Summary
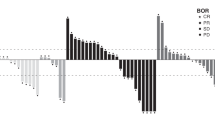
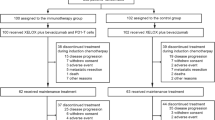
KRN330 is a recombinant, fully-human monoclonal antibody directed against A33, a surface differentiation antigen that is uniformly expressed in 95 % of colorectal cancers. A previous Phase 1 study of single-agent KRN330 identified a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of 3 mg/kg q2w and preliminary evidence of clinical activity among patients with advanced and metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). This Phase 1/2 trial sought to assess the safety and activity of second-line KRN330 plus irinotecan in patients with mCRC. Patients with mCRC who showed disease progression after FOLFOX/CapOx received intravenous doses of KRN330 (0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg qw or q2w) plus irinotecan (180 mg/m2) in a standard 3 + 3 dose escalation. The MTD of KRN330 with irinotecan in 19 patients was 0.5 mg/kg qw in the Phase 1 study with gastrointestinal effects and neutropenia being the predominant dose-limiting toxicities. In the Phase 2 study, the most frequent treatment-related Grade ≥3 toxicities in 44 patients were fatigue (15.9 %), neutropenia (13.6 %), leukopenia (6.8 %), diarrhea (4.5 %), and dehydration (4.5 %). Objective response rate (ORR) was 4.5 % and disease control rate was 45.5 % for the intent-to-treat population. Median progression-free survival was 87 days (95 % CI, 43–136 days). The prespecified ORR of KRN330 plus irinotecan was not met. Further investigation of KRN330 plus other agents may be warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohne CH, Lenz HJ (2009) Chemotherapy with targeted agents for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist 14(5):478–488
El Zhouhairi M, Charabaty A, Pishvaian MJ (2011) Molecularly targeted therapy for metastatic colon cancer; proven treatments and promising new agents. Gastrointest Cancer Res 4(1):15–21
Davies JM, Goldberg RM (2011) Treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol 38(4):552–560
Wu C, Goldberg RM (2013) Colorectal cancer in 2012: revisiting landmark trials and identifying new therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10(2):71–72
André T, Chibaudel B (2013) Aflibercept (Zaltrap®) approved in metastatic colorectal cancer. Bull Cancer 100(10):1023–1025
André T, Dumont SN (2013) Regorafenib approved in metastatic colorectal cancer. Bull Cancer 100(10):1027–1029
Garin-Chesa P, Sakamoto J, Welt S, Real F, Rettig W, Old L (1996) Organ-specific expression of the colon cancer antigen A33, a cell surface target for antibody-based therapy. Int J Oncol 9(3):465–471
Heath JK, White SJ, Johnstone CN, Catimel B, Simpson RJ, Moritz RL, Tu GF, Ji H, Whitehead RH, Groenen LC, Scott AM, Ritter G, Cohen L, Welt S, Old LJ, Nice EC, Burgess AW (1997) The human A33 antigen is a transmembrane glycoprotein and a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(2):469–474
Rageul J, Mottier S, Jarry A, Shah Y, Théoleyre S, Masson D, Gonzalez FJ, Laboisse CL, Denis MG (2009) KLF4-dependent, PPARgamma-induced expression of GPA33 in colon cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 125(12):2802–2809
Welt S, Divgi CR, Real FX, Yeh SD, Garin-Chesa P, Finstad CL, Sakamoto J, Cohen A, Sigurdson ER, Kemeny N (1990) Quantitative analysis of antibody localization in human metastatic colon cancer: a phase I study of monoclonal antibody A33. J Clin Oncol 8(11):1894–1906
Welt S, Divgi CR, Scott AM, Garin-Chesa P, Finn RD, Graham M, Carswell EA, Cohen A, Larson SM, Old LJ (1994) Antibody targeting in metastatic colon cancer: a phase I study of monoclonal antibody F19 against a cell-surface protein of reactive tumor stromal fibroblasts. J Clin Oncol 12(6):1193–1203
Welt S, Scott AM, Divgi CR, Kemeny NE, Finn RD, Daghighian F, Germain JS, Richards EC, Larson SM, Old LJ (1996) Phase I/II study of iodine 125-labeled monoclonal antibody A33 in patients with advanced colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 14(6):1787–1797
Welt S, Divgi CR, Kemeny N, Finn RD, Scott AM, Graham M, Germain JS, Richards EC, Larson SM, Oettgen HF (1994) Phase I/II study of iodine 131-labeled monoclonal antibody A33 in patients with advanced colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 12(8):1561–1571
Chong G, Lee FT, Hopkins W, Tebbutt N, Cebon JS, Mountain AJ, Chappell B, Papenfuss A, Schleyer P, U P, Murphy R, Wirth V, Smyth FE, Potasz N, Poon A, Davis ID, Saunder T, O’Keefe GJ, Burgess AW, Hoffman EW, Old LJ, Scott AM (2005) Phase I trial of 131I-huA33 in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11(13):4818–4826
Welt S, Ritter G, Williams C Jr, Cohen LS, John M, Jungbluth A, Richards EA, Old LJ, Kemeny NE (2003) Phase I study of anticolon-cancer humanized antibody A33. Clin Cancer Res 9(4):1338–1346
Welt S, Ritter G, Williams C Jr, Cohen LS, Jungbluth A, Richards EA, Old LJ, Kemeny NE (2003) Preliminary report of a phase I study of combination chemotherapy and humanized A33 antibody immunotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9(4):1347–1353
Ritter G, Cohen LS, Williams C Jr, Richards EC, Old LJ, Welt S (2001) Serological analysis of human anti-human antibody responses in colon cancer patients treated with repeated doses of humanized monoclonal antibody A33. Cancer Res 61(18):6851–6859
Ishida I, Tomizuka K, Yoshida H, Thahar T, Takahashi N, Ohguma A, Tanaka S, Umehashi M, Maeda H, Nozaki C, Halk E, Lonberg N (2002) Production of human monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies in TransChromo animals. Cloning Stem Cells 4(1):91–102
Sawada N, Taguchi E, Takahashi M, Nakajima K, Kobayashi N, Maeta K, Miura T, Tazunoki Y, Otani N, Harada K, Sudo T, Kanda H, Kato M, Kataoka S, Shibuya K (2011) In vitro and in vivo activities of KRN330, a fully-human monoclonal antibody against colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(suppl 4; abstr 432)
Berlin JD, Infante JR, Taguchi E, Goff LW, Jones SF, Chan E, Bendell JC, Rothenberg ML, Burris HA (2010) In vivo antibody binding to tumor in colorectal cancer patients and xenograft rodent models treated with anti-A33 antibody KRN330. Abstract #2431 presented at the 101st Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, 17–21 April 2010, Washington, DC
Infante JR, Bendell JC, Goff LW, Jones SF, Chan E, Sudo T, Burris HA, Berlin JD (2013) Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the anti-33 fully-human monoclonal antibody, KRN330, in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 49(6):1169–1175
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Camptosar (Irinotecan) Injection, intravenous infusion. Highlights of the prescribing information, 2012. http://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=533. Accessed 23 Sept 2013
Jiang XM, Arepally G, Poncz M, McKenzie SE (1991) Rapid detection of the Fc gamma RIIA-H/R 131 ligand-binding polymorphism using an allele-specific restriction enzyme digestion (ASRED). J Immunol Methods 199(1):55–59
Zhang W, Gordon M, Schultheis AM, Yang DY, Nagashima F, Azuma M, Chang HM, Borucka E, Lurje G, Sherrod AE, Iqbal S, Groshen S, Lenz HJ (2007) FCGR2A and FCGR3A polymorphisms associated with clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor expressing metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with single-agent cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 25(24):3712–3718
Simon R (1989) Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 10(1):1–10
Sobrero AF, Maurel J, Fehrenbacher L, Scheithauer W, Abubakr YA, Lutz MP, Vega-Villegas ME, Eng C, Steinhauer EU, Prausova J, Lenz HJ, Borg C, Middleton G, Kröning H, Luppi G, Kisker O, Zubel A, Langer C, Kopit J, Burris HA 3rd (2008) EPIC: phase III trial of cetuximab plus irinotecan after fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(14):2311–2319
Banck MS, Grothey A (2009) Biomarkers of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(24):7492–7501
Seymour L, Ivy SP, Sargent D, Spriggs D, Baker L, Rubinstein L, Ratain MJ, Le Blanc M, Stewart D, Crowley J, Groshen S, Humphrey JS, West P, Berry D (2010) The design of phase II clinical trials testing cancer therapeutics: consensus recommendations from the clinical trial design task force of the national cancer institute investigational drug steering committee. Clin Cancer Res 16(6):1764–1769
Acknowledgements
All authors contributed equally to the data interpretation and writing of the manuscript. The authors would like to thank the study investigators for their invaluable contribution to this study. The authors also acknowledge Janice Briscoe (Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Inc.) for study management, and Peter Todd, PhD (Tajut Ltd.) for review and critical revisions for important intellectual content and editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript. We thank Dr Wu Zhang (University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center) for performing Fc gamma receptor analysis.
Grant support
This work was supported by Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Inc. (Princeton, NJ) and Kyowa Hakko Kirin Company Limited (Tokyo, Japan). The research conducted was compliant with the current laws of the country in which it was performed.
Conflict of interest
DN is an employee of Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Inc. (Princeton, NJ). All other authors have confirmed they have no conflict of interest in the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bendell, J.C., Lenz, HJ., Ryan, T. et al. Phase 1/2 study of KRN330, a fully human anti-A33 monoclonal antibody, plus irinotecan as second-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs 32, 682–690 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0088-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0088-3