Summary
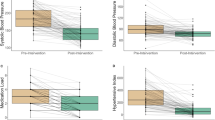
Background The purposes of this study were to establish a novel blood pressure (BP) scoring method and to correlate it with clinical response in advanced cancer patients treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies. Methods We retrospectively analyzed data for 368 patients from 23 clinical trials that included at least one anti-VEGF agent. We determined BP scores using the traditional Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.0 and our novel method that considers both BP readings and number of anti-hypertensive medications the patient received. BP scores were categorized at baseline and four months. Logistic regression analysis correlated elevated scores with clinical response. Agreement between the CTCAE and the new method was assessed. Results Under the new BP scoring method, partial response rates were 20 % in patients with an elevated score at four months versus 6 % in patients without elevated score (P < 0.001). When adjusted for tumor type, age, sex, history of anti-VEGF treatment, and number of anti-VEGF treatments, elevated BP under the new scoring method had an odds ratio of 3.8 (95 % confidence interval [CI]: 1.8, 8.2; P < 0.001). The kappa statistic for agreement between the CTCAE and new scoring methods was 0.57 (95 % CI: 0.47, 0.67; P < 0.001), indicating significant concordance. Conclusion Using the novel scoring method, an increase in BP scores was a marker for favorable clinical response in patients who received anti-VEGF treatment. This new method ultimately provides information with regard to clinical tumor response over and above that provided by the CTCAE scoring method.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ichihara E, Kiura K, Tanimoto M (2011) Targeting angiogenesis in cancer therapy. Acta Med Okayama 65(6):353–362
Folkman J (2006) Antiangiogenesis in cancer therapy–endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Exp Cell Res 312(5):594–607. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.015
Linkous AG, Yazlovitskaya EM (2012) Novel therapeutic approaches for targeting tumor angiogenesis. Anticancer Res 32(1):1–12
Kabbinavar F, Hurwitz HI, Fehrenbacher L, Meropol NJ, Novotny WF, Lieberman G, Griffing S, Bergsland E (2003) Phase II, randomized trial comparing bevacizumab plus fluorouracil (FU)/leucovorin (LV) with FU/LV alone in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 21(1):60–65
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski RM (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(2):125–134. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa060655
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(2):115–124. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065044
Chen HX, Cleck JN (2009) Adverse effects of anticancer agents that target the VEGF pathway. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(8):465–477. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.94
Wu S, Chen JJ, Kudelka A, Lu J, Zhu X (2008) Incidence and risk of hypertension with sorafenib in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 9(2):117–123. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70003-2
Le Tourneau C, Raymond E, Faivre S (2007) Sunitinib: a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor. A brief review of its therapeutic potential in the treatment of renal carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Ther Clin Risk Manag 3(2):341–348
Bergsland E, Dickler MN (2004) Maximizing the potential of bevacizumab in cancer treatment. Oncologist 9(Suppl 1):36–42
Sunshine SB, Dallabrida SM, Durand E, Ismail NS, Bazinet L, Birsner AE, Sohn R, Ikeda S, Pu WT, Kulke MH, Javaherian K, Zurakowski D, Folkman JM, Rupnick M (2012) Endostatin lowers blood pressure via nitric oxide and prevents hypertension associated with VEGF inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(28):11306–11311. doi:10.1073/pnas.1203275109
Scartozzi M, Galizia E, Chiorrini S, Giampieri R, Berardi R, Pierantoni C, Cascinu S (2009) Arterial hypertension correlates with clinical outcome in colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line bevacizumab. Ann Oncol 20(2):227–230. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn637
De Stefano A, Carlomagno C, Pepe S, Bianco R, De Placido S (2011) Bevacizumab-related arterial hypertension as a predictive marker in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68(5):1207–1213. doi:10.1007/s00280-011-1604-1
Rini BI, Cohen DP, Lu DR, Chen I, Hariharan S, Gore ME, Figlin RA, Baum MS, Motzer RJ (2011) Hypertension as a biomarker of efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(9):763–773. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr128
Institute NC (2009) Common terminology criteria for adverse events v4.0 In Edition 2009
Cifkova R, Erdine S, Fagard R, Farsang C, Heagerty AM, Kiowski W, Kjeldsen S, Luscher T, Mallion JM, Mancia G, Poulter N, Rahn KH, Rodicio JL, Ruilope LM, van Zwieten P, Waeber B, Williams B, Zanchetti A (2003) Practice guidelines for primary care physicians: 2003 ESH/ESC hypertension guidelines. J Hypertens 21(10):1779–1786. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000084773.37215.1b
Cuddy ML (2005) Treatment of hypertension: guidelines from JNC 7 (the seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure 1). J Pract Nurs 55(4):17–21, quiz 22–13
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Mir O, Coriat R, Cabanes L, Ropert S, Billemont B, Alexandre J, Durand JP, Treluyer JM, Knebelmann B, Goldwasser F (2011) An observational study of bevacizumab-induced hypertension as a clinical biomarker of antitumor activity. Oncologist 16(9):1325–1332. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0002
George S, Reichardt P, Lechner T, Li S, Cohen DP, Demetri GD (2012) Hypertension as a potential biomarker of efficacy in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated with sunitinib. Ann Oncol 23(12):3180–3187. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds179
Gallagher DJ, Al-Ahmadie H, Ostrovnaya I, Gerst SR, Regazzi A, Garcia-Grossman I, Riches J, Gounder SK, Flaherty AM, Trout A, Milowsky MI, Bajorin DF (2011) Sunitinib in urothelial cancer: clinical, pharmacokinetic, and immunohistochemical study of predictors of response. Eur Urol 60(2):344–349. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2011.05.034
Powe DG, Voss MJ, Zanker KS, Habashy HO, Green AR, Ellis IO, Entschladen F (2010) Beta-blocker drug therapy reduces secondary cancer formation in breast cancer and improves cancer specific survival. Oncotarget 1(7):628–638
Powe DG, Entschladen F (2011) Targeted therapies: using beta-blockers to inhibit breast cancer progression. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8(9):511–512. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.123
Melhem-Bertrandt A, Chavez-Macgregor M, Lei X, Brown EN, Lee RT, Meric-Bernstam F, Sood AK, Conzen SD, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2011) Beta-blocker use is associated with improved relapse-free survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(19):2645–2652. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4441
Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM, Takahashi R, Lu C, Jennings NB, Armaiz-Pena G, Bankson JA, Ravoori M, Merritt WM, Lin YG, Mangala LS, Kim TJ, Coleman RL, Landen CN, Li Y, Felix E, Sanguino AM, Newman RA, Lloyd M, Gershenson DM, Kundra V, Lopez-Berestein G, Lutgendorf SK, Cole SW, Sood AK (2006) Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med 12(8):939–944
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ, National Heart L, Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention DE, Treatment of High Blood P, National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating C (2003) The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA : J Am Med Assoc 289(19):2560–2572. doi:10.1001/jama.289.19.2560
Zhang W, Li N (2011) Prevalence, risk factors, and management of prehypertension. Int J Hypertens 2011:605359. doi:10.4061/2011/605359
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Sunita Patterson for scientific editing of the manuscript.
Disclosures
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilen, M.A., Durand, JB., McQuinn, L. et al. Evaluation of a novel blood pressure scoring method and its association with clinical response in cancer patients treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Invest New Drugs 32, 717–722 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0104-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0104-7