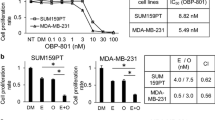
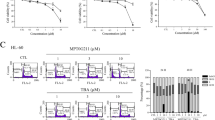
Summary
Nutlin-3, a small-molecule MDM2 inhibitor, restores p53 function and is, thus, an appealing candidate for the treatment of cancers retaining wild-type p53. However, nutlin-3 applied as single agent may be insufficient for cancer therapy. Therefore, we explored whether the anticancer activity of nutlin-3 could be enhanced by combination with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), i.e. vorinostat, sodium butyrate, MS-275 and apicidin. We found that nutlin-3 and HDACi cooperated to induce cell death in the p53 wild-type cell lines A549 and A2780, but not in the p53 null cell line PC-3, as assessed by Alamar Blue assay and flow cytometric analyses of propidium iodide uptake and mitochondrial depolarization. Combination index analysis showed that the effect was synergistic. For comparison, we tested nutlin-3 in combination with paclitaxel, revealing that nutlin-3 antagonized the cytotoxic activity of paclitaxel. To shed light on the underlying mechanism of the synergistic action of nutlin-3 and HDACi, we determined the acetylation status of p53 by immunoblotting and the mRNA levels of MDM2 and MDM4 by real-time RT-PCR. We observed vorinostat to induce p53 hyperacetylation, to reduce the constitutive gene expression of MDM2 and MDM4, and to counteract the nutlin-3-induced upregulation of MDM2 gene expression. In conclusion, our study shows that HDACi amplify the antitumor activity of nutlin-3—possibly by inducing p53 hyperacetylation and/or MDM2 and/or MDM4 downregulation—suggesting that treatment with a combination of nutlin-3 and HDACi may be an effective strategy for treating tumors with wild-type p53.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vousden KH, Lane DP (2007) p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:275–283
Brown CJ, Lain S, Verma CS, Fersht AR, Lane DP (2009) Awakening guardian angels: drugging the p53 pathway. Nat Rev Cancer 9:862–873
Shangary S, Wang S (2009) Small-molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction to reactivate p53 function: a novel approach for cancer therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:223–241
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, Fotouhi N, Liu EA (2004) In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303:844–848
Tovar C, Rosinski J, Filipovic Z, Higgins B, Kolinsky K, Hilton H, Zhao X, Vu BT, Qing W, Packman K, Myklebost O, Heimbrook DC, Vassilev LT (2006) Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in cancer: implications for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1888–1893
Hoffmann-La Roche (2007) A study of R7112 in patients with advanced solid tumors. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US). http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00559533. Accessed June 28, 2010. NLM Identifier: NCT00559533
Hoffmann-La Roche (2008) A study of R7112 in patients with hematologic neoplasms. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US). http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00623870. Accessed June 28, 2010. NLM Identifier: NCT00623870
Stimson L, Wood V, Khan O, Fotheringham S, La Thangue NB (2009) HDAC inhibitor-based therapies and haematological malignancy. Ann Oncol 20:1293–1302
Lane AA, Chabner BA (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 27:5459–5468
Buchwald M, Kramer OH, Heinzel T (2009) HDACi—targets beyond chromatin. Cancer Lett 280:160–167
Richon VM, Garcia-Vargas J, Hardwick JS (2009) Development of vorinostat: current applications and future perspectives for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 280:201–210
Campas-Moya C (2009) Romidepsin for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Drugs Today 45:787–795
Nolan L, Johnson PW, Ganesan A, Packham G, Crabb SJ (2008) Will histone deacetylase inhibitors require combination with other agents to fulfil their therapeutic potential? Br J Cancer 99:689–694
Wade M, Wahl GM (2009) Targeting Mdm2 and Mdmx in cancer therapy: better living through medicinal chemistry? Mol Cancer Res 7:1–11
Kruse JP, Gu W (2009) Modes of p53 regulation. Cell 137:609–622
Tang Y, Zhao W, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Gu W (2008) Acetylation is indispensable for p53 activation. Cell 133:612–626
Luo J, Su F, Chen D, Shiloh A, Gu W (2000) Deacetylation of p53 modulates its effect on cell growth and apoptosis. Nature 408:377–381
Terui T, Murakami K, Takimoto R, Takahashi M, Takada K, Murakami T, Minami S, Matsunaga T, Takayama T, Kato J, Niitsu Y (2003) Induction of PIG3 and NOXA through acetylation of p53 at 320 and 373 lysine residues as a mechanism for apoptotic cell death by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Res 63:8948–8954
Zhao Y, Lu S, Wu L, Chai G, Wang H, Chen Y, Sun J, Yu Y, Zhou W, Zheng Q, Wu M, Otterson GA, Zhu WG (2006) Acetylation of p53 at lysine 373/382 by the histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide induces expression of p21(Waf1/Cip1). Mol Cell Biol 26:2782–2790
Carlisi D, Vassallo B, Lauricella M, Emanuele S, D’Anneo A, Di Leonardo E, Di Fazio P, Vento R, Tesoriere G (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce in human hepatoma HepG2 cells acetylation of p53 and histones in correlation with apoptotic effects. Int J Oncol 32:177–184
Condorelli F, Gnemmi I, Vallario A, Genazzani AA, Canonico PL (2008) Inhibitors of histone deacetylase (HDAC) restore the p53 pathway in neuroblastoma cells. Br J Pharmacol 153:657–668
Carvajal D, Tovar C, Yang H, Vu BT, Heimbrook DC, Vassilev LT (2005) Activation of p53 by MDM2 antagonists can protect proliferating cells from mitotic inhibitors. Cancer Res 65:1918–1924
Tokalov SV, Abolmaali ND (2010) Protection of p53 wild type cells from taxol by nutlin-3 in the combined lung cancer treatment. BMC Cancer 10:57
O’Connor PM, Jackman J, Bae I, Myers TG, Fan S, Mutoh M, Scudiero DA, Monks A, Sausville EA, Weinstein JN, Friend S, Fornace AJ Jr, Kohn KW (1997) Characterization of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway in cell lines of the National Cancer Institute anticancer drug screen and correlations with the growth-inhibitory potency of 123 anticancer agents. Cancer Res 57:4285–4300
Brown R, Clugston C, Burns P, Edlin A, Vasey P, Vojtesek B, Kaye SB (1993) Increased accumulation of p53 protein in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cell lines. Int J Cancer 55:678–684
Chou TC (2010) Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 70:440–446
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB, Marks PA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene 26:5541–5552
Harms KL, Chen X (2007) Histone deacetylase 2 modulates p53 transcriptional activities through regulation of p53-DNA binding activity. Cancer Res 67:3145–3152
Patton JT, Mayo LD, Singhi AD, Gudkov AV, Stark GR, Jackson MW (2006) Levels of HdmX expression dictate the sensitivity of normal and transformed cells to Nutlin-3. Cancer Res 66:3169–3176
Hu B, Gilkes DM, Farooqi B, Sebti SM, Chen J (2006) MDMX overexpression prevents p53 activation by the MDM2 inhibitor Nutlin. J Biol Chem 281:33030–33035
Wade M, Wong ET, Tang M, Stommel JM, Wahl GM (2006) Hdmx modulates the outcome of p53 activation in human tumor cells. J Biol Chem 281:33036–33044
Hu B, Gilkes DM, Chen J (2007) Efficient p53 activation and apoptosis by simultaneous disruption of binding to MDM2 and MDMX. Cancer Res 67:8810–8817
Nakano K, Mizuno T, Sowa Y, Orita T, Yoshino T, Okuyama Y, Fujita T, Ohtani-Fujita N, Matsukawa Y, Tokino T, Yamagishi H, Oka T, Nomura H, Sakai T (1997) Butyrate activates the WAF1/Cip1 gene promoter through Sp1 sites in a p53-negative human colon cancer cell line. J Biol Chem 272:22199–22206
Vrana JA, Decker RH, Johnson CR, Wang Z, Jarvis WD, Richon VM, Ehinger M, Fisher PB, Grant S (1999) Induction of apoptosis in U937 human leukemia cells by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) proceeds through pathways that are regulated by Bcl-2/Bcl-XL, c-Jun, and p21CIP1, but independent of p53. Oncogene 18:7016–7025
Coll-Mulet D, Iglesias-Serret D, Santidrian AF, Cosialls AM, de Frias M, Castano E, Campas C, Barragan M, de Sevilla AF, Domingo A, Vassilev LT, Pons G, Gil J (2006) MDM2 antagonists activate p53 and synergize with genotoxic drugs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 107:4109–4114
Barbieri E, Mehta P, Chen Z, Zhang L, Slack A, Berg S, Shohet JM (2006) MDM2 inhibition sensitizes neuroblastoma to chemotherapy-induced apoptotic cell death. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2358–2365
Laurie NA, Donovan SL, Shih CS, Zhang J, Mills N, Fuller C, Teunisse A, Lam S, Ramos Y, Mohan A, Johnson D, Wilson M, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Quarto M, Francoz S, Mendrysa SM, Guy RK, Marine JC, Jochemsen AG, Dyer MA (2006) Inactivation of the p53 pathway in retinoblastoma. Nature 444:61–66
Secchiero P, Zerbinati C, di Iasio MG, Melloni E, Tiribelli M, Grill V, Zauli G (2007) Synergistic cytotoxic activity of recombinant TRAIL plus the non-genotoxic activator of the p53 pathway nutlin-3 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Curr Drug Metab 8:395–403
Ooi MG, Hayden PJ, Kotoula V, McMillin DW, Charalambous E, Daskalaki E, Raje NS, Munshi NC, Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Buon L, Clynes M, O’Gorman P, Richardson PG, Mitsiades CS, Anderson KC, Mitsiades N (2009) Interactions of the Hdm2/p53 and proteasome pathways may enhance the antitumor activity of bortezomib. Clin Cancer Res 15:7153–7160
Kurosu T, Wu N, Oshikawa G, Kagechika H, Miura O (2010) Enhancement of imatinib-induced apoptosis of BCR/ABL-expressing cells by nutlin-3 through synergistic activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis 15:608–620
Kranz D, Dobbelstein M (2006) Nongenotoxic p53 activation protects cells against S-phase-specific chemotherapy. Cancer Res 66:10274–10280
Sur S, Pagliarini R, Bunz F, Rago C, Diaz LA Jr, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N (2009) A panel of isogenic human cancer cells suggests a therapeutic approach for cancers with inactivated p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3964–3969
Ruefli AA, Ausserlechner MJ, Bernhard D, Sutton VR, Tainton KM, Kofler R, Smyth MJ, Johnstone RW (2001) The histone deacetylase inhibitor and chemotherapeutic agent suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) induces a cell-death pathway characterized by cleavage of Bid and production of reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10833–10838
Insinga A, Monestiroli S, Ronzoni S, Gelmetti V, Marchesi F, Viale A, Altucci L, Nervi C, Minucci S, Pelicci PG (2005) Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor pathway. Nat Med 11:71–76
Lindemann RK, Newbold A, Whitecross KF, Cluse LA, Frew AJ, Ellis L, Williams S, Wiegmans AP, Dear AE, Scott CL, Pellegrini M, Wei A, Richon VM, Marks PA, Lowe SW, Smyth MJ, Johnstone RW (2007) Analysis of the apoptotic and therapeutic activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors by using a mouse model of B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8071–8076
Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, Quinlan MP, Takahashi F, Maheswaran S, McDermott U, Azizian N, Zou L, Fischbach MA, Wong KK, Brandstetter K, Wittner B, Ramaswamy S, Classon M, Settleman J (2010) A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 141:69–80
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Becker and S. Wittig for their excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the “Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung, Neustadt/Donau”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palani, C.D., Beck, J.F. & Sonnemann, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance the anticancer activity of nutlin-3 and induce p53 hyperacetylation and downregulation of MDM2 and MDM4 gene expression. Invest New Drugs 30, 25–36 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9510-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9510-7