Summary
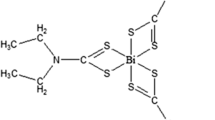
In the course of screening for novel anticancer compounds, B1 (N-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)-2-aminothiazonaphthalimide), a novel naphthalimide-based DNA intercalator, was generated as a new anticancer candidate. For the first time, our investigation demonstrates that B1 inhibited the growth of HeLa cells by the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Analysis of flow cytometry and western blots of HeLa cells treated with B1 revealed an appreciable cell cycle arrest and apoptotic induction in dose and time-dependent manner via the p53-dependent pathway. Furthermore, the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria was detected using confocal microscopy in HeLa cells treated with B1. Accordingly, these data demonstrate that the anticancer activity of B1 is associated with the activation of p53 and the release of cytochrome c, which suggest that B1 might have therapeutic potential against cervix carcinoma as an effective lead compound.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B1:
-
N-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)-2-aminothiazonaphthalimide
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- BCIP:
-
5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate
- NBT:
-
Nitro blue tet-razolium
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
References
Viglasky V, Danko P (2007) Intercalators: contra cruciform extrusion in DNA. Anal Biochem 360:7–13
Berman HM, Young PR (1981) The interaction of intercalating drugs with nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng 10:87–114
Wilson WD, Jones RL (1981) Intercalating drugs: DNA binding and molecular pharmacology. Adv Pharmacol Chemother 18:177–222
Martinez R, Chacon-Garcia L (2005) The search of DNA intercalators as antitumoral drugs: what it worked and what did not work. Curr Med Chem 12:127–151
Qian XH, Li ZG, Yang Q (2007) Highly efficient antitumor agents of heterocycles containing sulfur atom: Linear and angular thiazonaphthalimides against human lung cancer cell in vitro. Bioorgan Med Chem 15:6846–6851
Benchimol S (2001) P53-dependent pathways of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 8:1049–1051
Park HY, Kim MK, Moon SI et al (2006) Cell cycle arrest and apoptotic induction in LNCaP cells by MCS-C2, novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, through p53/p21WAF1/CIP1 pathway. Cancer Sci 97:430–436
Colman MS, Afshari CA, Barrett JC (2000) Regulation of p53 stability and activity in response to genotoxic stress. Mutat Res 462:179–188
Liu LJ, Yang F, Zhang Y, Li JL (2007) Studies on the cell immunosuppressive mechanism of Oridonin from Isodon serra. Int Immunopharm 7:945–954
Wang G, Chen HF, Huang MH et al (2006) Methyl protodioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Cancer Lett 241:102–109
Verma M, Singh SK, Bhushan S et al (2008) In vitro cytotoxic potential of Polyalthia longifolia on human cancer cell lines and induction of apoptosis through mitochondrial-dependent pathway in HL-60 cells. Chem-Biol Interact 171:45–56
Levites Y, Youdim MBH, Maor G, Mandel S (2002) Attenuation of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced nuclearfactor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) activation and cell death by tea extracts in neuronal cultures. Biochem Pharmacol 63:21–29
Zhang J, Shen YL, Liu JW, Wei DZ (2005) Antimetastatic effect of prodigiosin through inhibition of tumor invasion. Biochem Pharmacol 69:407–414
Liu Y, Zhang SP, Cai YQ (2007) Cytoprotective effects of selenium on cadmium-induced LLC-PK1 cells apoptosis by activating JNK pathway. Toxicol In Vitro 21:677–684
Dedov VN, Dedova IV, Nicholson GA (2003) Inhibition of topoisomerase II overrides the G2/M checkpoints of the cell cycle in EBV-lymphocytes. Apoptosis 8:399–406
Li CL, Wu HZ, Xu W et al (2008) 6-O-Angeloylenolin induces apoptosis through a mitochondrial/caspase and NF-κB pathway in human leukemia HL60 cell. Biomed Pharmacother 62:401–409
Rello S, Stockert JC, Moreno V et al (2005) Morphological criteria to distinguish cell death induced by apoptotic and necrotic treatments. Apoptosis 10:201–208
Shieh SY, Ahn J, Tamai K, Taya Y, Prives C (2000) The human homologs of checkpoint kinases Chk1 and Cds1 (Chk2) phosphorylate p53 at multiple DNA damage-inducible sites. Genes Dev 14:289–300
Andreassen PR, Lacroix FB, Lohez OD, Margolis RL (2001) Neither p21WAF1 nor 14-3-3 sigma prevents G2 progression to mitotic catastrophe in human colon carcinoma cells after DNA damage, but p21WAF1 induces stable G1 arrest in resulting tetraploid cells. Cancer Res 61:7660–7668
Haupt S, Berger M, Goldberg Z, Haupt Y (2003) Apoptosis—the p53 network. J Cell Sci 116:4077–4085
Innocente SA, Abrahamson JLA, Cogswell JP, Lee JM (1999) p53 regulates a G2 checkpoint through Cyclin B1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2147–2152
Sherr CJ (2000) The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res 60:3689–3695
Mousli M, Hopfner R, Abbady AQ et al (2003) ICBP90 belongs to a new family of proteins with an expression that is deregulated in cancer cells. Brit J Cancer 89:120–127
Arima Y, Hirota T, Bronner C et al (2004) Down-regulation of nuclear protein ICBP90 by p53/p21Cip1/WAF1-dependent DNA-damage checkpoint signals contributes to cell cycle arrest at G1/S transition. Genes Cells 9:131–142
Hu W, Kavanagh JJ (2003) Anticancer therapy targeting the apoptotic pathway. Lancet Oncol 4:721–729
Andrew M (1995) Cyclin ubiquitination: the destructive end of mitosis. Cell 81:149–152
Antonsson B, Martinou JC (2000) The Bcl-2 protein family. Exp Cell Res 256:50–57
Reed JC (1997) Double identity for proteins of the Bcl-2 family. Nature 387:773–776
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326:1–16
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptor: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project, Project No. B507, the National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Grant No. 2060204 and the 111 Project, Grant No. B07023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, X., Wu, A., Xu, Y. et al. B1, a novel naphthalimide-based DNA intercalator, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HeLa cells via p53 activation. Invest New Drugs 29, 646–658 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9403-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9403-9