Summary
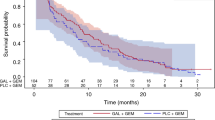
Background: The EGFR/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway is frequently deregulated in pancreatic cancer and contributes to cell growth, metastasis and chemoresistance. An isoflavone, genistein, inactivates Akt and NF-κB and enhances the anti-tumor activity of erlotinib and gemcitabine in experimental systems of pancreas cancer. This phase II study was undertaken to determine the effects of adding isoflavone to a regimen of gemcitabine and erlotinib on survival in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Methods: Eligibility included previously untreated patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Patients received gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15, and erlotinib 150 mg once daily P.O. on day 1 to day 28. Soy isoflavones (Novasoy®) were administered at a dose of 531 mg twice daily P.O. starting day -7 until the end of study participation. Results: Twenty patients with advanced pancreas cancer were enrolled (median age 57.9 years). Sixteen patients had stage IV disease. The median number of cycles was 2 per patient. The median survival time was 5.2 months (95% CI, 4.6—N/A months). The probability of survival at 6 months was 50% (95% CI, 32–78%). Conclusions: The addition of soy isoflavones to gemcitabine and erlotinib did not appear to increase the survival of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T et al (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58(2):71–96
El-Rayes BF, Philip PA (2002) Systemic therapy for advanced pancreatic cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2(4):426–436
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S et al (2007) Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 25(15):1960–1966
Philip PA, Benedetti J, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Zalupski M, Lenz H, O’Reilly E et al (2007) Phase III study of gemcitabine [G] plus cetuximab [C] versus gemcitabine in patients [pts] with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma [PC]: SWOG S0205 study. ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings Part I, Chicago, Il. J Clin Oncol 25 (18S, June 20 Supplement): Abstract number LBA4509
Vanhaesebroeck B, Alessi DR (2000) The PI3K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J 346(Pt 3):561–576
Downward J (1998) Signal transduction. New exchange, new target. Nature 396(6710):416–417
Jones DR, Broad RM, Madrid LV, Baldwin AS Jr, Mayo MW (2000) Inhibition of NF-kappaB sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Ann Thorac Surg 70(3):930–936, discussion 6–7
Patel NM, Nozaki S, Shortle NH, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Newton TR, Rice S et al (2000) Paclitaxel sensitivity of breast cancer cells with constitutively active NF-kappaB is enhanced by IkappaBalpha super-repressor and parthenolide. Oncogene 19(36):4159–4169
Ng SSW, Tsao MS, Chow S, Hedley DW (2000) Inhibition of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 60(19):5451–5455
Wang W, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Larry L, Cleary KR, Chiao PJ (1999) The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 5(1):119–127
Cheng JQ, Ruggeri B, Klein WM, Sonoda G, Altomare DA, Watson DK et al (1996) Amplification of AKT2 in human pancreatic cells and inhibition of AKT2 expression and tumorigenicity by antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(8):3636–3641
Li Y, Sarkar FH (2002) Gene expression profiles of genistein-treated PC3 prostate cancer cells. J Nutr 132(12):3623–3631
Li Y, Sarkar FH (2002) Down-regulation of invasion and angiogenesis-related genes identified by cDNA microarray analysis of PC3 prostate cancer cells treated with genistein. Cancer Lett 186(2):157–164
Alhasan SA, Aranha O, Sarkar FH (2001) Genistein elicits pleiotropic molecular effects on head and neck cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 7(12):4174–4181
Li Y, Sarkar FH (2002) Inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB activation in PC3 cells by genistein is mediated via Akt signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res 8(7):2369–2377
Sarkar FH, Li Y (2002) Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by soy isoflavone genistein. Cancer Metastasis Rev 21(3–4):265–280
Li Y, Ellis KL, Ali S, El-Rayes BF, Nedeljkovic-Kurepa A, Kucuk O et al (2004) Apoptosis-inducing effect of chemotherapeutic agents is potentiated by soy isoflavone genistein, a natural inhibitor of NF-kappaB in BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cell line. Pancreas 28(4):e90–e95
Ali S, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, El-Rayes BF, Philip PA, Sarkar FH (2008) Apoptosis-inducing effect of erlotinib is potentiated by 3,3′-diindolylmethane in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 7(6):1708–1719
Banerjee S, Zhang Y, Ali S, Bhuiyan M, Wang Z, Chiao PJ et al (2005) Molecular evidence for increased antitumor activity of gemcitabine by genistein in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 65(19):9064–9072
El-Rayes BF, Ali S, Ali IF, Philip PA, Abbruzzese J, Sarkar FH (2006) Potentiation of the effect of erlotinib by genistein in pancreatic cancer: the role of Akt and nuclear factor-kappaB. Cancer Res 66(21):10553–10559
Hussain M, Banerjee M, Sarkar FH, Djuric Z, Pollak MN, Doerge D et al (2003) Soy isoflavones in the treatment of prostate cancer. Nutr Cancer 47(2):111–117
Davis JN, Kucuk O, Djuric Z, Sarkar FH (2001) Soy isoflavone supplementation in healthy men prevents NF-kappa B activation by TNF-alpha in blood lymphocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 30(11):1293–1302
Simon R (1989) Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 10:1–10
Li Y, Ross-Viola JS, Shay NF, Moore DD, Ricketts ML (2009) Human CYP3A4 and murine Cyp3A11 are regulated by equol and genistein via the pregnane X receptor in a species-specific manner. J Nutr 139(5):898–904
Lu JF, Eppler SM, Wolf J, Hamilton M, Rakhit A, Bruno R et al (2006) Clinical pharmacokinetics of erlotinib in patients with solid tumors and exposure-safety relationship in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther 80(2):136–145
Cassileth BR, Deng G (2004) Complementary and alternative therapies for cancer. The Oncologist 9(1):80–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported in part by Cancer Center Support Grant CA-22453 and Pancreas SPORE P20 CA101936 from the National Cancer Institute, Archer Daniel Midland Company and by OSI Pharmaceuticals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Rayes, B.F., Philip, P.A., Sarkar, F.H. et al. A phase II study of isoflavones, erlotinib, and gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer. Invest New Drugs 29, 694–699 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9386-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9386-6