Abstract
Background
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are effective in healing reflux esophagitis and relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Prevention of recurrence of symptoms has become a therapeutic aim in patients with these conditions.
Aims
We investigated the effects of rebamipide, a mucosal protective anti-ulcer agent, on recurrence of reflux symptoms during PPI maintenance therapy.
Methods
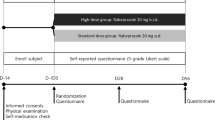
Patients with esophagitis of Los Angeles classification A or B were treated with PPIs for 8 weeks. Patients with relief of symptoms were enrolled for further study. Forty-one patients were randomized to maintenance therapy with 15 mg of lansoprazole daily or 15 mg of lansoprazole and 300 mg rebamipide daily, and recurrence of symptoms was monitored over 12 months. In some patients, concentration of rebamipide and interleukin(IL)-8 expression in the esophageal mucosa were estimated.
Results
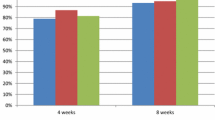
During the 12-month period, 11/20 patients (52.4%) taking lansoprazole 15 mg daily suffered recurrence of symptoms, compared to 4/20 patients (20%) treated with lansoprazole 15 mg and rebamipide 300 mg daily (P < 0.05). Rebamipide was detected in the esophageal mucosa 90–180 min after oral administration. IL-8 mRNA expression in the esophageal mucosa of patients with rebamipide was significantly decreased compared with that of patients without rebamipide.
Conclusions
Combination therapy with rebamipide and lansoprazole appears to be highly effective in preventing recurrence of symptoms during long-term maintenance treatment for GERD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dean BB, Gano AD Jr, Knight K, Ofman JJ, Fass R. Effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in nonerosive reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:656–664.
Tytgat GN. Review article: treatment of mild and severe cases of GERD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16(Suppl 4):73–78.
Matheson AJ, Jarvis B. Lansoprazole: an update of its place in the management of acid-related disorders. Drugs. 2001;61:1801–1833.
Freston JW, Jackson RL, Huang B, Ballard ED II. Lansoprazole for maintenance of remission of erosive oesophagitis. Drugs. 2002;62:1173–1184.
Hatlebakk JG, Berstad A. Lansoprazole 15 and 30 mg daily in maintaining healing and symptom relief in patients with reflux oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997;11:365–372.
Chiba N, De Gara CJ, Wilkinson JM, Hunt RH. Speed of healing and symptom relief in grade II to IV gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:1798–1810.
Vigneri S, Termini R, Leandro G, et al. A comparison of five maintenance therapies for reflux esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1106–1110.
Arakawa T, Higuchi K, Fujiwara Y, et al. 15th anniversary of rebamipide: looking ahead to the new mechanisms and new applications. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:S3–S11.
Arakawa T, Kobayashi K, Yoshikawa T, Tarnawski A. Rebamipide: overview of its mechanisms of action and efficacy in mucosal protection and ulcer healing. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43:5S–13S.
Kleine A, Kluge S, Peskar BM. Stimulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis mediates gastroprotective effect of rebamipide in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:1441–1449.
Sun WH, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, et al. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat gastric mucosa by rebamipide, a mucoprotective agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;295:447–452.
Suetsugu H, Ishihara S, Moriyama N, et al. Effect of rebamipide on prostaglandin EP4 receptor gene expression in rat gastric mucosa. J Lab Clin Med. 2000;136:50–57.
Tarnawski A, Arakawa T, Kobayashi K. Rebamipide treatment activates epidermal growth factor and its receptor expression in normal and ulcerated gastric mucosa in rats: one mechanism for its ulcer healing action? Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43:90S–98S.
Tarnawski AS, Chai J, Pai R, Chiou SK. Rebamipide activates genes encoding angiogenic growth factors and Cox2 and stimulates angiogenesis: a key to its ulcer healing action? Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49:202–209.
Udagawa A, Shiota G, Ichiba M, Murawaki Y. Effect of rebamipide on acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats: involvement of hepatocyte growth factor. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:141–146.
Ishihara K, Komuro Y, Nishiyama N, Yamasaki K, Hotta K. Effect of rebamipide on mucus secretion by endogenous prostaglandin-independent mechanism in rat gastric mucosa. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992;42:1462–1466.
Naito Y, Yoshikawa T, Tanigawa T. Hydroxyl radicals scavenging by rebamipide and related compounds: electron paramagnetic resonance study. Free Radical Biol Med. 1995;18:117–123.
Sakurai K, Sasabe H, Koga T, Konishi T. Mechanism of hydroxyl radical scavenging by rebamipide: identification of mono-hydroxylated rebamipide as a major reaction product. Free Radic Res. 2004;38:487–494.
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y, Tanigawa T, Kondo M. Free radical scavenging activity of the novel anti-ulcer agent rebamipide studied by electron spin resonance. Arzneimittelforschung. 1993;43:363–366.
Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T, Iinuma S, et al. Rebamipide protects against activation of neutrophils by Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci. 1996;41:1139–1144.
Murakami K, Okajima K, Harada N, Isobe H, Okabe H. Rebamipide prevents indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal lesion formation by inhibiting activation of neutrophils in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43:139S–142S.
Masamune A, Yoshida M, Sakai Y, Shimosegawa T. Rebamipide inhibits ceramide-induced interleukin-8 production in Kato III human gastric cancer cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;298:485–492.
Aihara M, Imagawa K, Funakoshi Y, Ohmoto Y, Kikuchi M. Effects of rebamipide on production of several cytokines by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43:160S–166S.
Yoshida N, Uchiyama K, Kuroda M, et al. Interleukin-8 expression in the esophageal mucosa of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:816–822.
Katada K, Yoshida N, Isozaki Y, et al. Prevention by rebamipide of acute reflux esophagitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50(Suppl 1):S97–S103.
Armstrong D, Bennett JR, Blum AL, et al. The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: a progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:85–92.
Carlsson R, Dent J, Bolling-Sternevald E, et al. The usefulness of a structured questionnaire in the assessment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:1023–1029.
Revicki DA, Wood M, Wiklund I, Crawley J. Reliability and validity of the gastrointestinal symptom rating scale in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Qual Life Res. 1998;7:75–83.
Naito Y, Yoshikawa T, Iinuma S, et al. Local gastric and serum concentrations of rebamipide following oral administration to patients with chronic gastritis. Arzneimittelforschung. 1996;46:698–700.
Mukaida N, Shiroo M, Matsushima K. Genomic structure of the human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor IL-8. J Immunol. 1989;143:1366–1371.
Robinson M, Lanza F, Avner D, Haber M. Effective maintenance treatment of reflux esophagitis with low-dose lansoprazole. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124:859–867.
Baldi F, Morselli-Labate AM, Cappiello R, Ghersi S. Italian lansoprazole study group. Daily low-dose versus alternate day full-dose lansoprazole in the maintenance treatment of reflux esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1357–1364.
Fass R. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98(3 Suppl):S2–S7.
Martinez SD, Malagon IB, Garewal HS, Cui H, Fass R. Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD)—acid reflux and symptom patterns. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:537–545.
Yoshida N. Inflammation and oxidative stress in gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007;40:13–23.
Isomoto H, Saenko VA, Kanazawa Y, et al. Enhanced expression of interleukin-8 and activation of nuclear factor kappa-B in endoscopy-negative gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:589–597.
Cunha FQ, Lorenzetti BB, Poole S, Ferreira SH. Interleukin-8 as a mediator of sympathetic pain. Br J Pharmacol. 1991;104:765–767.
Watkins LR, Maier SF, Goehler LE. Immune activation: the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain. 1995;63:289–302.
Summer GJ, Romero-Sandoval EA, Bogen O, Dina OA, Khasar SG, Levine JD. Proinflammatory cytokines mediating burn-injury pain. Pain. 2008;135:98–107.
Wetscher GJ, Hinder RA, Bagchi D, et al. Reflux esophagitis in humans is mediated by oxygen-derived free radicals. Am J Surg. 1995;170:552–556.
Olyaee M, Sontag S, Salman W, et al. Mucosal reactive oxygen species production in oesophagitis and Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 1995;37:168–173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, N., Kamada, K., Tomatsuri, N. et al. Management of Recurrence of Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Synergistic Effect of Rebamipide with 15 mg Lansoprazole. Dig Dis Sci 55, 3393–3398 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1166-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1166-9