Abstract
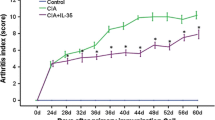
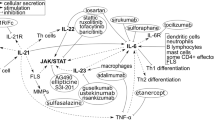
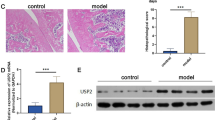
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by inflammation of the synovial membrane, which can result in joint destruction within the first few years after onset. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are glycolipids found in abundance on the outer membranes of all Gram-negative bacteria and incite a vigorous inflammatory response. We studied the potential involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase serine/threonine kinases in LPS-induced growth of HS synovial cells. Various concentrations of LPS were applied to cultured HS cells and growth rate, as well as changes in the phosphorylation states of extracellular regulated kinase 1/2, Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 were determined. As results, growth of LPS-treated HS cells was inhibited primarily by phosphorylated JNK and this phosphorylation was mediated by the LPS receptor. Our results suggest that LPS inhibits growth of HS cells primarily through the JNK pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delhanty PJ, van der Eerden BC, van der Velde M et al (2006) Ghrelin and unacylated ghrelin stimulate human osteoblast growth via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3 K) pathways in the absence of GHS-R1a. J Endocrinol 188:37–47
Desaki Y, Miya A, Venkatesh B et al (2006) Bacterial lipopolysaccharides induce defense responses associated with programmed cell death in rice cells. Plant Cell Physiol 47:1530–1540
Hsieh YY, Shen CH, Huang WS et al (2014) Resistin-induced stromal cell-derived factor-1 expression through Toll-like receptor 4 and activation of p38 MAPK/NFkappaB signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. J Biomed Sci 21:59
Im HJ, Park NH, Kwon YJ et al (2012) Bacterial lipopolysaccharides induce steroid sulfatase expression and cell migration through IL-6 pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 20:556–561
Lattuada D, Casnici C, Crotta K et al (2015) Proapoptotic activity of a monomeric smac mimetic on human fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation 38:102–109
Martirosyan A, Ohne Y, Degos C et al (2013) Lipopolysaccharides with acylation defects potentiate TLR4 signaling and shape T cell responses. PLoS ONE 8:e55117
Meyer A, Puhler A, Niehaus K (2001) The lipopolysaccharides of the phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris induce an oxidative burst reaction in cell cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Planta 213:214–222
Muller-Decker K, Manegold G, Butz H et al (2005) Inhibition of cell proliferation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in TLR4-positive epithelial cells: independence of nitric oxide and cytokine release. J Invest Dermatol 124:553–561
Reus GZ, Vieira FG, Abelaira HM et al (2014) MAPK signaling correlates with the antidepressant effects of ketamine. J Psychiatr Res 55:15–21
Rothenberg RJ, England D, Qureshi N et al (1988) Stimulation of rabbit synoviocyte prostaglandin E2 synthesis by lipopolysaccharides and their subunit structures. Arthritis Rheum 31:238–247
Urosevic J, Nebreda AR, Gomis RR (2014) MAPK signaling control of colon cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle 13:2641–2642
Wei C, Liu X, Long D et al (2014) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of mulberry MAPK gene family. Plant Physiol Biochem 77:108–116
Xiong H, Xu Y, Tan G et al (2015) Glycyrrhizin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice and inhibits TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 expression via NF-kappaB/MAPK in HaCaT cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:1335–1346
Yin G, Wang Y, Cen XM et al (2015) Lipid peroxidation-mediated inflammation promotes cell apoptosis through activation of NF-kappaB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells. Mediators Inflamm 2015:460310
Zrioual S, Ecochard R, Tournadre A et al (2009) Genome-wide comparison between IL-17A- and IL-17F-induced effects in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol 182:3112–3120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J., Peng, H. Lipopolysaccharides attenuates growth of HS cells through the JNK pathway. Cytotechnology 68, 2389–2394 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9954-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9954-5