Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a dreadful threaten to human health worldwide. Many circular RNAs were reported to influence the malignant development of HCC. The aim of this study was to elucidate the role of circ_0091579 in HCC progression and the molecular fundamentation.
Methods
Expression of circ_0091579, microRNA-1225-5p (miR-1225-5p), and phospholipase C, β1 (PLCB1) was examined by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction or Western blotting. Cell viability, clonogenicity capacity, and apoptosis were determined via Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, and flow cytometry, respectively. Transwell assay was employed to detect cell migration and invasion. Target relationship between miR-1225-5p and circ_0091579 or PLCB1 was demonstrated by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Moreover, role of circ_0091579 in vivo was assessed by Xenograft model assay.
Results
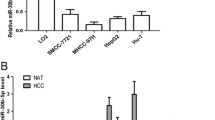
Expression of circ_0091579 and PLCB1 was increased, while miR-1225-5p expression was decreased in HCC tissues and cells. Circ_0091579 or PLCB1 depletion had inhibitory effects on HCC cell proliferation and metastasis. Circ_0091579 sponged miR-1225-5p to upregulate PLCB1 expression in HCC cells. Silencing of miR-1225-5p contributed to HCC progression, which was mitigated by PLCB1 depletion. Circ_0091579 deficiency could suppress HCC tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion
Circ_0091579 knockdown repressed HCC progression and tumorigenesis by regulating miR-1225-5p/PLCB1 axis, affording a novel molecular basis for HCC development.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492.
Kulik L, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:e471. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.065.
Lurje I, Czigany Z, Bednarsch J et al. Treatment strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma—a multidisciplinary approach. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061465.
Rong D, Tang W, Li Z et al. Novel insights into circular RNAs in clinical application of carcinomas. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2183–2188. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s134403.
Qiu L, Xu H, Ji M et al. Circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: biomarkers, functions and mechanisms. Life Sci. 2019;231:116660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116660.
Yao R, Zou H, Liao W. Prospect of circular RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: a novel potential biomarker and therapeutic target. Front Oncol. 2018;8:332. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00332.
Zhang C, Zhang C, Lin J et al. Circular RNA Hsa_Circ_0091579 serves as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell PhysiolBiochem. 2018;51:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495230.
Panda AC. Circular RNAs Act as miRNA sponges. AdvExp Med Biol. 2018;1087:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6.
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02871.
Mao B, Wang G. MicroRNAs involved with hepatocellular carcinoma (review). Oncol Rep. 2015;34:2811–2820. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4275.
Liu L, Zhang W, Hu Y et al. Downregulation of miR-1225-5p is pivotal for proliferation, invasion, and migration of HCC cells through NFκB regulation. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23474.
Kim D, Chang HR, Baek D. Rules for functional microRNA targeting. BMB Rep. 2017;50:554–559. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.11.179.
Lo Vasco VR, Cardinale G, Polonia P. Deletion of PLCB1 gene in schizophrenia-affected patients. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:844–851. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01363.x.
Li J, Zhao X, Wang D et al. Up-regulated expression of phospholipase C, β1 is associated with tumor cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:1697–1706. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s97189.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods 2001;25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Fu L, Jiang Z, Li T et al. Circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: functions and implications. Cancer Med. 2018;7:3101–3109. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1574.
Niu WY, Chen L, Zhang P et al. Circ_0091579 promotes proliferative ability and metastasis of liver cancer cells by regulating microRNA-490-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:10264–10273. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201912_19664.
Liu W, Yin C, Liu Y. Circular RNA circ_0091579 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through miR-490-5p/CASC3 axis. Cancer BiotherRadiopharm. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2019.3472.
Jiang P, Han W, Fu Y et al. The Hsa_circ_0091579/miR-940/TACR1 Axis regulates the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:9087–9096. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s259243.
Li D, Chi G, Chen Z et al. MicroRNA-1225-5p behaves as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma via targeting of IRS1. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:6339–6350. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s178001.
Zheng H, Zhang F, Lin X et al. MicroRNA-1225-5p inhibits proliferation and metastasis of gastric carcinoma through repressing insulin receptor substrate-1 and activation of β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 2016;7:4647–4663. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6615.
Sun P, Zhang D, Huang H et al. MicroRNA-1225-5p acts as a tumor-suppressor in laryngeal cancer via targeting CDC14B. Biol Chem. 2019;400:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2018-0265.
Wang S, Chen X, Zhang Z et al. MicroRNA-1225-5p inhibits the development and progression of thyroid cancer via targeting sirtuin 3. Pharmazie. 2019;74:423–427. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2019.9411.
Zhang W, Wei L, Sheng W et al. miR-1225-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting Sox9. DNA Cell Biol. 2020;39:78–91. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.5105.
Li B, Zhang F, Li H. miR-1225-5p inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and may be a prognostic biomarker. ExpTher Med. 2020;20:172. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.9302.
Sengelaub CA, Navrazhina K, Ross JB et al. PTPRN2 and PLCβ1 promote metastatic breast cancer cell migration through PI(4,5)P2-dependent actin remodeling. Emboj. 2016;35:62–76. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201591973.
Zhang T, Song X, Liao X et al. Distinct prognostic values of phospholipase C beta family members for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4256524. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4256524.
Fan Y, Wang L, Han XC et al. LncRNA MIF-AS1 aggravates the progression of ovarian cancer by sponging miRNA-31-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:2248–2255. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202003_20490.
Lu ML, Zhang Y, Li J et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and suppresses tumor growth by interacting with PLCB1 and regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:121–136. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201901_16756.
Lin D, Fu Z, Yang G et al. Exportin-5 SUMOylationpromoteshepatocellularcarcinoma progression. ExpCellRes 2020;395:112219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112219.
Acknowledgment
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and XZ contributed to conceptualization and methodology; HZ, XS, and YL performed formal analysis and data curation; DZ, YZ, and HZ were involved in validation and investigation; DZ, YZ, XZ, and HZ performed writing—original draft preparation, and writing—review and editing; all authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University. Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Consent for publication
Patients agree to participate in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Circ_0091579 Serves as a Tumor-Promoting Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through miR-1225-5p/PLCB1 Axis. Dig Dis Sci 67, 585–597 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06861-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06861-2