Abstract
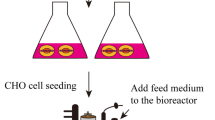
A serum-free medium (CHO-SFM) together with a fed-batch process was developed for the cultivation of a recombinant GS-CHO cell line producing TNFR-Fc. According to the metabolic characteristics of GS-CHO cell, a basal medium was prepared by supplementing DMEM:F12:RPMI1640 (2:1:1) with amino acids, insulin, transferrin, Pluronic F68 and some other ingredients. Statistical optimization approaches based on Plackett–Burman and central composite designs were then adopted to identify additional positive determinants and determine their optimal concentrations, which resulted in the final CHO-SFM medium formulations. The maximum antibody titer reached was 90.95 mg/l in the developed CHO-SFM, which was a 18 % and 10 fold higher than that observed in the commercial EX-CELL™ 302 medium (76.95 mg/l) and basal medium (8.28 mg/l), respectively. Subsequently, a reliable, reproducible and robust fed-batch strategy was designed according to the offline measurement of glucose, giving a final antibody yield of 378 mg/l, which was a threefold improvement over that in conventional batch culture (122 mg/l) using CHO-SFM. In conclusion, the use of design of experiment (DoE) method facilitated the development of CHO-SFM medium and fed-batch process for the production of recombinant antibody using GS-CHO cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdeen SH, Abdeen AM, EI-Enshasy HA, Shereef AAE (2011) HeLa-S3 cell growth conditions in serum-free medium and adaptability for proliferation in suspension culture. J Biol Sci 11:124–134
Bai Y, Wu C, Zhao J, Liu YH, Ding W, Ling WLW (2011) Role of iron and sodium citrate in animal protein-free CHO cell culture medium on cell growth and monoclonal antibody production. Biotechnol Prog 27:209–219
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, Markenson J, Finck BK (2000) A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 343:1586–1593
Box GEP, Hunter WG, Hunter JS (1978) Fractional factorial design at two levels. In: Statistics for experimenters. Wiley, New York, pp 374–418
Castro PML, Hayter PM, Ison AP, Bull AT (1992) Application of a statistical design to the optimization of culture medium for recombinant interferon-gamma production by Chinese hamster ovary cells. Appl Microbiol Biot 38:84–90
Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, FrySmith A, Burls A (2006) A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess 10:1–229
Chen Z, Iding K, Lütkemeyer D, Lehmann J (2000) A low-cost chemically defined protein free medium for a recombinant CHO cell line producing prothrombin. Biotechnol Lett 22:837–841
Clincke MF, Guedon E, Yen FT, Ogier V, Roitel O, Goergen JL (2011) Effect of surfactant pluronic F-68 on CHO cell growth, metabolism, production, and glycosylation of human recombinant IFN-gamma in mild operating conditions. Biotechnol Prog 27:181–190
Dee KU, Shuler ML, Wood HA (1997) Inducing single-cell suspension of BTI-TN5B1-4 insect cells: I. The use of sulfated polyanions to prevent cell aggregation and enhance recombinant protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 54:191–205
deZengotita VM, Miller WM, Aunins JG, Zhou WC (2000) Phosphate feeding improves high-cell-concentration NS0 myeloma culture performance for monoclonal antibody production. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:566–576
Dong J, Mandenius CF, Lübberstedt M, Urbaniak T, Nüssler AK, Knobeloch D, Gerlach JC, Zeilinger K (2008) Evaluation and optimization of hepatocyte culture media factors by design of experiments (DoE) methodology. Cytotechnology 57:251–261
Fan L, Zhao L, Sun Y, Kou T, Zhou Y, Tan WS (2009) A high-yielding, generic fed-batch process for recombinant antibody production of GS-engineered cell lines. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:1695–1702
Gilbert RS, Nagano Y, Yokota T, Hwan SF, Fletcher T, Lydersen K (1996) Effect of lipids on insect cell growth and expression of recombinant proteins in serum-free medium. Cytotechnology 22:211–216
González-Leal IJ, Carrillo-Cocom LM, Ramírez-Medrano A, López-Pacheco F, Bulnes-Abundis D, Webb-Vargas Y, Alvarez MM (2011) Use of a plackett–burman statistical design to determine the effect of selected amino acids on monoclonal antibody production in CHO cells. Biotechnol Prog 27:1709–1717
Hu S, Deng L, Wang H, Zhuang Y, Chu J, Zhang S, Li Z, Guo M (2011) Bioprocess development for the production of mouse-human chimeric anti-epidermal growth factor receptor vIII antibody C12 by suspension culture of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cytotechnology 63:247–258
Huang EP, Marquis CP, Gray PP (2007) Development of super-CHO protein-free medium based on a statistical design. J Chem Technol Biot 82:431–441
Huang YM, Hu W, Rustandi E, Chang K, Yusuf-Makagiansar H, Ryll T (2010) Maximizing productivity of CHO cell-based fed-batch culture using chemically defined media conditions and typical manufacturing equipment. Biotechnol Prog 26:1400–1410
Ishaque A, Al-Rubeai M (2002) Role of vitamins in determining apoptosis and extent of suppression by suppression by bcl-2 during hybridoma cell culture. Apoptosis 7:231–239
Janne J, Alhonen L, Pietila M, Keinanen TA (2004) Genetic approaches to the cellular functions of polyamines in mammals. Eur J Biochem 271:877–894
Jeon M, Lim JB, Lee G (2010) Development of a serum-free medium for in vitro expansion of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes using a statistical design. BMC Biotechnol 10:70
Kim DY, Lee JC, Chang HN, Oh DJ (2005) Effects of supplementation of various medium components on Chinese hamster ovary cell cultures producing recombinant antibody. Cytotechnology 47:37–49
Kim DY, Lee JC, Chang HN, Oh DJ (2006) Development of serum-free media for a recombinant CHO cell line producing recombinant antibody. Enzyme Microb Tech 39:426–433
Klareskog L, Gaubitz M, Rodríguez-Valverde V, Malaise M, Dougados M, Wajdula J; Etanercept Study 301 Investigators (2011) Assessment of long-term safety and efficacy of etanercept in a 5-year extension study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:238–247
Knöspel F, Schindler RK, Lübberstedt M, Petzolt S, Gerlach JC, Zeilinger K (2010) Optimization of a serum-free culture medium for mouse embryonic stem cells using design of experiments (DoE) methodology. Cytotechnology 62:557–571
Kou TC, Fan L, Zhou Y, Ye ZY, Zhao L, Tan WS (2011) Increasing the productivity of TNFR-Fc in GS-CHO cells at reduced culture temperatures. Biotechnol Bioproc E 16:136–143
Lee GM, Kim EJ, Kim NS, Yoon SK, Ahn YH, Song JY (1999) Development of a serum-free medium for the production of erythropoietin by suspension culture of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells using a statistical design. J Biotechnol 69:85–93
Liu CH, Chang TY (2006) Rational development of serum-free medium for Chinese hamster ovary cells. Process Biochem 41:2314–2319
Liu C, Chu I, Hwang S (2001) Factorial designs combined with the steepest ascent method to optimize serum-free media for CHO cells. Enzyme Microb Technol 28:314–321
Liu CH, Wu PS (2007) Optimization of adenoviral production in human embryonic kidney cells using response surface methodology. J Biosci Bioeng 103:406–411
Lovell DJ, Giannini EH, Reiff A, Cawkwell GD, Silverman ED, Nocton JJ, Stein LD, Gedalia A, Ilowite NT, Wallace CA, Whitmore J, Finck BK (2000) Etanercept in children with polyarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med 342:763–769
Lv G, Sun Z, Li N, Li S, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Yu W, Wang W, Ma X (2008) Design a chemically defined/medically approved medium for cell transplantation according to the metabolic characteristics of microencapsulated cells and the process of encapsulation. Biochem Eng J 39:157–163
Ma ZY, Yi XP, Zhang YX (2008) Enhanced intracellular accumulation of recombinant HBsAg in CHO cells by dimethyl sulfoxide. Process Biochem 43:690–695
Mease PJ, Goffe BS, Metz J, VanderStoep A, Finck B, Burge DJ (2000) Etanercept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis:a randomised trial. Lancet 356:385–390
Meghrous J, Mahmoud W, Jacob D, Chubet R, Cox M, Kamen AA (2009) Development of a simple and high-yielding fed-batch process for the production of influenza vaccines. Vaccine 28:309–316
Merten O-W (2006) Introduction to animal cell culture technology—past, present and future. Cytotechnology 50:1–7
Murakami H, Masui H, Sato GH, Sueoka N, Ghow TP, Kano-Sueoka T (1982) Growth of hybridoma cells in serum-free medium: ethanolamine is an essential component. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:1158–1162
Parampalli A, Eskridge K, Smith L, Meagher M, Mowry M, Subramanian A (2007) Development of serum-free media in CHO-DG44 cells using a central composite statistical design. Cytotechnology 54:57–68
Petiot E, Fournier F, Geny C, Pinton H, Marc A (2010) Rapid screening of serum-free media for the growth of adherent Vero cells by using a small-scale and non-invasive tool. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:1600–1615
Riebeling C, Schlechter K, Buesen R, Spielmann H, Luch A, Seiler A (2011) Defined culture medium for stem cell differentiation: applicability of serum-free conditions in the mouse embryonic stem cell test. Toxicol in Vitro 25:914–921
Rodrigues Goulart H, Arthuso FS (2010) Enhancement of human prolactin synthesis by sodium butyrate addition to serum-free CHO cell culture. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2010/405872
Rourou S, van der Ark A, van der Velden T, Kallel H (2009) Development of an animal-component free medium for Vero cells culture. Biotechnol Prog 25:1752–1761
Sandadi S, Ensari S, Kearns B (2006) Application of fractional factorial designs to screen active factors for antibody production by Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Prog 22:595–600
Spens E, Häggström L (2007) Defined protein and animal component-free NS0 fed-batch culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 98:1183–1194
Stein A (2007) Decreasing variability in your cell culture. Biotechniques 43:228–229
Sugahara T, Nishimoto S, Miyazaki Y (2008) Effects of polyamines on proliferation and IgM productivity of human–human hybridoma, HB4C5 cells. Cytotechnology 57:115–122
van der Valk J, Brunner D, De Smet K, Fex Svenningsen A, Honegger P, Knudsen LE, Lindl T, Noraberg J, Price A, Scarino ML, Gstraunthaler G (2010) Optimization of chemically defined cell culture media–replacing fetal bovine serum in mammalian in vitro methods. Toxicol in Vitro 24:1053–1063
Wlaschin KF, Hu WS (2006) Fedbatch culture and dynamic nutrient feeding. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 101:43–74
Yao CL, Liu CH, Chu IM, Hsieh TB, Hwang SM (2003) Factorial designs combined with the steepest ascent method to optimize serum-free media for ex vivo expansion of human hematopoietic progenitor cells. Enzyme Microb Tech 33:343–352
Zhang J, Robinson D (2005) Development of animal-free, protein-free and chemically-defined media for NS0 cell culture. Cytotechnology 48:59–74
Zhang J, Robinson D, Salmon P (2006) A novel function for selenium in biological system: selenite as a highly effective iron carrier for Chinese hamster ovary cell growth and monoclonal antibody production. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:1188–1197
Zhang L, Shen H, Zhang Y (2004) Fed-batch culture of hybridoma cells in serum-free medium using an optimized feeding strategy. J Chem Technol Biot 79:171–181
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial supports from the National Key Project for Basic Research (No. 2010CB1126102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wang, H., Liu, M. et al. Rational development of a serum-free medium and fed-batch process for a GS-CHO cell line expressing recombinant antibody. Cytotechnology 65, 363–378 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9488-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9488-4