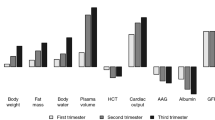
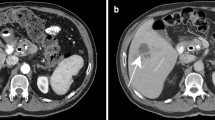
Abstract
Liver disorders associated with pregnancy include hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), preeclampsia, syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets (HELLP), and acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP). These conditions are relatively common and unique to pregnancy and are more likely to occur at certain terms of gestation specific to each condition. They can be associated with significant maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Although managing such patients may be very challenging, spontaneous resolution of the disease occurs shortly after termination of the pregnancy, usually without hepatic sequellae. Early diagnosis and timely treatment is a key to therapeutic success. This article explores the clinical features, pathophysiology, and management of these disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sibai BM, Ramadan MK, Chari RS, Friedman SA (1995) Pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets): subsequent pregnancy outcome and long-term prognosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 172:125–129
Sibai BM, Ramadan MK, Usta I, Salama M, Mercer BM, Friedman SA (1993) Maternal morbidity and mortality in 442 pregnancies with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP syndrome). Am J Obstet Gynecol 169:1000–1006
Riely CA (1996) Liver disease of pregnancy. In: Karlovitz N (ed) Liver and biliary diseases, 2nd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, pp 483–495
Sullivan CA, Magann EF, Perry KG Jr, Roberts WE, Blake PG, Martin JN Jr (1994) The recurrence risk of the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP) in subsequent gestations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 171:940–943
VanDyke RW (2003) The liver in pregnancy. In: Zakim D, Boyer T (eds) Hepatology: a text book of liver disease, 4th edn. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, PA, pp 1591–1598
Harish K, Nitha R, Harikumar R, Sunil Kumar K, Varghese T, Sreedevi NS, Bushrath K, Sandesh K, Tony J (2005) Prospective evaluation of abnormal liver function tests in pregnancy. Trop Gastroenterol 26:188–193
Reyes H, Sandoval L, Wainstein A, Ribalta J, Donoso S, Smok G, Rosenberg H, Meneses M (1994) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: a clinical study of 12 episodes in 11 patients. Gut 35:101–106
Wolf JL, Wolf JL (1996) Liver disease in pregnancy. Med Clin North Am 80:1167–1187
Bacq Y, Zarka O, Brechot JF, Mariotte N, Vol S, Tichet J, Weill J (1996) Liver function tests in normal pregnancy: a prospective study of 103 pregnant women and 103 matched controls. Hepatology 23:1030–1034
Potter JM, Nestel PJ (1979) The hyperlipidemia of pregnancy in normal and complicated pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 133:165–170
Everson GT (1992) Gastrointestinal motility in pregnancy. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 21:751–776
Ch’ng CL, Morgan M, Hainsworth I, Kingham JG (2002) Prospective study of liver dysfunction in pregnancy in Southwest Wales. Gut 51:876–880
Everson GT (1998) Liver problems in pregnancy: part 2—managing pre-existing and pregnancy-induced liver disease. Medscape Womens Health 3:2
Kallen B (1987) Hyperemesis during pregnancy and delivery outcome: a registry study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 26:291–302
Tan PC, Jacob R, Quek KF, Omar SZ (2006) The fetal sex ratio and metabolic, biochemical, haematological and clinical indicators of severity of hyperemesis gravidarum. BJOG 113:733–737
Abdel-Hadi AH, Rodriguez-Lafora BM, Cantarero GA (2004) Wernicke’s encephalopathy as a complication of hyperemesis gravidarum. An Med Interna 21:46–47
Chiossi G, Neri I, Cavazzuti M, Basso G, Facchinetti F (2006) Hyperemesis gravidarum complicated by Wernicke encephalopathy: background, case report, and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv 61:255–268
Eboue C, Carlier-Guerin C, de La Sayette V, Grall JY, Herlicoviez M (2006) A rare complication of vomiting in pregnancy: Wernicke’s encephalopathy. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 35:822–825
Indraccolo U, Gentile G, Pomili G, Luzi G, Villani C (2005) Thiamine deficiency and beriberi features in a patient with hyperemesis gravidarum. Nutrition 21:967–968
Erolu A, Kurkcuolu C, Karaolanolu N, Tekinba C, Cesur M (2002) Spontaneous esophageal rupture following severe vomiting in pregnancy. Dis Esophagus 15:242–243
Liang SG, Ooka F, Santo A, Kaibara M (2002) Pneumomediastinum following esophageal rupture associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 28:172–175
Soman R, Gohar S (2002) Boerhaave’s syndrome in pregnancy. J Assoc Physicians India 50:1456–1457
Hill JB, Yost NP, Wendel GD Jr (2002) Acute renal failure in association with severe hyperemesis gravidarum. Obstet Gynecol 100:1119–1121
Weng MT, Wei SC, Wong JM, Chang TC (2005) Hyperemesis gravidarum presenting as jaundice and transient hyperthyroidism complicated with acute pancreatitis. J Formos Med Assoc 104:194–197
Brunetti-Pierri N, Hunter JV, Boerkoel CF (2007) Gray matter heterotopias, brachytelephalangic chondrodysplasia punctata: a complication of hyperemesis gravidarum induced vitamin K deficiency? Am J Med Genet Part A 143:200–204
Bailit JL (2005) Hyperemesis gravidarium: epidemiologic findings from a large cohort. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:811–814
Paauw JD, Bierling S, Cook CR, Davis AT (2005) Hyperemesis gravidarum and fetal outcome. JPEN J Parent Enteral Nutr 29:93–96
Weigel MM, Weigel RM (1989) Nausea and vomiting of early pregnancy and pregnancy outcome. An epidemiological study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 96:1304–1311
Abell TL, Riely CA (1992) Hyperemesis gravidarum. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 21:835–849
Afifi A, Descamps PH, Hamoud A, Pariente EA (1990) Icteric complications related to pregnancy vomiting in the 1st trimester (hyperemesis gravidarum). Review of the literature apropos of a case. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 19:455–458
Lagiou P, Tamimi R, Mucci LA, Trichopoulos D, Adami HO, Hsieh CC (2003) Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy in relation to prolactin, estrogens, and progesterone: a prospective study. Obstet Gynecol 101:639–644
Aka N, Atalay S, Sayharman S, Kilic D, Kose G, Kucukozkan T (2006) Leptin and leptin receptor levels in pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarum. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 46:274–277
Arslan EO, Cengiz L, Arslan M (2003) Thyroid function in hyperemesis gravidarum and correlation with serum leptin levels. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 83:187–188
Unsel N, Benian A, Erel CT (2004) Leptin levels in women with hyperemesis gravidarum. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 84:162–163
Ustun Y, Engin-Ustun Y, Dokmeci F, Soylemez F (2004) Serum concentrations of lipids and apolipoproteins in normal and hyperemetic pregnancies. J Matern-Fetal Neonatal Med 15:287–290
Yoneyama Y, Suzuki S, Sawa R, Yoneyama K, Doi D, Otsubo Y, Araki T (2002) The T-helper 1/T-helper 2 balance in peripheral blood of women with hyperemesis gravidarum. Am J Obstet Gynecol 187:1631–1635
Kuscu NK, Yildirim Y, Koyuncu F, Var A, Uyanik BS (2003) Interleukin-6 levels in hyperemesis gravidarum. Arch Gynecol Obstet 269:13–15
Verberg MF, Gillott DJ, Al-Fardan N, Grudzinskas JG (2005) Hyperemesis gravidarum, a literature review. Hum Reprod Update 11:527–539
Sugito Y, Sekizawa A, Farina A, Yukimoto Y, Saito H, Iwasaki M, Rizzo N, Okai T (2003) Relationship between severity of hyperemesis gravidarum and fetal DNA concentration in maternal plasma. Clin Chem 49:1667–1669
Heinrichs L (2002) Linking olfaction with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, recurrent abortion, hyperemesis gravidarum, and migraine headache. Am J Obstet Gynecol 186:S215–219
Hummel T, von Mering R, Huch R, Kolble N (2002) Olfactory modulation of nausea during early pregnancy? BJOG 109:1394–1397
Karpel L, de Gmeline C (2004) Psychological approach to hyperemis gravidarum. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod 33:623–631
Munch S (2002) Women’s experiences with a pregnancy complication: causal explanations of hyperemesis gravidarum. Soc Work Health Care 36:59–76
Hiroi H, Kugu K, Hoshino H, Kozuma S, Taketani Y (2001) Hyperemesis gravidarum associated with thyrotoxicosis and a past history of an eating disorder. Arch Gynecol Obstet 265:228–230
Jacobson GF, Autry AM, Somer-Shely TL, Pieper KL (2003) Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and hyperemesis gravidarum. J Reprod Med 48:578–582
Kazerooni T, Taallom M, Ghaderi AA (2002) Helicobacter pylori seropositivity in patients with hyperemesis gravidarum. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 79:217–220
Lee RH, Pan VL, Wing DA (2005) The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in the hispanic population affected by hyperemesis gravidarum. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:1024–1027
Shirin H, Sadan O, Shevah O, Bruck R, Boaz M, Moss SF, Everon S, Glezerman M, Avni Y (2004) Positive serology for Helicobacter pylori and vomiting in the pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 270:10–14
Riely CA (1994) Hepatic disease in pregnancy. Am J Med 96:18S–22S
Outlaw WM, Ibdah JA (2005) Impaired fatty acid oxidation as a cause of liver disease associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. Med Hypotheses 65:1150–1153
Colin JF, Mathurin P, Durand F, Bettan L, Erlinger S, Benhamou JP, Bernuau J (1994) Hyperthyroidism: a possible factor of cholestasis associated with hyperemesis gravidarum of prolonged evolution. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 18:378–380
Goodwin TM, Montoro M, Mestman JH (1992) Transient hyperthyroidism and hyperemesis gravidarum: clinical aspects. Am J Obstet Gynecol 167:648–652
Krentz AJ, Redman H, Taylor KG (1994) Hyperthyroidism associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. Br J Clin Pract 48:75–76
Bacq Y, Riely CA (2003) The liver in nancy. In: Schiff ER, Sorrel MF, Maddrey WC (eds) Diseases of the liver, vol 2, 9th edn. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, pp 1435–1453
Larrey D, Rueff B, Feldmann G, Degott C, Danan G, Benhamou JP (1984) Recurrent jaundice caused by recurrent hyperemesis gravidarum. Gut 25:1414–1415
Nader S, Mastrobattista J (1996) Recurrent hyperthyroidism in consecutive pregnancies characterized by hyperemesis. Thyroid 6:465–466
Navaneethakrishnan R, Lindow SW, Masson EA, Allan B (2004) Recurrent gestational thyrotoxicosis presenting as recurrent hyperemesis gravidarum-report of two cases. J Obstet Gynaecol 24:774–775
Conchillo JM, Pijnenborg JM, Peeters P, Stockbrugger RW, Fevery J, Koek GH (2002) Liver enzyme elevation induced by hyperemesis gravidarum: aetiology, diagnosis and treatment. Neth J Med 60:374–378
Neri I, Allais G, Schiapparelli P, Blasi I, Benedetto C, Facchinetti F (2005) Acupuncture versus pharmacological approach to reduce hyperemesis gravidarum discomfort. Minerva Ginecol 57:471–475
Quinla JD, Hill DA (2003) Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Am Fam Physician 68:121–128
Bsat FA, Hoffman DE, Seubert DE (2003) Comparison of three outpatient regimens in the management of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. J Perinatol 23:531–535
Heazell AE, Langford N, Judge JK, Heazell MA, Downey GP (2005) The use of levomepromazine in hyperemesis gravidarum resistant to drug therapy—a case series. Reprod Toxicol 20:569–572
Guclu S, Gol M, Dogan E, Saygili U (2005) Mirtazapine use in resistant hyperemesis gravidarum: report of three cases and review of the literature. Arch Gynecol Obstet 272:298–300
Rohde A, Dembinski J, Dorn C (2003) Mirtazapine (Remergil) for treatment resistant hyperemesis gravidarum: rescue of a twin pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 268:219–221
Bondok RS, El Sharnouby NM, Eid HE, Abd Elmaksoud AM (2006) Pulsed steroid therapy is an effective treatment for intractable hyperemesis gravidarum. Crit Care Med 34:2781–2783
Chan LY, Lam MH, Lau TK, Chin RK (2003) Successful treatment of recurrent, intractable hyperemesis gravidarum with methylprednisolone. A case report. J Reprod Med 48:293–295
Chan LY, Lam MH, Lau TK, Chin RK (2003) Successful treatment of recurrent, intractable hyperemesis gravidarum with methylprednisolone. A case report. J Reprod Med 48:293–295
Ziaei S, Hosseiney FS, Faghihzadeh S (2004) The efficacy low dose of prednisolone in the treatment of hyperemesis gravidarum. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 83:272–275
Siu SS, Yip SK, Cheung CW, Lau TK (2002) Treatment of intractable hyperemesis gravidarum by ondansetron. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 105:73–74
Glantz A, Marschall HU, Lammert F, Mattsson LA (2005) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial comparing dexamethasone and ursodeoxycholic acid. Hepatology 42:1399–1405
Zapata R, Sandoval L, Palma J, Hernandez I, Ribalta J, Reyes H, Sedano M, Toha D, Silva JJ (2005) Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. A 12-year experience. Liver Int 25:548–554
Hempfling W, Dilger K, Beuers U (2003) Systematic review: ursodeoxycholic acid—adverse effects and drug interactions. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 18:963–972
Kondrackiene J, Beuers U, Kupcinskas L (2005) Efficacy and safety of ursodeoxycholic acid versus cholestyramine in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gastroenterology 129:894–901
Schumann R, Hudcova J (2004) Cholestasis of pregnancy, pruritus and 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptor antagonists. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 83:861–862
Vaisman N, Kaidar R, Levin I, Lessing JB (2004) Nasojejunal feeding in hyperemesis gravidarum—a preliminary study. Clin Nutrit 23:53–57
Folk JJ, Leslie-Brown HF, Nosovitch JT, Silverman RK, Aubry RH (2004) Hyperemesis gravidarum: outcomes and complications with and without total parenteral nutrition. J Reprod Med 49:497–502
Ghani R (2003) The use of total parenteral nutrition in protracted hyperemesis gravidarum. J Obstet Gynaecol 23:199–201
Paranyuk Y, Levine G, Figueroa R (2006) Candida septicemia in a pregnant woman with hyperemesis receiving parenteral nutrition. Obstet Gynecol 107:535–537
Zecca E, De Luca D, Marras M, Caruso A, Bernardini T, Romagnoli C (2006) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics 117:1669–1672
Ahlfeld F (1883) Berichte und Arbeten aus der geburtshilflich- gynaekologischen Klinik zu Giessen Leipzig: Grunow 148:1881–1882
Eppinger H (1937) Die Leberkrankhetten: allgemeine und spezielle Pathologie, Therapie der Leber. Springer-Verlag, Vienna
Thorling L (1955) Jaundice in pregnancy; a clinical study. Acta Med Scand Suppl 302:1–123
Ropponen A, Sund R, Riikonen S, Ylikorkala O, Aittomaki K (2006) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy as an indicator of liver and biliary diseases: a population-based study. Hepatology 43:723–728
Riely CA (1987) Familial intrahepatic cholestatic syndromes. Semin Liver Dis 7:119–133
Leevy CB, Koneru B, Klein KM (1997) Recurrent familial prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy associated with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology 113:966–972
Eloranta ML, Hakli T, Hiltunen M, Helisalmi S, Punnonen K, Heinonen S (2003) Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms of the bile salt export pump gene with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Scand J Gastroenterol 38:648–652
Keitel V, Vogt C, Haussinger D, Kubitz R (2006) Combined mutations of canalicular transporter proteins cause severe intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gastroenterology 131:624–629
Mullenbach R, Bennett A, Tetlow N, Patel N, Hamilton G, Cheng F, Chambers J, Howard R, Taylor-Robinson SD, Williamson C et al (2005) ATP8B1 mutations in British cases with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gut 54:829–834
de Vree JM, Jacquemin E, Sturm E, Cresteil D, Bosma PJ, Aten J, Deleuze JF, Desrochers M, Burdelski M, Bernard O et al (1998) Mutations in the MDR3 gene cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:282–287
Painter JN, Savander M, Ropponen A, Nupponen N, Riikonen S, Ylikorkala O, Lehesjoki AE, Aittomaki K (2005) Sequence variation in the ATP8B1 gene and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Eur J Human Genet 13:435–439
Wasmuth HE, Glantz A, Keppeler H, Simon E, Bartz C, Rath W, Mattsson LA, Marschall HU, Lammert F (2007) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: the severe form is associated with common variants of the hepatobiliary phospholipid transporter ABCB4 gene. Gut 56:265–270
Schneider G, Paus TC, Kullak-Ublick GA, Meier PJ, Wienker TF, Lang T, van de Vondel P, Sauerbruch T, Reichel C (2007) Linkage between a new splicing site mutation in the MDR3 alias ABCB4 gene and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Hepatology 45:150–158
Pauli-Magnus C, Lang T, Meier Y, Zodan-Marin T, Jung D, Breymann C, Zimmermann R, Kenngott S, Beuers U, Reichel C et al (2004) Sequence analysis of bile salt export pump (ABCB11) and multidrug resistance p-glycoprotein 3 (ABCB4, MDR3) in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Pharmacogenetics 14:91–102
Dixon PH, Weerasekera N, Linton KJ, Donaldson O, Chambers J, Egginton E, Weaver J, Nelson-Piercy C, de Swiet M, Warnes G et al (2000) Heterozygous MDR3 missense mutation associated with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: evidence for a defect in protein trafficking. Hum Mol Genet 9:1209–1217
Floreani A, Carderi I, Paternoster D, Soardo G, Azzaroli F, Esposito W, Variola A, Tommasi AM, Marchesoni D, Braghin C et al (2006) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: three novel MDR3 gene mutations. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23:1649–1653
Savander M, Ropponen A, Avela K, Weerasekera N, Cormand B, Hirvioja ML, Riikonen S, Ylikorkala O, Lehesjoki AE, Williamson C, Aittomaki K (2003) Genetic evidence of heterogeneity in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gut 52:1025–1029
Vallejo M, Briz O, Serrano MA, Monte MJ, Marin J (2006) Potential role of trans-inhibition of the bile salt export pump by progesterone metabolites in the etiopathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Hepatol 44:1150–1157
Reyes H, Sjovall J (2000) Bile acids and progesterone metabolites in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Ann Med 32:94–106
Bacq Y, Sapey T, Brechot MC, Pierre F, Fignon A, Dubois F (1997) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: a French prospective study. Hepatology 26:358–364
Reyes H, Baez ME, Gonzalez MC, Hernandez I, Palma J, Ribalta J, Sandoval L, Zapata R (2000) Selenium, zinc and copper plasma levels in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, in normal pregnancies and in healthy individuals, in Chile. J Hepatol 32:542–549
Kauppila A, Korpela H, Makila UM, Yrjanheikki E (1987) Low serum selenium concentration and glutathione peroxidase activity in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 294:150–152
Tanasescu C (2004) Correlation between cholestasis and infection. Rom J Gastroenterol 13:23–27
Bacq Y (1999) Liver and pregnancy. Pathol Biol (Paris) 47:958–965
Gilroy RK, Mailliard ME, Gollan JL (2003) Gastrointestinal disorders of the critically ill. Cholestasis of sepsis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17:357–367
Reyes H, Zapata R, Hernandez I, Gotteland M, Sandoval L, Jiron MI, Palma J, Almuna R, Silva JJ (2006) Is a leaky gut involved in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy? Hepatology 43:715–722
Fagan EA (1999) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Clin Liver Dis 3:603–632
Brites D (2002) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: changes in maternal–fetal bile acid balance and improvement by ursodeoxycholic acid. Ann Hepatol 1:20–28
Glantz A, Marschall HU, Mattsson LA (2004) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: relationships between bile acid levels and fetal complication rates. Hepatology 40:467–474
Egerman RS, Riely CA (2004) Predicting fetal outcome in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: is the bile acid level sufficient? Hepatology 40:287–288
Dann AT, Kenyon AP, Seed PT, Poston L, Shennan AH, Tribe RM (2004) Glutathione S-transferase and liver function in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and pruritus gravidarum. Hepatology 40:1406–1414
Dann AT, Kenyon AP, Wierzbicki AS, Seed PT, Shennan AH, Tribe RM (2006) Plasma lipid profiles of women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 107:106–114
Riely CA (1988) Case studies in jaundice of pregnancy. Semin Liver Dis 8:191–199
Germain AM, Carvajal JA, Glasinovic JC, Kato CS, Williamson C (2002) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: an intriguing pregnancy-specific disorder. J Soc Gynecol Invest 9:10–14
Romano TJ, Riely CA (1989) Pregnancy and the liver. In: Baker S (ed) Hepatology for the clinician: a problem-oriented approach. Alan R. Liss, Inc., Caracas, Venezuela, p 283
Binder T, Salaj P, Zima T, Vitek L (2006) Randomized prospective comparative study of ursodeoxycholic acid and S-adenosyl-l-methionine in the treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Perinat Med 34:383–391
Roncaglia N, Locatelli A, Arreghini A, Assi F, Cameroni I, Pezzullo JC, Ghidini A (2004) A randomised controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid and S-adenosyl-l-methionine in the treatment of gestational cholestasis. BJOG 111:17–21
Warren JE, Blaylock RC, Silver RM (2005) Plasmapheresis for the treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy refractory to medical treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol 192:2088–2089
Palmer DG, Eads J (2000) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: a critical review. J Perinat Neonat Nurs 14:39–51
Lucena JF, Herrero JI, Quiroga J, Sangro B, Garcia-Foncillas J, Zabalegui N, Sola J, Herraiz M, Medina JF, Prieto J et al (2003) A multidrug resistance 3 gene mutation causing cholelithiasis, cholestasis of pregnancy, and adulthood biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 124:1037–1042
Sibai BM (2005) Diagnosis, prevention, and management of eclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 105:402–410
Villegas HAJ, Maqueo M (1970) Spontaneous rupture of liver in toxemia of pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 8:836
Weinstein L (1982) Syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count: a severe consequence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 142:159–167
Araujo AC, Leao MD, Nobrega MH, Bezerra PF, Pereira FV, Dantas EM, Azevedo GD, Jeronimo SM (2006) Characteristics and treatment of hepatic rupture caused by HELLP syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195:129–133
Debette M, Samuel D, Ichai P, Sebagh M, Saliba F, Bismuth H (1999) Labor complications of the HELLP syndrome without any predictive factors. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 23:264–267
Romero Arauz JF, Lara Gonzalez AL, Ramos Leon JC, Izquierdo Puente JC (2001) Maternal morbidity and mortality in HELLP Syndrome. Ginecol Obstet Mex 69:189–193
Kathula SK, Bolla SR, Magann EF (2002) HELLP syndrome leading to a diagnosis of pregnancy. South Med J 95:934–935
Kawabata I, Nakai A, Takeshita T (2006) Prediction of HELLP syndrome with assessment of maternal dual hepatic blood supply by using Doppler ultrasound. Arch Gynecol Obstet 274:303–309
Strand S, Strand D, Seufert R, Mann A, Lotz J, Blessing M, Lahn M, Wunsch A, Broering DC, Hahn U et al (2004) Placenta-derived CD95 ligand causes liver damage in hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count syndrome. Gastroenterology 126:849–858
Terrone DA, Rinehart BK, May WL, Moore A, Magann EF, Martin JN Jr (2000) Leukocytosis is proportional to HELLP syndrome severity: evidence for an inflammatory form of preeclampsia. South Med J 93:768–771
Sibai BM (1990) The HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets): much ado about nothing? Am J Obstet Gynecol 162:311–316
Sibai BM (2004) Diagnosis, controversies, and management of the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. Obstet Gynecol 103:981–991
Martin JN Jr, Blake PG, Lowry SL, Perry KG Jr, Files JC, Morrison JC (1990) Pregnancy complicated by preeclampsia-eclampsia with the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count: how rapid is postpartum recovery? Obstet Gynecol 76:737–741
Pereira SP, O’Donohue J, Wendon J, Williams R (1997) Maternal and perinatal outcome in severe pregnancy-related liver disease. Hepatology 26:1258–1262
Pockros PJ, Peters RL, Reynolds TB (1984) Idiopathic fatty liver of pregnancy: findings in ten cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 63:1–11
Egerman RS, Witlin AG, Friedman SA, Sibai BM (1996) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome in pregnancy: review of 11 cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:950–956
Sibai BM, Ramadan MK (1993) Acute renal failure in pregnancies complicated by hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets. Am J Obstet Gynecol 168:1682–1687; discussion 1687–1690
Martin JN Jr, Blake PG, Perry KG Jr, McCaul JF, Hess LW, Martin RW (1991) The natural history of HELLP syndrome: patterns of disease progression and regression. Am J Obstet Gynecol 164:1500–1509; discussion 1509–1513
Dashe JS, Ramin SM, Cunningham FG (1998) The long-term consequences of thrombotic microangiopathy (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome) in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 91:662–668
Marder V, Martin SE, Francis CW, Colman RW (1987) Consumptive thrombo-hemorrhagic disorders. In: Colman R, Hirsh J, Marder VJ, Salzman EW (eds) Hemostasis, thrombosis: basic principles and clinical practice, 2nd edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 975–1015
Reubinoff BE, Schenker JG (1991) HELLP syndrome—a syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet count—complicating preeclampsia-eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 36:95–102
Sibai BM, Barton JR (2005) Dexamethasone to improve maternal outcome in women with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:1587–1590
O’Boyle JD, Magann EF, Waxman E, Martin JN Jr (1999) Dexamethasone-facilitated postponement of delivery of an extremely preterm pregnancy complicated by the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets. Mil Med 164:316–318
Magann EF, Perry KG Jr, Chauhan SP, Graves GR, Blake PG, Martin JN Jr (1994) Neonatal salvage by week’s gestation in pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome. J Soc Gynecol Invest 1:206–209
Tompkins MJ, Thiagarajah S (1999) HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome: the benefit of corticosteroids. Am J Obstet Gynecol 181:304–309
Magann EF, Perry KG Jr, Meydrech EF, Harris RL, Chauhan SP, Martin JN Jr (1994) Postpartum corticosteroids: accelerated recovery from the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP). Am J Obstet Gynecol 171:1154–1158
Magann EF, Bass D, Chauhan SP, Sullivan DL, Martin RW, Martin JN Jr (1994) Antepartum corticosteroids: disease stabilization in patients with the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP). Am J Obstet Gynecol 171:1148–1153
Martin JN Jr, Rose CH, Briery CM (2006) Understanding and managing HELLP syndrome: the integral role of aggressive glucocorticoids for mother and child. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195:914–934
O’Brien JM, Milligan DA, Barton JR (2000) Impact of high-dose corticosteroid therapy for patients with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183:921–924
Fonseca JE, Mendez F, Catano C, Arias F (2005) Dexamethasone treatment does not improve the outcome of women with HELLP syndrome: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:1591–1598
Mattar F, Sibai BM (2000) Eclampsia. VIII. Risk factors for maternal morbidity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 182:307–312
Isler CM, Rinehart BK, Terrone DA, Martin RW, Magann EF, Martin JN Jr (1999) Maternal mortality associated with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 181:924–928
Haddad B, Barton JR, Livingston JC, Chahine R, Sibai BM (2000) Risk factors for adverse maternal outcomes among women with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183:444–448
Abercrombie J (1877) Case of hemorrhage of the Liver. London Medical Gazzette 34
Ekele BA, Airede LR, Legbo JN, Yakubu A, Nnadi DC, Gana MA (2006) Spontaneous liver rupture in pre-eclampsia. Afr J Med Med Sci 35:103–105
Gonzalez-Martinez G, Aguirre-Suarez J, Alarcon-Sandoval A, Pulgar-Lehr A, Valbuena-Adrianza O (2004) Hepatic and splenic rupture associated with severe preeclampsia: a case report. Invest Clin 45:63–68
Chan AD, Gerscovich EO (1999) Imaging of subcapsular hepatic and renal hematomas in pregnancy complicated by preeclampsia and the HELLP syndrome. J Clin Ultrasound 27:35–40
Schwartz ML, Lien JM (1997) Spontaneous liver hematoma in pregnancy not clearly associated with preeclampsia: a case presentation and literature review. Am J Obstet Gynecol 176:1328–1332; discussion 1332–1323
Khong SY, James M, Smith P (2005) Diagnosis of liver infarction postpartum. Obstet Gynecol 105:1271–1273
Krueger KJ, Hoffman BJ, Lee WM (1990) Hepatic infarction associated with eclampsia. Am J Gastroenterol 85:588–592
Barton JR, Sibai BM (1996) Hepatic imaging in HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count). Am J Obstet Gynecol 174:1820–1825; discussion 1825–1827
Soyer P, This B, De Broucker F, Levesque M (1989) Spontaneous intrahepatic hemorrhage: a severe complication of the Hellp syndrome. Value of early radiologic diagnosis. Apropos of a case. J Radiol 70:641–644
Bettmann MA (2004) Frequently asked questions: iodinated contrast agents. Radiographics 24(Suppl 1):S3–10
Barton JR, Riely CA, Adamec TA, Shanklin DR, Khoury AD, Sibai BM (1992) Hepatic histopathologic condition does not correlate with laboratory abnormalities in HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count). Am J Obstet Gynecol 167:1538–1543
Pilco P, McCormack L, Perez D, Clavien PA (2006) Ruptured subcapsular hepatic hematoma associated with HELLP syndrome. Rev Gastroenterol Peru 26:207–210
Merchant SH, Mathew P, Vanderjagt TJ, Howdieshell TR, Crookston KP (2004) Recombinant factor VIIa in management of spontaneous subcapsular liver hematoma associated with pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 103:1055–1058
Usta IM, Barton JR, Amon EA, Gonzalez A, Sibai BM (1994) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: an experience in the diagnosis and management of fourteen cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 171:1342–1347
Stander HJCJ (1934) Acute yellow atrophy of the liver in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 28:61–69
Sheehan H (1940) The pathology of the acute yellow atrophy and delayed chlorophorm poisoning. J Obstet Gyneco Br Emp 47:49–62
Ibdah JA (2006) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: an update on pathogenesis and clinical implications. World J Gastroenterol 12:7397–7404
Riely C (1987) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Semin Liver Dis 7(47)
Mjahed K, Charra B, Hamoudi D, Noun M, Barrou L (2006) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 274:349–353
Kennedy S, Hall PM, Seymour AE, Hague WM (1994) Transient diabetes insipidus and acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 101:387–391
Bacq Y, Riely CA (1993) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: the hepatologist’s view. Gastroenterologist 1:257–264
Castro MA, Ouzounian JG, Colletti PM, Shaw KJ, Stein SM, Goodwin TM (1996) Radiologic studies in acute fatty liver of pregnancy. A review of the literature and 19 new cases. J Reprod Med 41:839–843
Van Le L, Podrasky A (1990) Computed tomographic and ultrasonographic findings in women with acute fatty liver of pregnancy. J Reprod Med 35:815–817
Ko H, Yoshida EM (2006) Acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Can J Gastroenterol 20:25–30
Castro MA, Fassett MJ, Reynolds TB, Shaw KJ, Goodwin TM (1999) Reversible peripartum liver failure: a new perspective on the diagnosis, treatment, and cause of acute fatty liver of pregnancy, based on 28 consecutive cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 181:389–395
Ockner SA, Brunt EM, Cohn SM, Krul ES, Hanto DW, Peters MG (1990) Fulminant hepatic failure caused by acute fatty liver of pregnancy treated by orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology 11:59–64
Browning MF, Levy HL, Wilkins-Haug LE, Larson C, Shih VE (2006) Fetal fatty acid oxidation defects and maternal liver disease in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 107:115–120
Yang Z, Zhao Y, Bennett MJ, Strauss AW, Ibdah JA (2002) Fetal genotypes and pregnancy outcomes in 35 families with mitochondrial trifunctional protein mutations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 187:715–720
Yang Z, Yamada J, Zhao Y, Strauss AW, Ibdah JA (2002) Prospective screening for pediatric mitochondrial trifunctional protein defects in pregnancies complicated by liver disease. JAMA 288:2163–2166
Santos L, Patterson A, Moreea SM, Lippiatt CM, Walter J, Henderson M (2007) Acute liver failure in pregnancy associated with maternal MCAD deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:103
Innes AM, Seargeant LE, Balachandra K, Roe CR, Wanders RJ, Ruiter JP, Casiro O, Grewar DA, Greenberg CR (2000) Hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency presenting as maternal illness in pregnancy. Pediatr Res 47:43–45
Mutze S, Ahillen I, Rudnik-Schoeneborn S, Eggermann T, Leeners B, Neumaier-Wagner PM, Kuse S, Rath W, Zerres K (2007) Neither maternal nor fetal mutation (E474Q) in the alpha-subunit of the trifunctional protein is frequent in pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome. J Perinat Med 35:76–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0251-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hepburn, I.S. Pregnancy-Associated Liver Disorders. Dig Dis Sci 53, 2334–2358 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0167-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0167-9