Abstract
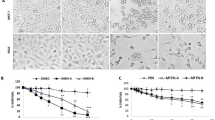
The goal of this study was to determine the effects of PGZ and MK886 on the mRNA expression of PPARα and other associated genes in MDA-MB-231 cells, and the biological mechanisms induced by both drugs were also assessed. The levels of PPARα mRNA expression in PGZ-treated and MK886-treated MDA-MB-231 cells were determined using real-time PCR; the growth inhibitory effects of PGZ and MK886 were determined using the trypan blue exclusion assay; the induction of apoptosis by PGZ and MK886 was determined using DNA fragmentation assay and real-time PCR; and the invasion of PGZ-treated and MK886-treated MDA-MB-231 cells was determined using the wound healing and transwell migration assays. In addition, we correlated the expression of PPARα mRNA with other genes, including PPARγ, FGF4 and 5LOX, in drug-treated MDA-MB-231 cells. Our results demonstrated that the treatment of MDA-MB-231 cells with PGZ increased the expression of PPARα/γ mRNA and that this expression could be inhibited by treatment with MK886. Both drugs reduced the viability of MDA-MB-231 cells independently of PPARα/γ mRNA expression but did not induce apoptosis. The wound caused by invasion was not healed by PGZ-treated MDA-MB-231 cells, but it was healed by MK886-treated cancer cells, indicating that the reduction of invasion in PGZ-treated MDA-MB-231 cells was eliminated by treatment with MK886, and this finding was validated by the transwell migration assay. This phenomenon might also be associated with the expression of PPARα/γ, FGF4 and 5LOX mRNA in the treated cancer cells. This study provides useful information regarding the mRNA expression levels of PPARα and other related genes in MDA-MB-231 cells. These genes could be attractive targets for reducing the invasion of breast cancer.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PGZ:
-
Pioglitazone
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- PPARα:
-
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma
- FGF4:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 4
- 5LOX:
-
5-Lipoxygenase
- Caspase-9:
-
Cysteine–aspartic acid protease 9
- Caspase-3:
-
Cysteine–aspartic acid protease 3
- ALPI:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- IL6:
-
Interleukin 6
- HIF1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Al-Amran FG, Hadi NR, Hashim AM (2011) Leukotriene biosynthesis inhibition ameliorates acute lung injury following hemorrhagic shock in rats. J Cardiothorac Surg 6:81. doi:10.1186/1749-8090-6-81
Alwayn IP, Andersson C, Lee S, Arsenault DA, Bistrian BR, Gura KM, Nose V, Zauscher B, Moses M, Pude M (2006) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases increase PPAR-alpha and IL-6 and prevents dietary-induced hepatic steatosis and injury in a murine model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G1011–G1019
Avis I, Hong SH, Martinez A, Moody T, Choi YH, Trepel J, Das R, Jett M, Mulshine JL (2001) Five-lipoxygenase inhibitors can mediate apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines through complex eicosanoid interactions. FASEB J 15:2007–2009
Biscetti F, Gaetani E, Flex A, Aprahamian T, Hopkins T, Straface G, Pecorini G, Stigliano E, Angelini F, Castellot JJ Jr, Pola R (2008) Selective activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)alpha and PPARgamma induces neoangiogenesis through a vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent mechanism. Diabetes 57:1394–1404. doi:10.2337/db07-0765
Bocca C, Bozzo F, Martinasso G, Canuto RA, Miglietta A (2008) Involvement of PPARα in the growth inhibitory effect of arachidonic acid on breast cancer cells. Br J Nutr 100:739–750. doi:10.1017/S0007114508942161
Chaffer CL, Thomas DM, Thompson EW, Williams ED (2006) PPARγ-independent induction of growth arrest and apoptosis in prostate and bladder carcinoma. BMC Cancer 6:53
Clay CE, Namen AM, Atsumi G, Willingham MC, High KP, Kute TE, Trimboli AJ, Fonteh AN, Dawson PA, Chilton FH (1999) Influence of J series prostaglandins on apoptosis and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 20:1905–1911
Datta K, Biswal SS, Kehrer JP (1999) The 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP) inhibitor, MK886, induces apoptosis independently of FLAP. Biochem J 340:371–375
Elstner E, Muller C, Koshizuka K, Williamson EA, Park D, Asou H, Shintaku P, Said JW, Heber D, Koeffler HP (1998) Ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and retinoic acid receptor inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of human breast cancer cells in vitro and in BNX mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8806–8811
Gillies PS, Dunn CJ (2000) Pioglitazone. Drugs 60:333–345
Kehrer JP, Biswal SS, La E, Thuillier P, Datta K, Fischer SM, Heuvel JPV (2001) Inhibition of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)alpha by MK886. Biochem J 356:899–906
Lanson M, Bougnoux P, Besson P, Lansac J, Hubert B, Couet C, Le Floch O (1990) n-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids in human breast carcinoma phosphatidylethanolamine and early relapse. Br J Cancer 61:776–778
Lim JY, Oh JH, Jung JR, Kim SM, Ryu CH, Kim HT, Jeun SS (2010) MK886-induced apoptosis depends on the 5-LO expression level in human malignant glioma cells. J Neurooncol 97:339–346. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-0036-9
Liu H, Zang C, Fenner MH, Possinger K, Elstner E (2003) PPARgamma ligands and ATRA inhibit the invasion of human breast cancer cells in vitro. Breast Cancer Res Treat 79:63–74
Martelli ML, Iuliano R, Le Pera I, Sama’ I, Monaco C, Cammarota S, Kroll T, Chiariotti L, Santoro M, Fusco A (2002) Inhibitory effects of peroxisome poliferator-activated receptor gamma on thyroid carci- noma cell growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4728–4735
Master SR, Hartman JL, D’Cruz CM, Moody SE, Keiper EA, Ha SI, Cox JD, Belka GK, Chodosh LA (2002) Functional microarray analysis of mammary organogenesis reveals a developmental role in adaptive thermogenesis. Mol Endocrinol 16:1185–1203
Nwankwo JO, Robbins ME (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma expression in human malignant and normal brain, breast and prostate-derived cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 64:241–245
Papi A, Storci G, Guarnieri T, Carolis DS, Bertoni S, Avenia N, Sanguinetti A, Sidoni A, Santini D, Ceccarelli C, Tafurelli M, Orlandi M, Bonafe M (2013) Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α/Hypoxia inducible factor-1α interplay sustains carbonic anhydrase IX and apoliprotein E expression in breast cancer stem cells. PLoS One 8:e54968. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054968
Patzer A, Zhao Y, Stock I, Gohike P, Herdegen T, Culman J (2008) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma (PPARgamma) differently modulate the interleukin-6 expression in the peri-intact cortical tissue in the acute and delayed phases of cerebral ischaemia. Eur J Neurosci 28:1786–1794
Peters JM, Cattley RC, Gonzalez FJ (1997) Role of PPARα in the mechanism of action of the nongenotoxic carcinogen and peroxisome proliferator Wy-14,643. Carcinogenesis 18:2029–2033
Roberts RA, James NH, Woodyatt NJ, Macdonald N, Tugwood JD (1998) Evidence for the suppression of apoptosis by the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARα). Carcinogenesis 19:43–48
Roberts-Thomson SJ, Snyderwine EG (2000) Characterization of peroxisome proliferator-actiaved receptor alpha in normal rat mammary gland and 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazol[4,5-b]pyridine-induced mammary gland tumors from rats fed high and low fat diets. Toxicol Lett 118:79–86
Shimada T, Kojima K, Yoshiura K, Hiraishi H, Terano A (2002) Characteristics of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligand induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Gut 50:658–664
Singh AK, Pandey A, Tewari M, Kumar R, Sharma A, Singh KA, Pandey HP, Shukla HS (2013) Advanced stage of breast cancer hoist alkaline phosphatase activity: risk factor for females in India. 3 Biotech 3:517–520
Smith U (2001) Pioglitazone: mechanism of action. Int J Clin Pract Suppl 121:13–18
Srinivasan S, Hatley ME, Reilly KB, Danziger EC, Hedrick CC (2004) Modulation of PPARalpha expression and inflammatory interleukin-6 production by chronic glucose increases monocyte/endhothelial adhesion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:851–857
Stunes AK, Westbroek I, Gustafsson BI, Fossmark R, Waarsing JH, Eriksen EF, Petzold C, Reseland JE, Syversen U (2011) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)alpha agonist fenofibrate maintains bone mass, while the PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone exaggerates bone loss, in ovariectomized rats. BMC Endocr Disord 11:11
Suchanek KM, May FJ, Robinson JA, Lee WJ, Holman NA, Monteith GR, Roberts-Thomson SJ (2002) Peroxisome proliferator-actiavted receptor α; in the human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Mol Carcinog 34:165–171
Tachibana K, Yamasaki D, Ishimoto K, Doi T (2008) The role of PPARs in cancer. PPAR Res 2008:102737. doi:10.1155/2008/102737
Toyoda M, Takagi H, Horiguchi N, Kakizaki S, Sato K, Takayama H, Mori M (2002) A ligand for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells. Gut 50:563–567
Wang YL, Frauwirth KA, Rangwala SM, Lazar MA, Thompson CB (2002) Thiazolidine-dione activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma can enhance mitochondrial potential and promote cell survival. J Biol Chem 277:31781–31788
Wu M, Harvey KA, Ruzmetov N, Welch ZR, Sech L, Jackson K, Stillwell W, Zaloga GP, Siddiqui RA (2005) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids attenuate breast cancer growth through activation of a neutral sphingomyelinase-mediated pathway. Int J Cancer 117:340–348
Yamamoto Y, Nakajima M, Yamazaki H, Yokoi T (2001) Cytotoxicity and apoptosis produced by troglitazone in human hepatoma cells. Life Sci 70:471–482
Yasudaa E, Tokuda H, Ishisaki A, Hirade K, Kanno Y, Hanai Y, Nakamura N, Noda T, Katagiri Y, Kozawa O (2005) PPAR-gamma ligands up-regulate basic fibroblast growth factor-induced VEGF release through amplifying SAPK/JNK activation in osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328:137–143
Yoshizawa K, Cioca DP, Kawa S, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K (2002) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand troglitazone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer 95:2243–2251
Zhao G, Li WY, Chen D, Henry JR, Li HY, Chen Z, Zia-Ebrahimi M, Bloem L, Zhai Y, Huss K, Peng SB, McCann DJ (2011) A novel, selective inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptors that shows a potent broad spectrum of antitumor activity in several tumor xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2200–2210. doi:10.1158/1535-7163
Zhou J, Zhang W, Liang B, Casimiro MC, Whitaker-Menezes D, Wang M, Lisanti MP, Lanza-Jacoby S, Pestell RG, Wang C (2009) PPARgamma activation induces autophagy in breast cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:2334–2342. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.06.007
Zhou G, Zhu C, Ding X, Zhang H, Zhang H, Cao W, Iang QH, Xu Z (2011) Inhibitory effect of MK886 and celecoxib on the growth of pancreatic cancer cell line SW1990 and angiogenesis. Chin J Pancreatol 11:407–409
Zhu H, Wang D, Liu Y, Su Z, Zhang L, Chen F, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Yu M, Zhang Z, Shao G (2013) Role of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha induced autophagy in the conversion of non-stem pancreatic cancer cells into CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Cell Int 13:119. doi:10.1186/1475-2867-13-119
Acknowledgments
The PPARα study was supported by a Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) Fasa 2/2010 (Grant No. 203/CIPPM/6711162). The study using MDA-MB-231 cells was funded by the Universiti Sains Malaysia for Research University (Grant No. 1001/CIPPM/811200). The first author would like to thank the Graduate Assistant scheme (GA) from USM, MoHe for MyMasters scheme under MyBrain15 and Dr. Chew Ai Lan, who proofread the manuscript prior to its submission for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadarajan, K., Balaram, P. & Khoo, B.Y. MK886 inhibits the pioglitazone-induced anti-invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells is associated with PPARα/γ, FGF4 and 5LOX. Cytotechnology 68, 1771–1787 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-015-9930-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-015-9930-5