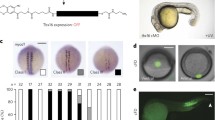
Abstract
In early development of animals, hedgehog (Hh) genes function as morphogen in the axis determination and the organ formation. In Xenopus, three hedgehog genes, sonic (shh), banded (bhh), and cephalic (chh), were identified and might organize various tissues and organs in embryogenesis. Here, we report the spatial and temporal regulation of Xchh which is expressed in endoderm cells differentiating to digestive organs. Xchh expression in endoderm was inhibited by ectopic expression of the dominant-negative activin receptor, tAR. Moreover, a maternally inherited transcription factor VegT and its downstream regulators activated Xchh expression. These indicates that Xchh is regulated by the factor involved in the cascade originated from VegT via activin/nodal signals. Using the Sox17α-VP16-GR construct, we showed that Xchh expression might be induced directly by transcription factor Sox17.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bFGF:
-
basic fibroblast growth factor
- BMP:
-
bone morphogenic protein
- TGFβ:
-
transforming growth factor β
References
Afouda B, Ciau-Uitz A, Patient R (2005) GATA4, 5 and 6 mediate TGFbeta maintenance of endodermal gene expression in Xenopus embryos. Development 132:763–774
Amaya E, Musci TJ, Kiescner MW (1991) Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell 66:257–270
Asashima M, Uchiyama H, Nakano H, Eto Y, Ejima D, Sugino H, Davids M, Plessow S, Born J, Hoppe P, Tiedemann H, Tiedemann N (1991) The vegetalizing factor from chicken embryos: its EDF (activin A)-like activity. Mech Dev 34:135–141
Bartkowski S, Zapp D, Weber H, Eberle G, Zoidl C, Senkel S, Clein-Hitpass L, Ryffel GU (1993) Developmental regulation and tissue distribution of the liver transcription factor LFB1 (HNF1) in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol 13:421–431
Casey ES, Tada M, Fairclough L, Wylie CC, Heasman J, Smith JC (1999) Bix4 is activated directly by VegT and mediates endoderm formation in Xenopus development. Development 126:4193–4200
Clements D, Cameleyre I, Woodland HR (2003) Redundant early and overlapping larval roles of Xsox17 subgroup genes in Xenopus endoderm development. Mech Dev 120:337–348
Clements D, Friday RV, Woodland HR (1999) Mode of action of VegT in mesoderm and endoderm formation. Development 126:4903–4911
Clements D, Woodland HR (2003) VegT induces endoderm by a self-limiting mechanism and by changing the competence of cells to respond to TGF-beta signals. Dev Biol 258:454–463
Demartis A, Maffei M, Vignali R, Barsacchi G, De Simone V (1994) Cloning and developmental expression of LFB3/HNF1 beta transcription factor in Xenopus laevis. Mech Dev 47:19–28
Dohrmann CE, Hemmati-Brivanlou A, Thomsen GH, Fields A, Woolf TM, Melton DA (1993) Expression of activin mRNA during early development in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol 157:474–483
Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP (1993) Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell 75:1417–1430
Ecochard V, Cayrol C, Rey S, Foulquier F, Caillol D, Lemaire P, Duprat AM (1998) A novel Xenopus mix-like gene milk involved in the control of the endomesodermal fates. Development 125:2577–2585
Ekker SC, McGrew LL, Lai CJ, Lee JJ, Von Kessler DP, Moon RT, Beachy PA (1995) Distinct expression and shared activities of members of the hedgehog gene family of Xenopus laevis. Development 121:2337–2347
Engleka MJ, Craig EJ, Kessler DS (2001) VegT activation of Sox17 at the midblastula transition alters the response to Nodal signals in the vegetal endoderm domain. Dev Biol 237:159–172
Fan CM, Tessier-Lavigne M (1994) Patterning of mammalian somites by surface ectoderm and notochord: evidence for sclerotome induction by a hedgehog homolog. Cell 79:1175–1186
Hammerschmidt M, Brook A, McMahon AP (1997) The world according to hedgehog. Trends Genet 13:14–21
Harland RM (1991) In situ hybridazation: an improved whole-mount method for Xenopus embryos. Methods Cell Biol 36:685–695
Hemmati-Brivanlou A, Melton DA (1992) A truncated activin receptor inhibits mesoderm induction and formation of axial structures in Xenopus embryos. Nature 359:609–614
Henry GL, Melton DA (1998) Mixer, a homeobox gene required for endoderm development. Science 281:91–96
Hudson C, Clements D, Friday RV, Stott D, Woodland HR (1997) Xsox17alpha and -beta mediate endoderm formation in Xenopus. Cell 91:397–405
Ito Y, Kuhara S, Tashiro K (2001) In synergy with noggin and follistatin, Xenopus nodal-related gene induces sonic hedgehog on notochord and floor plate. Biochem Biophys Res Com 281:714–719
Jiang Y, Evans T (1996) The Xenopus GATA-4/5/6 genes are associated with cardiac specification and can regulate cardiac-specific transcription during embryogenesis. Dev Biol 174:258–270
Jones EA, Abel MH, Woodland HR (1993) The possible role of mesodermal growth factors in the formation of endoderm in Xenopus laevis. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 202:233–239
Joseph EM, Melton DA (1997) Xnr4: A Xenopus nodal-related gene expressed in the Spemann organizer. Dev Biol 184:367–372
Kelley C, Blumberg H, Zon LI, Evans T (1993) GATA-4 is a novel transcription factor expressed in endocardium of the developing heart. Development 118:817–827
Krauss S, Concordet JP, Ingham PW (1993) A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos. Cell 75:1431–1444
Lemaire P, Darras S, Caillol D, Kodjabachian L (1998) A role for the vegetally expressed Xenopus gene Mix.1 in endoderm formation and in the restriction of mesoderm to the marginal zone. Development 125:2371–2380
Nieuwkoop PD, Faber J (1967) Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). Elsevier North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam
Nüsslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E (1980) Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287:795–801
Peng HB (1991) Xenopus laevis: Practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Solutions and protocols. Methods i Cell Biol 36:657–662
Roelink H, Augsburger A, Heemskerk J, Korzh V, Norlin S, Ruiz i Altaba A, Tanabe Y, Placzek M, Edlund T, Jessell TM, Dodd J (1994) Floor plate and motor neuron induction by vhh-1, a vertebrate homolog of hedgehog expressed by the notochord. Cell 76:761–775
Rosa F (1989) Mix.1, a homeobox mRNA inducible by mesoderm inducers, is expressed mostly in the presumptive endodermal cells of Xenopus embryos. Cell 57:965–974
Sasai Y, Lu B, Piccolo S, De Robertis E (1996) Endoderm induction by the organizer-secreted factors chordin and noggin in Xenopus animal caps. EMBO J 15:4547–4555
Shi YBO, Hayes WP (1994) Thyroid hormone-dependent regulation of the intestinal fatty acid-binding protein gene during amphibian metamorphosis. Dev Biol 161:48–58
Sinner D, Rankin S, Lee M, Zorn AM (2004) Sox17 and β-catenin cooperate to regulate the transcription of endodermal genes. Development 131:3069–3080
Sive HL (2000) Early Development of Xenopus Laevis Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Sun BI, Bush SM, Collins-Racie LA, LaVallie ER, DiBlasio-Smith E A, Wolfman NM, McCoy JM, Sive HL (1999) derrière: a TGF-b family member required for posterior development in Xenopus. Development 126:1467–1482
Suzuki A, Ties RS, Yamaji N, Song JJ, Wonzney JM, Murakami K, Ueno N (1994) A truncated bone morphogenetic protein receptor affects dorsal-ventral patterning in the early Xenopus embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:10255–10259
Tada M, Casey E, Fairclough L, Smith J (1998) Bix1, a direct target of Xenopus T-box genes, causes formation of ventral mesoderm and endoderm. Development 125:3997–4006
Takahashi S, Yokota C, Takano K, Tanegashima K, Onuma Y, Goto J, Asashima M (2000) Two novel nodal-related genes initiate early inductive events in Xenopus Nieuwkoop center. Development 127:5319–5329
Thomsen GH, Melton DA (1993) Processed Vg1 is an axial mesoderm inducer in xenopus. Cell 74:433–441
Vize PD (1996) DNA sequences mediating the transcriptional response of the Mix.2 homeobox gene to mesoderm induction. Dev Biol 177:226–231
Weber H, Symes C, Walmsley M, Rodaway A, Patient R (2000) A role for GATA5 in Xenopus endoderm specification. Development 127:4345–4360
Wright C, Schnegelsberg P, De Robertis E (1989) XlHbox 8: a novel Xenopus homeo protein restricted to a narrow band of endoderm. Development 105:787–794
Xanthos JB, Kofron M, Wylie C, Heasman J (2001) Maternal VegT is the initiator of a molecular network specifying endoderm in Xenopus laevis. Development 128:167–180
Yisraeli JK, Melton DA (1988) The material mRNA Vg1 is correctly localized following injection into Xenopus oocytes. Nature 336:592–595
Zhang C, Basta T, Fawcett SR, Klymkowsky MW (2005a) SOX7 is an immediate-early target of VegT and regulates Nodal-related gene expression in Xenopus. Dev Biol 278:526–541
Zhang C, Basta T, Jensen E, Klymkowsky M (2003) The beta-catenin/VegT-regulated early zygotic gene Xnr5 is a direct target of SOX3 regulation. Development 130:5609–5624
Zhang C, Basta T, Klymkowsky M (2005b) SOX7 and SOX18 are essential for cardiogenesis in Xenopus. Dev Dyn 234:878–891
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, Y., Ito, Y., Kuhara, S. et al. Cephalic hedgehog expression is regulated directly by Sox17 in endoderm development of Xenopus laevis . Cytotechnology 57, 151–159 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-008-9127-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-008-9127-2