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J, Group SIS (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–90
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34
Qin S, Bai Y, Ye S, Al E (2010) Phase III study of oxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin (FOLFOX4) versus doxorubicin as palliative systemic chemotherapy in advanced HCC in Asian patients. J Clin Oncol 28
Gish RG, Porta C, Lazar L, Ruff P, Feld R, Croitoru A, Feun L, Jeziorski K, Leighton J, Gallo J, Kennealey GT (2007) Phase III randomized controlled trial comparing the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with nolatrexed or doxorubicin. J Clin Oncol 25:3069–75
Lai CL, Wu PC, Chan GC, Lok AS, Lin HJ (1988) Doxorubicin versus no antitumor therapy in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. A prospective randomized trial. Cancer 62:479–83
Cheng A (2011) Phase III trial of sunitinib (Su) versus Sorafenib (So) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In 2011 ASCO Annual Meeting, J Clin Oncol Vol. 29
Johnson PJ, Qin S, Park JW, Poon RT, Raoul JL, Philip PA, Hsu CH, Hu TH, Heo J, Xu J, Lu L, Chao Y, Boucher E, Han KH, Paik SW, Robles-Aviña J, Kudo M, Yan L, Sobhonslidsuk A, Komov D, Decaens T, Tak WY, Jeng LB, Liu D, Ezzeddine R, Walters I, Cheng AL (2013) Brivanib versus Sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with unresectable, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-FL study. J Clin Oncol 31:3517–24
Cainap C, Qin S, Huang W-T, Chung IJ, Pan H, Cheng Y, Kudo M, Kang YK, Chen PJ, Toh HC, Gorbunova V, Eskens F, Qian J, McKee MD, Ricker JL, Carlson DM, El Nowiem S (2012) Phase III trial of linifanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin Oncol 30: (suppl 34; abstr 249)
Zhu AX, RO, Evans J, et al (2012) SEARCH: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sorafenib plus erlotinib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In 37th Annual European Society for Medical Oncology Congress, Vienna, Austria
Izzo, C., Ramucirumab Misses Primary Endpoint in Phase III HCC Trial. 2014
Llovet JM, Decaens T, Raoul JL, Boucher E, Kudo M, Chang C, Kang YK, Assenat E, Lim HY, Boige V, Mathurin P, Fartoux L, Lin DY, Bruix J, Poon RT, Sherman M, Blanc JF, Finn RS, Tak WY, Chao Y, Ezzeddine R, Liu D, Walters I, Park JW (2013) Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom Sorafenib failed: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J Clin Oncol 31:3509–16
Zhu AX, Kudo M, Assenat E, Cattan S, Kang Y-K, Lim HY, Poon RTP, Blanc J-F, Vogel A, Chen C-L, Dorval E, Peck-Radsavljevic M, Santoro A, Daniele B, Furuse J, Jappe A, Perraud KP, Anak O, Sellami DB, Chen L-T (2014) In EVOLVE-1: Phase 3 study of everolimus for advanced HCC that progressed during or after Sorafenib. Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, JCO, San Francisco
Trepel J, Mollapour M, Giaccone G, Neckers L (2010) Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10:537–49
Whitesell L, Lindquist SL (2005) HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5:761–72
Mimnaugh EG, Chavany C, Neckers L (1996) Polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the p185c-erbB-2 receptor protein-tyrosine kinase induced by geldanamycin. J Biol Chem 271:22796–801
Schneider C, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Nimmesgern E, Ouerfelli O, Danishefsky S, Rosen N, Hartl FU (1996) Pharmacologic shifting of a balance between protein refolding and degradation mediated by Hsp90. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:14536–41
Pascale RM, Simile MM, Calvisi DF, Frau M, Muroni MR, Seddaiu MA, Daino L, Muntoni MD, De Miglio MR, Thorgeirsson SS, Feo F (2005) Role of HSP90, CDC37, and CRM1 as modulators of P16 (INK4A) activity in rat liver carcinogenesis and human liver cancer. Hepatology 42:1310–9
Lee CL, Hsiao HH, Lin CW, Wu SP, Huang SY, Wu CY, Wang AH, Khoo KH (2003) Strategic shotgun proteomics approach for efficient construction of an expression map of targeted protein families in hepatoma cell lines. Proteomics 3:2472–86
Leng AM, Liu T, Yang J, Cui JF, Li XH, Zhu YN, Xiong T, Zhang G, Chen Y (2012) The apoptotic effect and associated signalling of HSP90 inhibitor 17-DMAG in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Biol Int 36:893–9
Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ding, W.; Zheng, K.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Xia, M.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y., The Hsp90 inhibitor SNX-2112 induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells: The role of ER stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014.
Ying W, Du Z, Sun L, Foley KP, Proia DA, Blackman RK, Zhou D, Inoue T, Tatsuta N, Sang J, Ye S, Acquaviva J, Ogawa LS, Wada Y, Barsoum J, Koya K (2012) Ganetespib, a unique triazolone-containing Hsp90 inhibitor, exhibits potent antitumor activity and a superior safety profile for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 11:475–84
Sang J, Acquaviva J, Friedland JC, Smith DL, Sequeira M, Zhang C, Jiang Q, Xue L, Lovly CM, Jimenez JP, Shaw AT, Doebele RC, He S, Bates RC, Camidge DR, Morris SW, El-Hariry I, Proia DA (2013) Targeted inhibition of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 overcomes ALK inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov 3:430–43
Jhaveri, K.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Lake, D.; Gilewski, T.; Robson, M.; Goldfarb, S.; Drullinsky, P.; Sugarman, S.; Leiblich, C. W.; Fasano, J.; Moynahan, M. E.; D’Andrea, G.; Lim, K.; Reddington, L.; Haque, S.; Patil, S.; Bauman, L.; Vukovic, V.; El-Hariry, I.; Hudis, C.; Modi, S., A Phase II Open-Label Study of Ganetespib, a Novel Heat Shock Protein 90 Inhibitor for Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 2013
Socinski MA, Goldman J, El-Hariry I, Koczywas M, Vukovic V, Horn L, Paschold E, Salgia R, West H, Sequist LV, Bonomi P, Brahmer J, Chen LC, Sandler A, Belani CP, Webb T, Harper H, Huberman M, Ramalingam S, Wong KK, Teofilovici F, Guo W, Shapiro GI (2013) A multicenter phase II study of ganetespib monotherapy in patients with genotypically defined advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:3068–77
Goldman JW, Raju RN, Gordon GA, El-Hariry I, Teofilivici F, Vukovic VM, Bradley R, Karol MD, Chen Y, Guo W, Inoue T, Rosen LS (2013) A first in human, safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity phase I study of once weekly administration of the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib (STA-9090) in patients with solid malignancies. BMC Cancer 13:152
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 362:1907–17
Patel H, Egorin MJ, Remick SC, Mulkerin D, Takimoto CHM, Doroshow JH, Potter D, Ivy SP, Murgo AJ, Ramanathan RK (2004) Comparison of child-Pugh (CP) criteria and NCI organ dysfunction working group (NCI-ODWG) criteria for hepatic dysfunction (HD): implications for chemotherapy dosing. In J Clin Oncol 22:14s, (suppl;abst 6051), 2004
Supko JG, Hickman RL, Grever MR, Malspeis L (1995) Preclinical pharmacologic evaluation of geldanamycin as an antitumor agent. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 36:305–15
Saif MW, Erlichman C, Dragovich T, Mendelson D, Toft D, Burrows F, Storgard C, Von Hoff D (2013) Open-label, dose-escalation, safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of intravenously administered CNF1010 (17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin [17-AAG]) in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71:1345–55
Strassburg CP, Kalthoff S, Ehmer U (2008) Variability and function of family 1 uridine-5’-diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGT1A). Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 45:485–530
Acquaviva, J.; He, S.; Zhang, C.; Jimenez, J. P.; Nagai, M.; Sang, J.; Sequeira, M.; Smith, D. L.; Shin Ogawa, L.; Inoue, T.; Tatsuta, N.; Knowles, M. A.; Bates, R. C.; Proia, D. A., FGFR3 Translocations in Bladder Cancer: Differential Sensitivity to HSP90 Inhibition Based on Drug Metabolism. Mol Cancer Res 2014
Strassburg CP, Oldhafer K, Manns MP, Tukey RH (1997) Differential expression of the UGT1A locus in human liver, biliary, and gastric tissue: identification of UGT1A7 and UGT1A10 transcripts in extrahepatic tissue. Mol Pharmacol 52:212–20
Kamal A, Thao L, Sensintaffar J, Zhang L, Boehm MF, Fritz LC, Burrows FJ (2003) A high-affinity conformation of Hsp90 confers tumour selectivity on Hsp90 inhibitors. Nature 425:407–10
Ramalingam, S., GD; Andric, Z.; Bondarenko, I.; Zaric, B.; Ceric, T.; al., e., A randomized study of ganetespib, a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel versus docetaxel alone for second-line therapy of lung adenocarcinoma (GALAXY-1). In ASCO, J Clin Oncol 31, s.; CRA8007), a., Eds. Chicago, 2013
Guo, W.; Yan, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; E, Q.; Gao, P.; Ye, X.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J., Targeting GRP75 Improves HSP90 Inhibitor Efficacy by Enhancing p53-Mediated Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85766
Chen Y, Chen J, Loo A, Jaeger S, Bagdasarian L, Yu J, Chung F, Korn J, Ruddy D, Guo R, McLaughlin ME, Feng F, Zhu P, Stegmeier F, Pagliarini R, Porter D, Zhou W (2013) Targeting HSF1 sensitizes cancer cells to HSP90 inhibition. Oncotarget 4:816–29
Acknowledgments
We received research support for this trial from Synta Pharmaceuticals.
Conflict of interest
AXZ has served consultant/advisory roles for Sanofi-aventis, Eisai, Daiichi Sankyo, and Exelixis. MDK and JC compensated by Synta. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, L., Wadlow, R.C., Blaszkowsky, L.S. et al. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of ganetespib (STA-9090) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 33, 128–137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0164-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0164-8