Summary
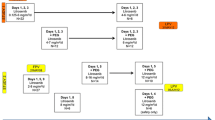
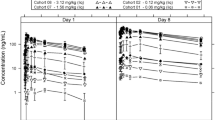
Purpose Sagopilone has recently been identified and preferentially used for the treatment of taxane-resistant cancer. The purpose of this dose-escalation study was to investigate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of sagopilone in refractory solid tumors. Methods A total of 17 Japanese patients received sagopilone in this Phase I study. Sagopilone was given as a 30-min intravenous infusion once every 3 weeks (one course) with an initial dose of 12.4 mg/m2 up to 22.0 mg/m2 for a maximum of 6 courses. Results The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was determined to be 16.5 mg/m2. The major dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) was peripheral sensory neuropathy. The PK data demonstrated that sagopilone did not accumulate after repeated administration. Two patients had stable disease (SD) over a period of 12 weeks. Conclusions Our study demonstrated clinically favorable safety, tolerability, and efficacy of sagopilone, which will help define the treatment of advanced tumors in more extensive clinical trials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jordan MA, Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4:253–65
Kavallaris M (2010) Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer 10:194–204
Gerth K, Bedorf N, Hofle G et al (1996) Epothilons A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). Production, physico-chemical and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 49:560–563
Bollag DM, McQueney PA, Zhu J et al (1995) Epothilones, a new class of microtubule-stabilizing agents with a taxol-like mechanism of action. Cancer Res 55:2325–2333
Altmann KH, Bold G, Caravatti G et al (2000) Synthesis and biological evaluation of highly potent analogues of epothilones B and D. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:2765–2768
Klar U, Buchmann B, Schwede W et al (2006) Total synthesis and antitumor activity of ZK-EPO: the first fully synthetic epothilone in clinical development. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 45:7942–7948
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A et al (2003) CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13:176–181
Schmid P, Kiewe P, Possinger K et al (2010) Phase I study of the novel, fully synthetic epothilone sagopilone (ZK-EPO) in patients with solid tumors. Ann Oncol 21:633–639
Vasey PA, Paul J, Birt A et al (1999) Docetaxel and cisplatin in combination as first-line chemotherapy for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Scottish Gynaecological Cancer Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 17:2069–2080
Arnold D, Voigt W, Kiewe P et al (2009) Weekly administration of sagopilone (ZK-EPO), a fully synthetic epothilone, in patients with refractory solid tumors: results of a Phase I trial. Br J Cancer 101:1241–1247
Trivedi M, Budihardjo I, Loureiro K et al (2008) Epothilones: a novel class of microtubule-stabilizing drugs for the treatment of cancer. Future Oncol 4:483–500
Morrow PK, Divers S, Provencher L et al (2010) Phase II study evaluating the efficacy and safety of sagopilone (ZK-EPO) in patients with metastatic breast cancer that has progressed following chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:837–842
DeConti RC, Algazi AP, Andrews S et al (2010) Phase II trial of sagopilone, a novel epothilone analog in metastatic melanoma. Br J Cancer 103:1548–1553
Rustin G, Reed N, Jayson GC et al (2011) A Phase II trial evaluating two schedules of sagopilone (ZK-EPO), a novel epothilone, in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol (2011) mdq780 first published online March 3, 2011 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq780
Fischer JR, Pawel JV, Schmittel A et al (2008) Phase II trial of sagopilone (ZK-EPO), a novel epothilone, as second-line therapy in patients with stage IIIB-IV non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol 19(Suppl 8):viii110–viii111, 301P (abstract)
Beer TM, Smith DC, Hussain A et al (2009) Phase II study of first-line sagopilone combined with prednisone in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) May 2009 vol. 27 no. 15S 5059
Hoffmann J, Buchmann B, Schwede W et al (2005) New synthetic epothilone derivative ZK-EPO inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 46:Abst 3424
Hammer S, Sommer S, Fichtner I et al (2010) Comparative profiling of the novel epothilone, sagopilone, in xenografts derived from primary non–small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:1452–65
Acknowledgments
This research is sponsored by Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd.
Ethical standards
The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araki, K., Kitagawa, K., Mukai, H. et al. First clinical pharmacokinetic dose-escalation study of sagopilone, a novel, fully synthetic epothilone, in Japanese patients with refractory solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 30, 2327–2333 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9773-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9773-7