Summary
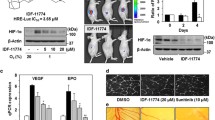
Cumulative evidence has established that hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and its downstream target, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), play a critical role in hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis, invasiveness and metastasis. 3-(4-bromophenyl)-2-(ethylsulfonyl)-6-methylquinoxaline 1,4-dioxide (Q39) has recently shown great antiproliferative activity in extensive cell lines in normoxia and hypoxia. In this study, Q39 exhibited high antiproliferative activity against hepatoma both in vitro and in vivo, mainly by inducing apoptosis. In addition, suppression of HIF-1α by Q39 resulted in a drastic decrease in VEGF expression. These results indicate that Q39 is an effective inhibitor of HIF-1α and provide new perspectives into the mechanism of its anticancer activity. Interestingly, neither the HIF-1α degradation rate nor the HIF-1α steady-state mRNA level was affected by Q39. Instead, suppression of HIF-1α accumulation by Q39 correlated with prominent dephosphorylation of mTOR and 4E-BP1, a pathway known to regulate protein expression at the translational level.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HIF-1:
-
hypoxia inducible factor-1
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- Akt:
-
oncogene from AKR mouse thymoma
- 4E-BP1:
-
initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1
- mTOR:
-
mammalian target of rapamycin
- p70S6K:
-
p70 S6 kinase
- PI3K:
-
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- eIF4E:
-
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E
References
Sheng R, Xu Y, Weng QJ, Xia Q, He QJ, Yang B, Hu YZ (2007) Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of 3-phenyl-2-thio-quinoxaline 1, 4-dioxide derivatives in hypoxia and in normoxia. Drug Discov Ther 1:119–123
Weng Q, Wang D, Guo P, Fang L, Hu Y, He Q, Yang B (2008) Q39, a novel synthetic Quinoxaline 1, 4-Di-N-oxide compound with anti-cancer activity in hypoxia. Eur J Pharmacol 581:262–269
Semenza GL (2002) HIF-1 and tumor progression: pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 8:S62–S67
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2003) Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med 9:677–684
Fang J, Ding M, Yang L, Liu LZ, Jiang BH (2007) PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling regulates prostate tumor angiogenesis. Cell Signal 19:2487–2497
Jackson MW, Roberts JS, Heckford SE, Ricciardelli C, Stahl J, Choong C, Horsfall DJ, Tilley WD (2002) A potential autocrine role for vascular endothelial growth factor in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 62:854–859
Soker S, Kaefer M, Johnson M, Klagsbrun M, Atala A, Freeman MR (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated autocrine stimulation of prostate tumor cells coincides with progression to a malignant phenotype. Am J Pathol 159:651–659
Li XM, Tang ZY, Zhou G, Lui YK, Ye SL (1998) Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression in invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 17:13–17
Li ZD, Liu LZ, Shi X, Fang J, Jiang BH (2007) Benzo[a]pyrene-3, 6-dione inhibited VEGF expression through inducing HIF-1alpha degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:517–523
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS, Kaelin WG Jr (2001) HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 292:464
Epstein AC, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O’Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI, Dhanda A, Tian YM, Masson N, Hamilton DL, Jaakkola P, Barstead R, Hodgkin J, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell 107:43–54
Beibei Fu, Xue J, Li Z, Shi X, Jiang B-H, Fang J (2007) Chrysin inhibits expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α through reducing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α stability and inhibiting its protein synthesis. Mol Cancer Ther 6:220–226
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E, Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM, Simons JW, Semenza GL (2000) Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res 60:1541–1545
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC, Semenza GL (2001) HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol Cell Biol 21:3995–4004
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F, Giaccia AJ, Abraham RT (2002) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol 22:7004–7014
Thomas GV, Tran C, Mellinghoff IK, Welsbie DS, Chan E, Fueger B, Czernin J, Sawyers CL (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factor determines sensitivity to inhibitors of mTOR in kidney cancer. Nat Med 12:122–127
Topisirovic I, Ruiz-Gutierrez M, Borden KLB (2004) Phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E contributes to its transformation and mRNA transport activities. Cancer Res 64:8639–8642
Belozerov VE, Van Meir EG (2005) Hypoxia inducible factor-1: a novel target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16:901–909
Fang J, Xia C, Cao Z, Zheng JZ, Reed E, Jiang B-H (2005) Apigenin inhibits VEGF and HIF-1 expression via PI3K/AKT/p70S6K1 and HDM2/p53 pathways. FASEB J 19:342–353
Powis G, Kirkpatrick L (2004) Hypoxia inducible factor 1α as a cancer drug target. Mol Cancer Ther 3:647–654
Dai M, Miao ZH, Ren X, Tong LJ, Yang N, Li T, Lin LP, Shen YM, Ding J (2009) MFTZ-1 reduces constitutive and inducible HIF-1alpha accumulation and VEGF secretion independent of its topoisomerase II inhibition. J Cell Mol Med, in press.
Li MH, Miao ZH, Tan WF, Yue JM, Zhang C, Lin LP, Zhang XW, Ding J (2004) Pseudolaric acid B inhibits angiogenesis and reduces hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha by promoting proteasome-mediated degradation. Clin Cancer Res 10:8266–8274
Hagen T, D’Amico G, Quintero M, Palacios-Callender M, Hollis V, Lam F, Moncada S (2004) Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by the anticancer agent 2-methoxyestradiol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:923–929
Nagasawa H, Mikamo N, Nakajima Y, Matsumoto H, Uto Y, Hori H (2003) Antiangiogenic hypoxic cytotoxin TX-402 inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway. Anticancer Res 23:4427–4434
McKeown SR, Cowen RL, Williams KJ (2007) Bioreductive drugs: from concept to clinic. Clin Oncol 19:427–442
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Yamazaki M, Kikukawa M, Tsujinoue H, Nakatani T, Fukui H (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor tightly regulates in vitro development of murine hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 28:1489–1496
Moon WS, Rhyu KH, Kang MJ, Lee DG, Yu HC, Yeum JH, Koh GY, Tarnawski AS (2003) Overexpression of VEGF and angiopoietin 2: a key to high vascularity of hepatocellular carcinoma? Mod Pathol 16:552–557
Poon RT, Lau CP, Cheung ST, Yu WC, Fan ST (2003) Quantitative correlation of serum levels and tumor expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with hepatocellularcarcinoma. Cancer Res 63:3121–3126
Lu L, Yang Z, Zhu B, Fang S, Yang X, Cai W, Li C, Ma JX, Gao G (2007) Kallikrein-binding protein suppresses growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by anti-angiogenic activity. Cancer Lett 257:97–106
Jin X, Jin HR, Lee D, Lee JH, Kim SK, Lee JJ (2008) A quassinoid 6alpha-tigloyloxychaparrinone inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1 pathway by inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation. Eur J Pharmacol 592:41–47
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation (No. 30873096 and 20602030), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. R2080326 and Z2090053), and Education Department Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. 20070166 and No. 20080116). We also extend our heartfelt thanks to Dr. Huijun Zhou and Jiali Zhang for their help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Qinjie Weng and Jun Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
Q39 exhibits potential antiangiogenic activity. Inhibition of angiogenesis was determined using the CAM assay. The sterile filter paper square saturated with Q39 (2 and 8 μg), TPT (as a positive control) or physiological saline solution was placed in areas between vessels but never onto any large vessels. After 48 h, the CAMs were carefully isolated and were fixed in methanol/acetone. Results of the samples were photographed (PDF 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, Q., Zhang, J., Cao, J. et al. Q39, a quinoxaline 1,4-Di-N-oxide derivative, inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression and the Akt/mTOR/4E-BP1 signaling pathway in human hepatoma cells. Invest New Drugs 29, 1177–1187 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9462-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9462-y