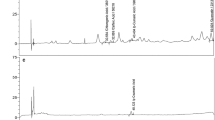
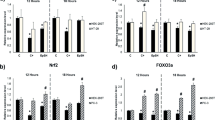
Abstract
Bauhinia holophylla (Bong.) Steud. (Fabaceae) is a plant used in Brazilian folk medicine to treat diabetes and inflammation. This study evaluated the phytochemical properties, cytotoxic, apoptotic, mutagenic/antimutagenic effects and alterations in gene expression (RNAm) in HepG2 cells treated with the B. holophylla extract. The phytochemical profile highlight the presence of flavonoids isorhamentin and quercetin derivates. The MTT assay was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of different concentrations for different treatment times. Three concentrations (7.5, 15, 30 µg/mL) were chosen for assessment of apoptosis (AO/EB), mutagenicity (micronucleus), and cell cycle kinetics (flow cytometry). Thereafter, the concentration of 7.5 µg/mL was chosen to evaluate the protective effects against DNA damage induced by benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P). At concentrations higher than 7.5 µg/mL (between 10 and 50 µg/mL), the extract was cytotoxic, induced apoptosis, and caused antiproliferative effects. However, it did not induce micronucleus and a reduction of apoptotic and micronucleated cells was observed in treatments that included the extract and B[a]P. The protective effect is attributable to the presence of flavonoids, described as antioxidants, inhibitors of DNA adduct and activators of detoxifying enzymes. The results of the present study such as absence of cytotoxic and mutagenic effects and protective effects against known carcinogens suggest that B. holophylla has potential for use soon as herbal medicine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal RC, Pandey S (2009) Evaluation of anticarcinogenic and antimutagenic potential of Bauhinia variegata extract in Swiss albino mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 10:913–916
Andersen OM, Markhan KR (2006) Flavonoides: chemistry, biochemistry and applications. Taylor & Francis group, New York
Aranda PS, LaJoie DM, Jorcyk CL (2012) Bleach gel: a simple agarose gel for analyzing RNA quality. Electrophoresis 33:366–369
Atienzar FA, Novik EI, Gerets HH, Parekh A, Delatour C, Cardenas A, MacDonald J, Yarmush ML, Dhalluin S (2014) Predictivity of dog co-culture model, primary human hepatocytes and HepG2 cells for the detection of hepatotoxic drugs in humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 275:44–61
Bresolin S, Vargas VMF (1993) Mutagenic potencies of medicinal plants screened in the Ames test. Phytother Res 7:260–262
Burczynski ME, Penning TM (2000) Genotoxic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ortho-quinones generated by aldo-keto reductases induce CYP1A1 via nuclear translocation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Cancer Res 60:908–915
Caiment F, Gaj S, Claessen S, Kleinjans J (2015) High-throughput data integration of RNA–miRNA–circRNA reveals novel insights into mechanisms of benzo[a]pyrene-induced carcinogenicity. Nucleic Acids Res 43:2525–2534
Cardozo TA, Rosa DP, Feiden IR, Rocha JAV, D’Avila de Oliveira NC, Pereira TS, Pastoriza TF, Marques DM, Lemos CT, Terra NR, Vargas VMF (2006) Genotoxicity and toxicity assessment in urban hydrographic basins. Mutat Res 603:83–96
Cechinel Filho V (2009) Chemical composition and biological potential of plants from the genus Bauhinia. Phytother Res 23:1347–1354
Chen Z, Zheng S, Li L, Jiang H (2014) Metabolism of flavonoids in human: a comprehensive review. Curr Drug Metab 15:48–61
Cuyckens F, Claeys M (2004) Mass spectrometry in the structural analysis of flavonoids. J Mass Spectrom 39:1–15
Da Justa Neves DB, Caldas ED (2015) Dietary supplements: International legal framework and adulteration profiles, and characteristics of products on the Brazilian clandestine market. Regul Toxicol Pharm 73:93–104
Da Silva KL, Cechinel Filho VC (2002) Plantas do gênero Bauhinia: composição química e potencial farmacológico. Quim Nova 25:449–454
David B, Wolfender JL, Dias DA (2015) The pharmaceutical industry and natural products: historical status and new trends. Phytochem Rev 14:299–315
Delgado ME, Haza AI, Arranz N, García A, Morales P (2008) Dietary polyphenols protect against N-nitrosamines and benzo(a)pyrene induced DNA damage (strand breaks and oxidized purines/pyrimidines) in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Eur J Nutr 47:479–490
Eastmond DA, Tucker JD (1989) Identification of aneuploidy-inducing agents using cytokinesis-blocked human lymphocytes and an antikinetochore antibody. Environ Mol Mutagen 13:34–43
Estrada O, Hasegawa M, Gonzalez-Mujíca F, Motta N, Perdomo E, Solorzano A, Mendéz J, Mendéz B, Zea EG (2005) Evaluation of flavonoids from Bauhinia megalandra leaves as inhibitors of glucose-6-phosphatase system. Phytother Res 19:859–863
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2008) Guidance document on the submission of a dossier on a substance to be used in Food Contact Materials for evaluation by EFSA by the Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC). http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/21r.pdf. Accessed 8 Jan 2017
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) (2006) Guidance for industry and review staff recommended approaches to integration of genetic toxicology study results. http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm. Accessed 18 Dec 2016
Fenech M (2007) Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Nat Prot 2:1084–1104
Geller FC, Teixeira MR, Pereira ABD, Dourado LPA, Souza DG, Braga FC, Simões CMO (2015) Evaluation of the wound healing properties of Hancornia speciosa leaves. Phytother Res 29:1887–1893
Gonzalez-Mujica F, Motta N, Márquez AH, Capote-Zulueta J (2003) Effects of Bauhinia megalandra aqueous leaf extract on intestinal glucose absorption and uptake by enterocyte brush border membrane vesicles. Fitoterapia 74:84–90
Gonzalez-Mujica F, Motta N, Estrada O, Perdomo E, Méndez J, Hasegawa M (2005) Inhibition of hepatic neoglucogenesis and glucose-6-phosphatase by quercetin 3-o-α (2″-galloyl) rhamnoside isolated from Bauhinia megalandra leaves. Phytother Res 19:624–627
Hatia S, Septembre-Malaterre A, Le Sage F, Badiou-Bénéteau A, Baret P, Payet B, Lefebvre d’hellencourt C, Gonthier MP (2014) Evaluation of antioxidant properties of major dietary polyphenols and their protective effect on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and red blood cells exposed to oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 48:387–401
Kim KC, Lee IK, Kang KA, Kim HS, Kang SS, Hyun JW (2012) Baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone) reduces oxidative stress-induced DNA damage by upregulating the DNA repair system. Cell Biol Toxicol 28:421–433
Kirsch-Volders M, Sofuni T, Aardema M, Albertini S, Eastmond D, Fenech M, Ishidate M, Lorge E, Norppa H, Surrales J, Von der Hude W, Wataka A (2000) Report from the in vitro micronucleus assay working group. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:167–172
Lee SH, Yumnam S, Hong GE, Raha S, Venkatarame Gowda Saralamma V, Lee HJ, Heo JD, Lee SJ, Lee W-S, Kim E-H, Park HS, Kim GS (2015) Flavonoids of Korean Citrus aurantium L. Induce apoptosis via intrinsic pathway in human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells. Phytother Res 29:1940–1949
Lewis GP, Schrire BD, Mackinder BA, Lock JM (2005) Legumes of the world. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London
Llana-Ruiz-Cabello M, Pichardo S, Maisanaba S, Puerto M, Prieto AI, Gutiérrez-Praena D, Jos A, Cameán AM (2015) In vitro toxicological evaluation of essential oils and their main compounds used in active food packaging: a review. Food Chem Toxicol 81:9–27
McGahon AJ, Martin SJ, Bissonnette RP, Mahboudi A, Shi Y, Mogil RJ, Nishioka WK, Green DR (1995) The end of the (cell) line: methods for the study of apoptosis in vitro. In: Schurartz LM, Osbourne BA (eds) Methods in cell biology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 153–184
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Obici S, Otobone FJ, Sela VRS, Ishida K, Silva JC, Nakamura CV, Cortez DAG, Audi EA (2008) Preliminary toxicity study of dichloromethane extract of Kielmeyera coriacea stems inmiceandrats. J Ethnopharmacol 115:131–139
OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) (2010) Series on testing and assessment, No. 129. Guidance document on using cytotoxicity tests to estimate starting doses for acute oral systemic toxicity, Paris
Ormerod MG (2000) Analysis of DNA—general methods, in flow cytometry. In: Ormerod MG (ed) A practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 83–97
Pandey S, Agrawal RC (2010) Clastogenic analysis of Bauhinia variegata bark extract using micronucleus assay in mouse bone marrow cells. Am-Eurasian J Toxicol Sci 2:112–114
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36
Rajkapoor B, Jayakar B, Murugesh N, Sakthisekaran D (2006) Chemoprevention and cytotoxic effect of Bauhinia variegata against N-nitrosodiethylamine induced liver tumors and human cancer cell lines. J Ethnopharmacol 104:407–409
Ramos AA, Lima CF, Pereira ML, Fernandes-Ferreira M, Pereira-Wilson C (2008) Antigenotoxic effects of quercetin, rutin and ursolic acid on HepG2 cells: evalution by the comet assay. Toxicol Lett 177:66–73
Ribeiro DL, Cilião HL, Specian AFL, Serpeloni JM, De Souza MF, Tangerina MMP, Vilegas W, Boldrin PK, Resende FA, Varanda EA, Martínez-López W, Cólus IMS (2015) Chemical and biological characterisation of Machaerium hirtum (Vell.) Stellfeld: absence of cytotoxicity and mutagenicity and possible chemopreventive potential. Mutagenesis 31:147–160
Rodeiro I, Delgado R, Garrido G (2014) Effects of a Mangifera indica L. stem bark extract and mangiferin on radiation-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes and lymphoblastoid cells. Cell Prolif 47:48–55
Roleira FM, Tavares-da-Silva EJ, Varela CL, Costa SC, Silva T, Garrido J, Borges F (2015) Plant derived and dietary phenolic antioxidants: anticancer properties. Food Chem 183:235–258
Rozza AL, Cesar DAS, Pieroni LG, Saldanha LL, Dokkedal AL, De-Faria FM, Souza-Brito ARM, Vilegas W, Takariha RK, Pellizzon CH (2015) Antiulcerogenic activity and toxicity of Bauhinia holophylla hydroalcoholic extract. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:1–9
Rupasinghe HV, Nair SV, Robinson RA (2014) Chemopreventive properties of fruit phenolic compounds and their possible mode of actions. Stud Nat Prod Chem 42:229
Santos FJBD, Moura DJ, Péres VF, Sperotto ARM, Camarão EB, Cavalcante AACM, Saffi J (2012) Genotoxic and mutagenic properties of Bauhinia platypetala extract, a traditional Brazilian medicinal plant. J Ethnopharmacol 144:474–482
Serpeloni JM, Specian AFL, Ribeiro DL, Tuttis K, Vilegas W, Martínez-López W, Dokkedal AL, Saldanha LL, Cólus IMS, Varanda EA (2015) Antimutagenicity and induction of antioxidant defense by flavonoid rich extract of Myrcia bella Cambess. in normal and tumor gastric cells. J Ethnopharmacol 176:345–355
Shiizaki K, Kawanishi M, Yagi T (2013) Dioxin suppresses benzo[a]pyrene-induced mutations and DNA adduct formation through cytochrome P450 1A1 induction and (±)-anti-benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide inactivation in human hepatoma cells. Mutat Res 750:77–85
Sisenando HAAACN, Macedo MFS, Saturnino ACRD, Coelho LCBB, Medeiros SRB (2009) Evaluation of the genotoxic potential of Bauhinia monandra leaf lectin (BmoLL). Food Chem Toxicol 47:303–308
Sison-Young RL, Mitsa D, Jenkins RE, Mottram D, Alexandre E, Richert L, Aerts H, Weaver RJ, Jones RP, Johann E, Hewitt PG, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Goldring CEP, Kitteringham NR, Park K (2015) Comparative proteomic characterization of 4 human liver-derived single cell culture models reveals significant variation in the capacity for drug disposition, bioactivation, and detoxication. Toxicol Sci 147:412–424
Verschaeve L, Kestens V, Taylor JLS, Elgorashi EE, Maes A, Van Puyvelde L, DeKimpe N, Van Staden J (2004) Investigation of the antimutagenic effects of selected South African medicinal plant extracts. Toxicol In Vitro 18:29–35
Waizenegger J, Lenze D, Luckert C, Seidel A, Lampen A, Hessel S (2015) Dose-dependent induction of signaling pathways by the flavonoid quercetin in human primary hepatocytes: a transcriptomic study. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:1117–1129
Waters MD, Brady AL, Stack HF, Brockman HE (1990) Antimutagenicity profiles for some model compounds. Mutat Res 238:57–85
Wu XJ, Lu WQ, Mersch-Sundermann V (2003) Benzo(a)pyrene induced micronucleus formation was modulated by persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in metabolically competent human HepG2 cells. Toxicol Lett 144:143–150
Zhang H, Zhang M, Yu L, Zhao Y, He N, Yang X (2012) Antitumor activities of quercetin and quercetin-5′,8-disulfonate in human colon and breast cancer cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol 50:1589–1599
Acknowledgements
The authors also wish to thank Dr. E. N. Itano for the use of the spectrophotometer; the Service of Flow Cytometry and Cell Classification of the Institute of Biological Research Clemente Estable (Uruguay) for the use of the FACSVantage Flow Cytometer.
Funding
The authors thank the financial support from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) in the BIOTA Program (2009/52237-9; 2009/16147-5; 2012/01996-0) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior CAPES-PROAP); the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for a scholarship granted to masters student Ribeiro, D.L and for productivity grant to Cólus, I.M.S, Varanda, E.A. and Vilegas, W.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, D.L., Cilião, H.L., Specian, A.F.L. et al. Phytochemical study and evaluation of cytotoxicity, mutagenicity, cell cycle kinetics and gene expression of Bauhinia holophylla (Bong.) Steud. in HepG2 cells in vitro. Cytotechnology 70, 713–728 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0173-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-017-0173-5