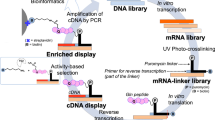
Abstract
Transglutaminase (TGase) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes cross-linking reaction between glutamine- and lysine residue of substrate proteins in several mammalian biological events. Substrate proteins for TGase and their physiological relevance have been still in research, continuously expanding. In this study, we have established a novel screening system that enables identification of cDNA sequence encoding favorable primary structure as a substrate for tissue-type transglutaminase (TGase 2), a multifunctional and ubiquitously expressing isozyme. By the screening, we identified several T7 phage clones that displayed substrate peptides for TGase 2 as a translated product from human brain cDNA library. Among the selected clones, the C-terminal region of IKAP, IkappaB kinase complex associated protein, appeared as a highly reactive substrate sequence for TGase 2. This system will open possibility of rapid identification of substrate sequences for transglutaminases at a genetic level.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson SL, Coli R, Daly IW, Kichula EA, Rork MJ, Volpi SA, Ekstein J, Rubin BY (2001) Familial dysautonomia is caused by mutation of the IKAP gene. Am J Hum Genet 68:753–758
Chen Y-T, Hims MM, Shetty RS, Mull J, Liu L, Leyne M, Slaugenhaupt SA (2009) Loss of mouse Ikbkap, a subunit of elongator, leads to transcriptional deficits and embryonic lethality that can be rescued by human IKAKAP. Mol Cell Biol 29:736–744
Cohen L, Henzel WJ, Baeuerie PA (1998) IKAP is a scaffold protein of the IkB kinase complex. Nature 395:292–296
Csosz E, Mesko B, Fésüs L (2009) Transdab wiki: the interactive transglutaminase substrate database on web 2.0 surface. Amino Acids 36:615–617
Eckert RL, Sturniolo MT, Broome AM, Ruse M, Rorke EA (2005) Transglutaminase function in epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 124:481–492
Esposito C, Caputo I (2005) Mammalian transglutaminases: identification of substrates as a key to physiological function and physiological relevance. FEBS J 272:615–631
Facchiano A, Facchiano F (2009) Transglutaminases and their substrates in biology and human diseases: 50 years of growing. Amino Acids 36:599–614
Fésüs L, Piacentini M (2002) Transglutaminase 2: an enigmatic enzyme with diverstic functions. Trends Biochem Sci 27:534–539
Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002) Transglutaminases: nature’s biological glues. Biochem J 368:377–396
Hitomi K (2005) Transglutaminase in skin epidermis. Eur J Dermatol 15:313–319
Hitomi K, Kitamura M, Sugimura Y (2009) Preferred substrate sequences for transglutaminase 2: screening using a phage-displayed peptide library. Amino Acids 36:619–624
Ichikawa A, Ishizaki J, Morita M, Tanaka K, Ikura K (2008) Identification of new amine acceptor protein substrate candidate of transglutaminase in rat liver extract: use of 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine as a probe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:1056–1062
Ichinose A (2001) Physiopathology and regulation of factor XIII. Thromb Haemost 86:57–65
Ikura K, Kita K, Fujita I, Hashimoto H, Kawabata N (1998) Idetification of amine acceptor protein substrates of transglutaminase in liver extracts: use of 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine as a probe. Arch Biochem Biophys 356:280–286
Jeitner TM, Pinto JT, Krasnikov BF, Horswill M, Cooper AJL (2009) Transglutaminase and neurogeneration. J Neurochem 109(1):160–166
Johansen LD, Naumanen T, Knudsen A, Westerlund N, Gromova I, Junttilla M, Nielsen C, Bottzauw T, Tolkovsky A, Wastermarck J, Coffey ET, Jaattela M, Kallunki T (2008) IKAP localizes to membrane ruffles with filamin A and regulates actin cytoskeleton organization and cell migration. J Cell Sci 121:854–864
Keresztessy Z, Csosz É, Hársfalvi J, Csomós K, Gray J, Lightowlers RN, Lakey JH, Balajthy Z, Fésüs L (2006) Phage display selection of efficient glutamine-donor substrate peptides for transglutaminase 2. Protein Sci 15:2466–2480
Lee KN, Maxwell MD, Patterson MK, Birckbichler PJ, Conway E (1992) Identification of transglutaminase substrates in HT29 colon cancer cells: use of 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine as a transglutaminase-specific probe. Biochim Biophys Acta 1136:12–16
Lorand L, Graham RM (2003) Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:140–156
Morohashi K, Yoshino A, Yoshimori A, Saito S, Tanuma S, Sakaguchi K, Sugawara F (2005) Identification of a drug target motif: an anti-tumor drug NK109 interacts with a PNxxxxP. Biochem Pharmacol 70:37–46
Orru S, Caputo I, D’Amato A, Ruoppolo M, Esposito C (2003) Proteomics identification of acyl-acceptor and acyl-donor substrates for transglutaminase in a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem 278:31766–31773
Slaugenhaupt SA, Blumenfeld A, Gill SP, Leyne M, Mull J, Cuajungco MP, Liebert CB, Chadwick B, Idelson M, Reznik L, Robbins CM, Makalowska I, Brownstein M, Krappman D, Scheidereit C, Maayan C, Axelrod FB, Gusella JF (2001) Tissue-specific expression of a splicing mutation in the IKABKAP gene causes familial dysautonomia. Am J Hum Genet 68:598–605
Sollid LM (2002) Coeliac disease: dissecting a complex inflammatory disorder. Nat Rev Immunol 2:647–655
Sugimura Y, Hosono M, Wada F, Yoshimura T, Maki M, Hitomi K (2006) Screening for the preferred substrate sequence of transglutaminase using a phage-displayed peptide library: identification of peptide substrates for TGase 2 and factor XIIIa. J Biol Chem 281:17699–17706
Sugimura Y, Hosono M, Kitamura M, Tsuda T, Yamanishi K, Maki M, Hitomi K (2008a) Identification of preferred substrate sequences for transglutaminase 1-development of a novel peptide that can efficiently detect cross-linking enzyme activity in the skin. FEBS J 275:5667–5677
Sugimura Y, Yokoyma K, Nio N, Maki M, Hitomi K (2008b) Identification of preferred substrate sequences of microbial transglutaminase from Streptomyces mobaraensis using a phage-displayed peptide library. Arch Biochem Biophys 477:379–383
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate Dr. Masatoshi Maki and Dr. Hideki Shibata in our laboratory for providing valuable suggestions. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (No. 20200072) from the Ministry of Education, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT, Japan) (to K. H.) and also Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists Research (No. 186701) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (to Y. S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugimura, Y., Yamashita, H. & Hitomi, K. Screening of substrate peptide sequences for tissue-type transglutaminase (TGase 2) using T7 phage cDNA library. Cytotechnology 63, 111–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-010-9308-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-010-9308-7