Abstract
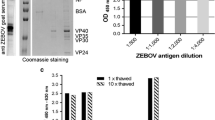
Since 2008, enterovirus 71 (EV71) has been responsible for high-mortality seasonal epidemics of hand, foot and mouth disease in China. Currently many groups in the world are in the process of developing EV71 vaccines to combat this deadly disease. We have developed three EV71-specific monoclonal antibodies, and in this study we report the establishment of a fast and cost-effective sandwich ELISA kit for measurement of virus concentration in EV71 vaccines using a pair of mouse anti-EV71 monoclonal antibodies. The system is specific for EV71 virus, with no cross-reactivity to coxsackievirus A16, H1N1, rabies, and hepatitis A. Using a reference EV71 vaccine standard, the sensitivity of the assay kit was determined to be 0.82 U/ml, with a linear range between 3.75 and 120 U/ml.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua KB, Kasri AR (2011) Hand foot and mouth disease due to Enterovirus 71 in malaysia. Virol Sin 26:221–228
Dong C, Liu L, Zhao H, Wang J, Liao Y, Zhang X, Na R, Liang Y, Wang L, Li Q (2011) Immunoprotection elicited by an Enterovirus type 71 experimental inactivated vaccine in mice and rhesus monkeys. Vaccine 29:6269–6275
Infectious Case Report for July 2012 by Ministry of Public Health of China
Kim KH (2009) Enterovirus 71 infection: an experience in Korea. Korean J Pediatr 53(2010):616–622
Li X, Mao C, Ma S, Wang X, Sun Z, Yi Y, Guo M, Shen X, Sun L, Bi S (2009) Generation of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against Enterovirus 71 using synthetic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:1126–1128
Li YP, Liang ZL, Gao Q, Huang LR, Mao QY et al (2012) Safety and immunogenicity of a novel human Enterovirus 71 (EV71) vaccine: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind. Phase I clinical trial. Vaccine 30:3295–3303
Liang Z, Mao Q, Gao Q, Li X, Dong C, Yu X, Yao X, Li F, Yin W, Li Q, Shen X, Wang J (2011) Establishing China’s national standards of antigen content and neutralizing antibody responses for evaluation of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) vaccines. Vaccine. 29:9668–9674
Liu CC, Lian WC, Butler M, Wu SC (2007) High immunogenic Enterovirus 71 strain and its production using serum-free microcarrier vero cell culture. Vaccine 25:19–24
Mao Q, Li N, Yu X, Yao X, Li F, Lu F, Zhuang H, Liang Z, Wang J (2011) Antigenicity, animal protective effect and genetic characteristics of candidate vaccine strains of Enterovirus 71. Arch Virol 157:37–41
Mao Q, Dong C, Li X, Gao Q, Guo Z, Yao X, Wang Y, Gao F, Li F, Xu M, Yin W, Li Q, Shen X, Liang Z, Wang J (2012) Comparative analysis of the immunogenicity and protective effects of inactivated EV71 vaccines in mice. PLoS One 7:e46043
Ong KC, Devi S, Cardosa MJ, Wong KT (2010) Formadehyde-inactivated whole-virus vaccine protects a murine model of Enterovirus 71 encephalomyelitis against disease. J Virol 84:661–665
Tan X, Huang X, Zhu S, Chen H, Yu Q, Wang H, Huo X, Zhou J, Wu Y, Yan D, Zhang Y, Wang D, Cui A, An H, Xu W (2011) The persistent circulation of Enterovirus 71 in People’s republic of CHINA: causing emerging nationwide epidemics since 2008. PLoS One 6:e25662
Xu WB (2009) Virus Surveillance on HFMD in China. Beijing International Symposium on HFMD, January 13–14, 2009
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Research Grants for small business from Beijing Science and Technology Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shujun Ma and Qunying Mao have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, S., Mao, Q., Liang, Z. et al. Development of a sandwich ELISA for the quantification of enterovirus 71. Cytotechnology 66, 413–418 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-013-9588-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-013-9588-9