Summary
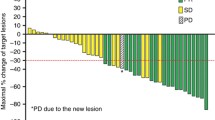
Vorinostat (Zolinza®) is a histone deacetylase inhibitor that has demonstrated activity in patients with advanced solid tumors in phase I trials. A multicenter, open-label phase II trial of oral vorinostat 200, 300 or 400 mg bid for 14 days followed by a 7-day rest until disease progression or intolerable toxicity was conducted. Patients with measurable, relapsed or refractory breast or non-small cell lung cancer who had received ≥1 prior therapy or colorectal cancer who had received ≥2 prior therapies were eligible. The response rate, safety and tolerability were evaluated. Sixteen patients (median age, 62 years; median 5.5 prior therapies) were enrolled. Six patients received 400 mg bid, six received 300 mg bid and four received 200 mg bid (14 days/3 weeks). Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) at the 400 or 300 mg bid levels were anorexia, asthenia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, vomiting, and weight loss. No DLTs were observed at the 200 mg bid level. Disease stabilization was observed in eight patients, but there were no confirmed responses. The median TTP was 33.5 days. Eleven patients discontinued due to clinical adverse experiences (AEs). The most common drug-related AEs were anorexia (81%), fatigue (62%), nausea (62%), diarrhea (56%), vomiting (56%), thrombocytopenia (50%) and weight loss (50%). Drug-related AEs ≥ grade 3 included thrombocytopenia (50%), anemia (12%), asthenia (12%) and nausea (12%). Vorinostat in a daily oral schedule for 14 days/3 weeks was tolerable at 200 mg bid only, and no responses were observed in this study. Most patients, however, had limited drug exposure which did not allow a reliable efficacy analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dokmanovic M, Clarke C, Marks PA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Mol Cancer Res 5:981–989
Rasheed WK, Johnstone RW, Prince HM (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 16:659–678
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB, Marks PA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene 26:5541–5552
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika P, Kelly C, Chiao JH, Reilly JF, Ricker JL, Richon VM, Frankel SR (2007) Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood 109:31–39
Olsen EA, Kim YH, Kuzel TM, Pacheco TR, Foss FM, Parker S, Frankel SR, Chen C, Ricker JL, Arduino JM, Duvic M (2007) Phase IIb multicenter trial of vorinostat in patients with persistent, progressive, or treatment refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:3109–3115
Bali P, Pranpat M, Swaby R, Fiskus W, Yamaguchi H, Balasis M, Rocha K, Wang HG, Richon V, Bhalla K (2005) Activity of suberoylanilide hydroxamic Acid against human breast cancer cells with amplification of her-2. Clin Cancer Res 11:6382–6389
Butler LM, Agus DB, Scher HI, Higgins B, Rose A, Cordon-Cardo C, Thaler HT, Rifkind RA, Marks PA, Richon VM (2000) Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 60:5165–5170
Komatsu N, Kawamata N, Takeuchi S, Yin D, Chien W, Miller CW, Koeffler HP (2006) SAHA, a HDAC inhibitor, has profound anti-growth activity against non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep 15:187–191
Munster PN, Troso-Sandoval T, Rosen N, Rifkind R, Marks PA, Richon VM (2001) The histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid induces differentiation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:8492–8497
Kelly WK, O’Connor OA, Krug LM, Chiao JH, Heaney M, Curley T, MacGregore-Cortelli B, Tong W, Secrist JP, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Chu E, Olgac S, Marks PA, Scher H, Richon VM (2005) Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:3923–3931
Kelly WK, Richon VM, O’Connor O, Curley T, MacGregor-Curtelli B, Tong W, Klang M, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Rosa E, Drobnjak M, Cordon-Cordo C, Chiao JH, Rifkind R, Marks PA, Scher H (2003) Phase I clinical trial of histone deacetylase inhibitor: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid administered intravenously. Clin Cancer Res 9:3578–3588
Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferrajoli A, Cortes J, Wierda WG, Faderl S, Koller C, Morris G, Rosner G, Loboda A, Fantin VR, Randolph SS, Hardwick JS, Reilly JF, Chen C, Ricker JL, Secrist JP, Richon VM, Frankel SR, Kantarjian HM (2008) Phase I study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) in patients with advanced leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 111:1060–1066
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Fujiwara Y, Yamamoto N, Yamada K, Koizumi F, Shimoyama T, Nishio K, Otsuki T, Frankel SR, Tamura T (2007) Phase I trial of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) in patients with solid tumors. J Thorac Oncol 2:S459
Tobinai K, Watanabe T, Kobayashi S, Yamasaki S, Morita-Hoshi Y, Yokoyama H, Morishima Y, Kato H, Frankel SR, Otsuki T (2007) Phase I study of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in Japan. J Clin Oncol 25:703s
Ramalingam SS, Parise RA, Ramananthan RK, Lagattuta TF, Musguire LA, Stoller RG, Potter DM, Argiris AE, Zwiebel JA, Egorin MJ, Belani CP (2007) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel for advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 13:3605–3610
Schelman WR, Kolesar J, Schell K, Marnocha R, Eickhoff J, Alberti D, Wilding G, Bailey H (2007) A phase I study of vorinostat in combination with bortezomib in refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:3573
Daud A, Schmitt M, Marchion D, Bicaku E, Minton S, Egorin M, Zwiebel J, Chiappori A, Sullivan D, Munster P (2007) Phase I trial of a sequence-specific combination of the HDAC inhibitor, vorinostat (SAHA) followed by doxorubicin in advanced solid tumor malignancies. J Clin Oncol 25:3502
Tang P, Oza A, Townsley C, Siu L, Pond G, Sarveswaran P, Webster S, Zwiebel J, Chen E (2007) A phase I study of vorinostat (VOR) in combination with capecitabine (CAP) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:3576
Fakih MG, Pendyala L, Smith P, Creaven P, Toth K, Zwiebel J, Frankel S, Litwin A, Huffman L, Egorin M (2007) A phase I study of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) in combination with 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) in patients with advanced colorectal cancer (CRC). J Clin Oncol 25:4088
O’Connor OA, Heaney ML, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Willim R, Macgregor-Cortelli B, Curly T, Moskowitz C, Portlock C, Horwitz S, Zelenetz AD, Frankel S, Richon V, Marks P, Kelly WK (2006) Clinical experience with intravenous and oral formulations of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 24:166–173
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research funding from Merck Research Laboratories.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vansteenkiste, J., Van Cutsem, E., Dumez, H. et al. Early phase II trial of oral vorinostat in relapsed or refractory breast, colorectal, or non-small cell lung cancer. Invest New Drugs 26, 483–488 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-008-9131-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-008-9131-6