Summary
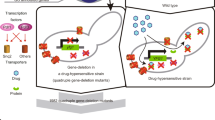
The cell-based assay using yeast deletion mutants has been recognized as an efficient analysis to discover therapeutic compounds and reveal their mode of action. In this study, S. pombe deletion mutants-based HTS screening was carried out to identify potential anti-cancer agents. The NCI chemical library of 5700 compounds was screened using kit strains, which consisted of S. pombe mutants harboring deletions in genes involved in DNA repair and mitotic control. During the screening, we identified 40 compounds conferring growth inhibition of S. pombe. Their anti-tumorigenic properties were examined by phenotypic effect on S. pombe, flow cytometry and apoptosis analysis of human cancer. Here, we report hit compounds inducing apoptosis for development of anti-cancer agents suggesting that S. pombe deletion mutants are useful in identifying potential anti-cancer agents in human cancer therapeutics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood V, Gwilliam R, Rajandream MA, Lyne M, Lyne R, Stewart A, Sgouros J, Peat N, Hayles J, Baker S, Basham D, Bowman S, Brooks K, Brown D, Brown S, Chillingworth T, Churcher C, Collins M, Connor R, Cronin A, Davis P, Feltwell T, Fraser A, Gentles S, Goble A, Hamlin N, Harris D, Hidalgo J, Hodgson G, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huckle EJ, Hunt S, Jagels K, James K, Jones L, Jones M, Leather S, McDonald S, McLean J, Mooney P, Moule S, Mungall K, Murphy L, Niblett D, Odell C, Oliver K, O, Neil S, Pearson D, Quail MA, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Saunders D, Seeger K, Sharp S, Skelton J, Simmonds M, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Taylor K, Taylor RG, Tivey A, Walsh S, Warren T, Whitehead S, Woodward J, Volckaert G, Aert R, Robben J, Grymonprez B, Weltjens I, Vanstreels E, Rieger M, Schafer M, Muller-Auer S, Gabel C, Fuchs M, Dusterhoft A, Fritzc C, Holzer E, Moestl D, Hilbert H, Borzym K, Langer I, Beck A, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, Pohl TM, Eger P, Zimmermann W, Wedler H, Wambutt R, Purnelle B, Goffeau A, Cadieu E, Dreano S, Gloux S, Lelaure V, Mottier S, Galibert F, Aves SJ, Xiang Z, Hunt C, Moore K, Hurst SM, Lucas M, Rochet M, Gaillardin C, Tallada VA, Garzon A, Thode G, Daga RR, Cruzado L, Jimenez J, Sanchez M, del Rey F, Benito J, Dominguez A, Revuelta JL, Moreno S, Armstrong J, Forsburg SL, Cerutti L, Lowe T, McCombie WR, Paulsen I, Potashkin J, Shpakovski GV, Ussery D, Barrell BG, Nurse P, Cerrutti L (2002) The genome sequence of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nature 415:871–880
Nagata A, Igarashi M, Jinno S, Suto K, Okayama H (1991) An additional homolog of the fission yeast cdc25+gene occurs in humans and is highly expressed in some cancer cells. New Biol 3:959–968
Choi JK, Choi JY, Kim DG, Choi DW, Kim BY, Lee KH, Yeom YI, Yoo HS, Yoo OJ, Kim S (2004) Integrative analysis of multiple gene expression profiles applied to liver cancer study. FEBS Lett 565:93–100
Giaever G, Shoemaker DD, Jones TW, Liang H, Winzeler EA, Astromoff A, Davis RW (1999) Genomic profiling of drug sensitivities via induced haploinsufficiency. Nat Genet 21:278–283
Fisher E, Scambler P (1994) Human haploinsufficiency—one for sorrow, two for joy. Nat Genet 7:5–7
Parsons AB, Brost RL, Ding H, Li Z, Zhang C, Sheikh B, Brown GW, Kane PM, Hughes TR, Boone C (2004) Integration of chemical–genetic and genetic interaction data links bioactive compounds to cellular target pathways. Nat Biotechnol 22:62–69
Lum PY, Armour CD, Stepaniants SB, Cavet G, Wolf MK, Butler JS, Hinshaw JC, Garnier P, Prestwich GD, Leonardson A, Garrett-Engele P, Rush CM, Bard M, Schimmack G, Phillips JW, Roberts CJ, Shoemaker DD (2004) Discovering modes of action for therapeutic compounds using a genome-wide screen of yeast heterozygotes. Cell 116:121–137
Park J-Y, Jang YJ, You SJ, Kil YS, Kang E, Ahn J, Ryoo YK, Lee M, Park S, Lee H, Yang W, Song KB, Park HM, Chung Y, Kim H, Hoe K, Chung KS, Kim DU, Yoo HS, Won M (2003) Drug-induced haploinsufficiency of fission yeast provides a powerful tool for identification of drug targets. J Microbiol Biotechnol 13:317–320
Simon JA, Szankasi P, Nguyen DK, Ludlow C, Dunstan HM, Roberts CJ, Jensen EL, Hartwell LH, Friend SH (2000) Differential toxicities of anticancer agents among DNA repair and checkpoint mutants of saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cancer Res 60:328–333
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren JT, Bokesch H, Kenney S, Boyd MR (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1107–1112
Chung KS, Won M, Lee SB, Jang YJ, Hoe KL, Kim DU, Lee JW, Kim KW, Yoo HS (2001) Isolation of a novel gene from schizosaccharomyces pombe: Stm1+encoding a seven-transmembrane loop protein that may couple with the heterotrimeric galpha 2 protein, gpa2. J Biol Chem 276:40190–40201
Jang YJ, Won M, Chung KS, Kim DU, Hoe KL, Park C, Yoo HS (1997) A novel protein, psp1, essential for cell cycle progression of schizosaccharomyces pombe is phosphorylated by cdc2-cdc13 upon entry into g0-like stationary phase of cell growth. J Biol Chem 272:19993–20002
Won M, Jang YJ, Chung KS, Kim DU, Hoe KL, Han MY, Kim HB, Lee SH, Oh HW, Yoo HS (2001) Pleckstrin homology domain interacts with rkp1/cpc2, a rack1 homolog, to modulate pck2-mediated signaling process in schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:987–992
Dickens ML, Strohl WR (1996) Isolation and characterization of a gene from streptomyces sp. Strain c5 that confers the ability to convert daunomycin to doxorubicin on streptomyces lividans tk24. J Bacteriol 178:3389–3395
Wang J, Galgoci A, Kodali S, Herath KB, Jayasuriya H, Dorso K, Vicente F, Gonzalez A, Cully D, Bramhill D, Singh S (2003) Discovery of a small molecule that inhibits cell division by blocking ftsz, a novel therapeutic target of antibiotics. J Biol Chem 278:44424–44428
Jeller AH, Silva DH, Liao LM, Bolzani Vda S, Furlan M (2004) Antioxidant phenolic and quinonemethide triterpenes from cheiloclinium cognatum. Phytochemistry 65:1977–1982
Setzer WN, Holland MT, Bozeman CA, Rozmus GF, Setzer MC, Moriarity DM, Reeb S, Vogler B, Bates RB, Haber WA (2001) Isolation and frontier molecular orbital investigation of bioactive quinone-methide triterpenoids from the bark of salacia petenensis. Planta Med 67:65–69
Lamb JR, Goehle S, Ludlow C, Simon JA (2001) Thymidine incorporation is highly predictive of colony formation and can be used for high-throughput screening. Biotechniques 30:1118–1125
Dunstan HM, Ludlow C, Goehle S, Cronk M, Szankasi P, Evans DR, Simon JA, Lamb JR (2002) Cell-based assays for identification of novel double-strand break-inducing agents. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:88–94
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the Grant KRIBB Initiative from the Korea Research Council of Fundamental Science and Technology, a grant from the 21st Century Frontier for Functional Analysis of the Human Genome.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kyung-Sook Chung, Nam-Hui Yim and Seung-Hee Lee were equally contributed.
Supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table 1
(PPT 52.5 KB)
Fig. 1
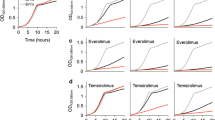
Determination of IC50 by [3H]-thymidine incorporation assay. IC50 was measured with a modified [3H]-thymidine incorporation assay as described previously [18, 19]. To test their apoptotic effect on cancer cells, A549 (lung cancer), MCF7JK (breast cancer), Hct-116 (colon cancer), HeLa cell (cervic cancer), DU-145 (prostate cancer), IGROV1 (ovary cancer), Ovcar3 (ovary cancer), Ovcar8 (ovary cancer), SKOV3 (ovary cancer), MDA-MB 435 (breast cancer), NCI H460 (colon cancer), Daudi (Lymphoma), HFF, human foreskin cell and NCIH460 cells (colon cancer) were used. A. 1, NSC 15627; 2, NSC 280891; 3, NSC 280892; 4, NSC 126188. B. 1, NSC 337859; 2, NSC 280891; 3, NSC 280892. C. 1, NSC 658139; 2, NSC 87538; 3, NSC 205357; 4, NSC 10120.(PPT 81.5 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, KS., Yim, NH., Lee, SH. et al. Identification of small molecules inducing apoptosis by cell-based assay using fission yeast deletion mutants. Invest New Drugs 26, 299–307 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9100-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-007-9100-5