Abstract
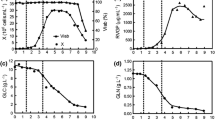
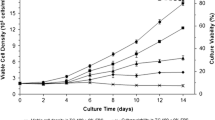
Although several reports have been published on recombinant protein expression using Drosophila cells, information on their metabolism and growth in vitro is relatively scarce. In the present study, we have analyzed the growth and metabolism of transfected S2 cells (S2AcRVGP) in bioreactor cultures with serum-free medium Sf900 II, to evaluate its potential for mass production of a rabies virus glycoprotein (RVGP). Cells were cultured in a 3 l-stirred-tank bioreactor at 28 °C with pH controlled at 6.2 and dissolved oxygen at 50% air saturation. The cells attained a specific growth rate and maximum cell density as high as 0.084 h−1 and 2.3 × 107 cell ml−1, respectively. The main substrates consumed during this rapid growth phase were glucose, glutamine and proline. An atypical accumulation of ammonia and alanine was observed in the culture medium, up to 62 mM and 47 mM, respectively, but lactate was produced in low levels. After exhaustion of glutamine and proline as energy sources, alanine was consumed and production of ammonia increased. The production of recombinant RVGP reached concentrations as high as 178 μg l−1. Premature exhaustion of glutamine, serine and cysteine could be related to degradation of the recombinant glycoprotein. In general, the results demonstrated that S2AcRVGP can be considered an effective vehicle for large-scale recombinant glycoprotein expression and that several critical factors of the bioprocess could be optimized to increase the quality and productivity of the RVGP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astray RM, Augusto E, Yokomizo AY et al (2008) Analytical approach for the extraction of recombinant membrane viral glycoprotein from stably transfected Drosophila melanogaster cells. Biotechnol J 3:98–103
Bidlingmeyer BA, Cohen SA, Tarvin TL (1985) Rapid analysis of amino acids using precolumn derivatization. J Chromatogr 336:93–104
Borash DJ, Pierce VA, Gibbs AG et al (2000) Evolution of ammonia and urea tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster: resistance and cross-tolerance. J Insect Physiol 46:763–769
Cha HJ, Shin HS, Lim HJ et al (2005) Comparative production of human interleukin-2 fused with green fluorescent protein in several recombinant expression systems. Biochem Eng J 24:225–233
Cho HS, Kim YK, Cha HJ (2004) Expression of double foreign protein types following recombinant baculovirus infection of stably transfected Drosophila S2 cells. Enzyme Microbial Technol 35:525–531
Doyle A, Griffths JB (1998) Cell and tissue culture: laboratory procedures in biotechnology. Hardcover, England
Freedman R. (1984) Native disulphide bond formation in protein biosynthesis: evidence for the role of protein disulphide isomerase. Trends Biochem Sci 9:438–441
Jentoft N (1990) Why are proteins O-glycosylated? Trends Biochem Sci 15:291–294
Johansson DX, Drakenberg K, Hopmann KH et al (2007) Efficient expression of recombinant human monoclonal antibodies in Drosophila S2 cells. J Immunol Methods 318:37–46
Kim KR, Kim YK, Cha HJ (2008) Recombinant baculovirus-based multiple protein expression platform for Drosophila S2 cell culture. J Biotechnol 133:116–122
Lim HJ, Cha HJ (2006) Observation and modeling of induction effect on human transferring production from stably transfected Drosophila S2 cells culture. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:208–214
Öhman L, Ljunggren J, Häggstrom L (1995) Introduction of a metabolic switch in insect cells by substrate-limited fed-batch cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:1–8
Perret BG, Wagner R, Lecat S et al (2003) Expression of EGFP-amino-tagged human mu opioid receptor in Drosophila Schneider 2 cells: a potential expression system for large-scale production of G-protein coupled receptors. Protein Expr Purif 31:123–132
Schmid G (1996) Insect cell cultivation: growth and kinetics. Cytotechnology 20:43–56
Swiech K, Silva CS, Arantes MK et al (2008) Characterization of growth and metabolism of Drosophila Melanogaster cells transfected with the rabies virus glycoprotein gene. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 49:41–49
Valle MA, Kester MB, Burns AL et al (2001) Production and purification of human menin from Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells using stirred tank reactor. Cytotechnology 35:127–135
Yokomizo AY, Jorge SAC, Astray RM et al (2007) Rabies virus glycoprotein expression in Drosophila S2 cells. I. functional recombinant protein in stable co-transfected cell line. Biotechnol J 2:102–109
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from FAPESP (02/09482-3, 01/09038-3, 01/08914-4), Fundação Butantan and CNPq (141099/2003-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swiech, K., Rossi, N., Silva, B.G. et al. Bioreactor culture of recombinant Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells: characterization of metabolic features related to cell growth and production of the rabies virus glycoprotein. Cytotechnology 57, 61–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-008-9130-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-008-9130-7