Abstract
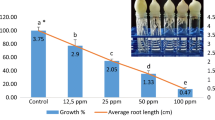
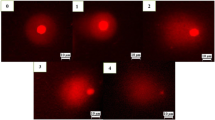
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) is a synthetic plant growth regulator that is highly toxic to most broad leaved plants and relatively nontoxic to monocotyledonous plants; is frequently used as weed killer. The study aimed to investigate cytogenetic effects of different concentrations of 2,4-D (0.67, 1.34, 2.01, 2.68, 3.35 and 4.02 mg/L) on Allium cepa bulblets’ root tips treated for 24 and 48 h. The results showed six types of structural aberrations: C-mitosis, stickiness, laggards, bridges, fragments and multipolarity that varied numerically compared to control. It significantly affected mitotic index (MI) at 24 and 48 h treatment. In the Allium test, MI increased significantly at three lower concentrations (0.67, 1.34, 2.01 mg/L) after treatment with 2,4-D for 24 h and decreased significantly at higher concentration. Whereas, 2,4-D treatment for 48 h increased MI at all concentrations with significantly decreased MI at the highest concentration. The experiment was extended using comet test that did not reveal significant difference among treatments except for application of 4.02 mg/L 2,4-D for 48 h; where cell damages were verified by comet test. Rest of the concentrations for any duration of time were not damaging and toxic to cells. The results showed, visible mitodepressive action of 4.02 mg/L 2,4-D when treated for 48 h that had tendency to become toxic if the roots had been in touch with 2,4-D for a longer time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajay KJ, Sorbhoy RK (1988) Cytogenetic studies on the effect of some chlorinated pesticide. Cytologia 53:427–436
Anonymous (2015a) Extension toxicology network. Pesticide information profile—2,4-D. June 1996. Accessed 18 Oct 2015
Anonymous (2015b). https://www.testbiotech.org/sites/default/files/Risks%20of%20herbicide%202_4-D0.pdf. Accessed 18 Oct 2015
Ateeq B, Farah MA, Ali MN, Ahmad V (2002) Clastogeneticity of pentachlorophenol, 2,4-D and butachlor evaluated by Allium root tip test. Mutat Res 514:105–113
Cecchini E, Natali L, Cavallini A, Durante M (1992) DNA variations in regenerated plants of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theor Appl Genet 84:874–879
Cogliano VJ, Baan R, Straif K et al (2011) Preventable exposures associated with human cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:1827–1839
Coppen GDA, Jepsons PC (1996) The effects of the duration of exposure on the toxicity of diflubenzuron, hexaflumuron and teflubenzuron to various stages of II instar Schistocerca gregaria. Pestic Sci 46:191–197
Darlington CD, La Cour LE (1976) The handing of chromosomes. George Allen and Unwin Ltd., London, p 201
Don-Pedro KN (1996) Fumigant toxicity is the major route of ınsecticidal activity of citruspeel essential oils. Pestic Sci 46:71–78
El-Ghamery AA, El-Nahas AI, Mansour MM (2000) The action of atrazine herbicide as an indicator of cell division on chromosomes and nucleic acids content in root meristems of Allium cepa and Vicia faba. Cytologia 65:277–287
Fantel AG (1996) Reactive oxygen species in developmental toxicity: review and hypothesis. Teratology 53:96–217
Fernandes TCC, Mazzeo DEC, Marin-Morales MA (2007) Mechanism of micronuclei formation in polyploidizated cells of Allium cepa exposed to trifluralin herbicide. Pestic Biochem Physiol 88:252–259
Filkowski J, Besplug J, Burke P et al (2003) Genotoxicity of 2,4-D and dicamba revealed by transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants harboring recombination and point mutation markers. Mutat Res 542:23–32
Fiskesjo G (1988) The Allium test—an alternative in environmental studies: the relative toxicity of metal ions. Mutat Res 197:243–260
Fiskesjo G (1993) The Allium test in waste-water monitoring. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 8:291–298
Franklin CI, Dixoni RA (1994) Initation and maintenance of callus and cell suspension cultures. In: Dixon RA, Gonzales RA (eds) Plant tissue culture—a pratical approach, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 1–27
George EF (1993) Plant propagation by tissue culture. Part I. The technology, second education. Exegenetics Ltd, England, p 57
Gilbert SG (2014) 2,4-D. In: McKeen S (ed). http://www.toxipedia.org/display/toxipedia/2,4-D. Accessed 18 Oct 2015
Grant WF (1999) Higher plant assays for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and gene mutations–a brief historical background on their use for screening and monitoring environmental chemicals. Mutat Res 426:107–112
Hardell L (2008) Pesticides soft-tissue sarcoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma—historical aspects on the precautionary principle in cancer prevention. Acta Oncol 47:347–354
Heiden TK, Carvan MJ III, Hutz RJ (2006) Inhibition of follicular development, vitellogenesis, and serum 17 beta-estradiol concentrations in zebrafish following chronic, sublethal dietary exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Sci 90:490–499
Hoshina MM (2002) Avaliação da possível contaminação das águas do Ribeirão Claro município de Rio Claro, pertencente à bacia do rio Corumbataí, por meio de testes de mutagenicidade em Allium cepa, Trabalho de conclusão (Bacharel e Licenciatura - Ciências Biológicas). Universidade Estadual Paulista, Rio Claro, p 52
Juchimiuk J, Gnys A, Maluszynska J (2006) DNA damage induced by mutagens in plant and human cell nuclei in acellular comet assay. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 44:127–131
Justyna GUZY, Zgórska A, Ziembińska A (2012) Comet assay optimization with Allium cepa as an indicator for ecotoxicological usage. Archit Civ Eng Environ 5:109–116
Kaynak L, Memiş M (1997) Bitki büyüme engelleyici ve geciktiricilerinin etki mekanizmaları. Akd Üniv Zir Fak Dergisi 10:237–248
Kocaman Y, Güven B (2015) In vitro genotoxicity assessment of the synthetic plant growth regulator, 1-naphthaleneacetamide. Cytotechnology 1–10
Koduru PRK, Rao MK (1981) Cytogenetics of synaptic mutants in higher plants. Theor Appl Genet 59:197–214
Kumar S (2010) Effect of 2,4-D and isoproturon on chromosomal disturbances during mitotic division in root tip cells of Triticum aestivum L. Cytol Genet 44:14–21
Kumar NKH, Jagannath S (2015) Cytological effects of herbicide butachlor 50 EC on Somatic cells of Triticum aestivum L. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 3:30–34
Kumari TS, Vaidyanath K (1989) Testing of genotoxic effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) using multiple genetic assay systems of plants. Mutat Res 226:235–238
Levan A (1938) The effect of colchicine on root mitosis in Allium. Hereditas 24:471–486
Liman R, Ciğerci IH, Akyıl D et al (2011) Determination of genotoxicity of Fenaminosulf by Allium and Comet tests. Pestic Biochem Physiol 99:61–64
Mohandas T, Grant WF (1972) Cytogenetic effects of 2,4-D and amitrole in relation to nuclear volume and DNA content in some higher plants. Can J Genet Cytol 14:773–783
Morais Leme D, Marin-Morales MA (2009) Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: a review on its application. Mutat Res 682:71–81
Mortensen DA, Egan JT, Maxwell BD et al (2012) Navigating a critical juncture for sustainable weed management. Bioscience 62:75–84
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) Revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol 15:473–479
Prasad G, Das K (1977) Effects of some growth substances on mitosis. Cytologia 42:323–329
Pulate PV, Tarar JL (2014) Cytogenetic effects of tilt on root tip meristem of onion Allium cepa L. Int J Plant Anim Environ Sci 4:53–57
Puolimatka M, Karp A (1993) Effect of genotype on chromosome variation in tissue culture of inbred and outbred rye. Heredity 71:138–144
Qian XW, Luo WH, Zheng OX (2006) Joint effects of microwave and chromium trioxide on root tip cells of Vicia faba. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 7:221–227
Schrader KK, Rimando AM, Tucker CS, Duke SO (1999) Factors affecting toxicity of ferulate towards the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria cf chalybea. Pestic Sci 55:726–732
Setha CS, Misraa V, Chauhanb LKS, Singh RR (2008) Genotoxicity of cadmium on root meristem cells of Allium cepa: cytogenetic and comet assay approach. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:711–716
Smith R (1992) Plant tissue culture techniques and experiments. Academic Press Inc, University College Station, pp 1–22
Song Y (2014) Insight into the mode of action of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) as an herbicide. J Integr Plant Biol 56:106–113
Tarar JL, Dyansagar VR (1980) Effect of gamma rays and EMS on growth sand branching in Turneria ulmifolia L. J Cytol Genet 14:118–124
Tartar G, Kaymak F, Muranli FDG (2006) Genotoxic effects of avenoxan on Allium cepa L. and Allium sativum L. Caryologia 59:241–247
Tomkins DJ, Grant WF (1976) Monitoring natural vegetation for herbicide induced chromosomal aberrations. Mutat Res 36:73–84
Truta E, Zamfirache MM, Rosu C et al (2011) Cytogenetic effects induced by 2,4-D and kinetin in radish and common bean root meristems. Rom Agric Res 28:207–215
Türkoğlu Ş (2012) Determination of genotoxic effects of chlorfenvinphos and fenbuconazole in Allium cepa root cells by mitotic activity, chromosome aberration, DNA content, and comet assay. Pestic Biochem Physiol 103:224–230
USEPA (2005) 2,4-D red facts. http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/factsheets/24d_fs.htm. Accessed 18 Oct 2015
Ventura L, Giovannini A, Savio M et al (2013) Single cell gel electrophoresis (comet) assay with plants: research on DNA repair and ecogenotoxicity testing. Chemosphere 92:1–9
Vogue PA, Kerle EA, Jenkins JJ (2004) 2,4-D technical fact sheet. Osu extension pesticide properties database. Oregon State University, Corvallis
Von Stackelberg K (2013) A systematic review of carcinogenic outcomes and potential mechanisms from exposure to 2,4-D and MCPA in the environment. J Toxicol 2013:1–53
Yıldız M, Ciğerci IH, Konuk M et al (2009) Determination of genotoxic effects of copper sulphate and cobalt chloride in Allium cepa root cells by chromosome aberration and comet assays. Chemosphere 75:934–938
Yüzbaşıoğlu D, Ünal F, Sancak C (2003) Cytological effects of the herbicide racer “flurochloridone” on Allium cepa. Caryologia 56:97–105
Zeljezic D, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2004) Chromosomal aberrations, micronuclei and nuclear buds induced in human lymphocytes by 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid pesticide formulation. Toxicology 200:39–47
Zheng S (1991) Chromosome variation in callus culture of Gossypium hirsutum L. In: Adams RP (ed) Conservation of plant genes, DNA banking and in vitro biotechnology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 211–221
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Gazi University Research Fund for financial support under Grant No. 04/2014-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkul, M., Özel, Ç.A., Yüzbaşıoğlu, D. et al. Does 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) induce genotoxic effects in tissue cultured Allium roots?. Cytotechnology 68, 2395–2405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9956-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9956-3