Summary
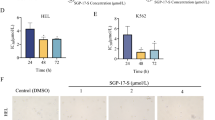
To identify purine analogs that could be effective in treating neuroblastomas, we tested the anticancer properties of sulfinosine, 8-Cl-cAMP and 8-Cl-adenosine in the SK-N-SH cell line. First we examined the effects of these three agents on cell growth inhibition and cell viability by the BrdU and Sulforhodamine B assay. Treatment of SK-N-SH cells with increasing concentrations of these compounds led to a significant inhibition of cell proliferation and decrease of cell viability in a time- and dose-dependant manner at micromolar concentration (<10 μM). Treatment with a combination of sulfinosine and 8-Cl-cAMP resulted in synergistic effects on growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis. Flow-cytometric analysis showed that 8-Cl-cAMP arrested the cells in the G0/G1 phase and sulfinosine blocked cell cycle progression at the G2/M stage, in contrast to the combined effects of both agents that did not arrest growth at any particular phase of the cell cycle. Further analysis of apoptosis induction demonstrated an increase from 17 to 24% of both early and late apoptotic cells and a very low percentage of necrotic cells. These results indicate that apoptosis was the predominant type of cell death after treatment of SK-N-SH cells with both substances, as well as with their combinations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Noesel MM, Versteeg R: Pediatric neuroblastomas: Genetic and epigenetic ‘danse macabre’. Gene 325:1–15, 2004
Brodeur GM, Nakagawara A: Molecular basis of clinical heterogeneity in neuroblastoma. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 14(2):111–116, 1992
Goldsby RE, Matthay KK: Neuroblastoma: Evolving therapies for a disease with many faces. Paediatr Drugs 6(2):107–122, 2004
Srivastava RK, Srivastava AR, Cho-Chung YS: Synergistic effects of 8-chlorocyclic-AMP and retinoic acid on induction of apoptosis in Ewing's sarcoma CHP-100 cells. Clin Cancer Res 4(3):755–761, 1998
Beebe, SJ, Corbin, JD: Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein-kinases. In: PD Boyer and EG Krebs (eds), The Enzymes: Control by Phosphorilation, Vol. 17, pp 43–111. New York Academic Press, 1986
Cho-Chung YS: Role of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in growth, differentiation, and suppression of malignancy: New approaches to therapy. Cancer Res 50(22):7093–8100, 1990
Schwartz DA, Rubin CS: Identification and differential expression of two forms of regulatory subunits (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II in Friend erythroleukemic cells. J Biol Chem 260(10):6296–6303, 1985
Katsaros D, Tortora G, Tagliaferri P, Clait T, Ally S, Neckers LM, Robins RK, Cho-Chung YS: Site-selective cyclic AMP analogs provide a new approach in the control of cancer cell growth. FEBS Letters 223: 97–103, 1987
Ally S, Tortora G, Clair T, Grieco D, Merlo G, Katsaros D, Øgreid D, Døskeland SO, Jahnsen T, Cho-Chung YS: Selective modulation of protein kinase isozymes by the site selective analog 8-Chloro adenosine 3′5′–cyclic monophosphate provides a biological means for control of human colon cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6319–6322, 1988
Ally S, Clair T, Katsaros D, Tortora G, Yokozaki H, Finch RA, Avery TL, Cho-Chung YS: Inhibition of growth and modulation of gene expression in human lung carcinoma in athymic mice by site-selective 8-Cl-cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Cancer Res 49:5650–5655, 1989
Grbovic O, Jovic V, Ruzdijic S, Pejanovic V, Rakic L, Kanazir S: 8-Cl-cAMP affects glioma cell-cycle kinetics and selectively induces apoptosis. Cancer Invest 20(7–8):972–982, 2002
McDaid HM, Johnston PG: Synergistic interaction between paclitaxel and 8-chloro-adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 5(1):215–220, 1999
Krebs EG, Beavo JA: Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 48:923–959, 1979
Halgren RG, Traynor AE, Pillay S, Zell JL, Heller KF, Krett NL, Rosen ST: 8Cl-cAMP cytotoxicity in both steroid sensitive and insensitive multiple myeloma cell lines is mediated by 8Cl-adenosine. Blood. 15; 92(8):2893–2898, 1998
Gandhi V, Ayres M, Halgren RG, Krett NL, Newman RA, Rosen ST: 8-chloro-cAMP and 8-chloro-adenosine act by the same mechanism in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res. 61(14):5474–5479, 2001
Stellrecht CM, Rodriguez CO Jr, Ayres M, Gandhi V: RNA-directed actions of 8-chloro-adenosine in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res 63(22):7968–7974, 2003
Revankar GR, Hanna NB, Imamura N, Lewis AF, Larson SB, Finch RA, Avery TL: Synthesis and in vivo antitumor activity of 2-amino-9-beta-D-ribofuranosylpurine-6-sulfenamide, -sulfinamide, -sulfonamide and related purine ribonucleosides. J Med Chem 33:121–128, 1990
Avery TL, Finch RA, Vasquez KM, Radparvar S, Hanna NB, Revanker GR, Robins RK: Chemotherapeutic characterization in mice of 2-amino-9-beta-D-ribofuranosylpurine-6-sulfinamide (sulfinosine), a novel purine nucleoside with unique antitumor properties. Cancer Res 50:2625–2630, 1990
Milosevic J, Kanazir S, Medic-Mijacevic L, Pejanovic V, Stokic Z, Konjevic G, Rakic L, Ruzdijic S: Sulfinosine-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in human lung carcinomas in vitro. Invest New Drugs 20(3):229–40, 2002
Tortora G, di Isernia G, Sandomenico C, Bianco R, Pomatico G, Pepe S, Bianco AR, Ciardiello F: Synergistic inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis by 8-chloro-cAMP and paclitaxel or cisplatin in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 57(22):5107–5111, 1997
Pesic M, Drabek K, Esler C, Ruzdijic S, Pejanovic V, Pietrzkowski Z: Inhibition of cell growth and proliferation in human glioma cells and normal human astrocytes induced by 8-Cl-cAMP and tiazofurin. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 19(5–6):963–975, 2000
Koricanac LB, Todorovic DV, Popovic NM, Demajo MA, Ruzdijic SD, Risti-Fira AM: Inhibition of B16 Mouse Melanoma Cell Growth and Induction of Apoptotic Cell Death with 8-Chloroadenosine-3′,5′-monophosphate and Tiazofurin. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1030:384–392, 2004
Kim SN, Kim SG, Park JH, Lee MA, Park SD, Cho-Chung YS, Hong SH: Dual anticancer activity of 8-Cl-cAMP: Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptotic cell death. Biochem Biop Ress Comm 273:404–410, 2000
Kim SN, Ahn YH, Kim SG, Park SD, Cho-Chung YS, Hong SH: 8-Cl-cAMP induces cell cycle-specific apoptosis in human cancer cells. Int J Cancer 93(1):33–41, 2001
Park GH, Choe J, Choo HJ, Park YG, Sohn J, Kim MK: Genome-wide expression profiling of 8-chloroadenosine- and 8-chloro-cAMP-treated human neuroblastoma cells using radioactive human cDNA microarray. Exp Mol Med 34(3):184–193, 2002
Muneyama K, Bauer RJ, Shuman DA, Robins RK, Simon LN: Chemical synthesis and biological activity of 8-substituted adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate derivatives. Biochemistry 10(12):2390–2395, 1971
Chou J, Chou TC: Dose-effect analysis with microcomputers: Quantitation of ED50, LD50, synergism, antagonism, low-dose risk, receptor-ligand binding and enzyme kinetics. In Manual and software for IBM-PC. Cambrige, England: Biosoft, 1987
Chou TC, Talalay P: Applications of median-effect principle for the assessment of low-dose risk of carcinogenesis and for the quantification os synergism and antagonism of chemotherapeutic anents. In New Avenues in Development Cancer Chemotherapy, Bristol-Myers Series, New York: Academic Press, 1987, pp. 37–64
Schwede F, Maronde E, Genieser HG, Jastorff B: Cyclic nucleotide analogs as biochemical tools and prospective drugs. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 87:199–226 (2000)
Tortora G, Ciardiello F, Pepe S, Tagliaferri P, Ruggiero A, Bianco C, Guarrasi R, Miki K, Bianco AR: Phase I clinical study with 8-chloro-cAMP and evaluation of immunological effects in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 1(4):377–384, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janković, D., Pesić, M., Marković, J. et al. The combination of sulfinosine and 8-Cl-cAMP induces synergistic cell growth inhibition of the human neuroblastoma cell line in vitro . Invest New Drugs 24, 15–25 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-005-4539-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-005-4539-8