Abstract
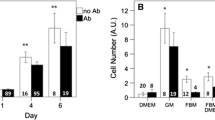
Cell- and tissue culture methodology form an important base for biological, biochemical and biomedical research. Most cell culture techniques require the use of animal sera for the successful propagation of cells. However, the varying composition between batches has fuelled the need for alternatives. In the case of serum derived from animal foetuses, ethical concerns have also been raised. Here we compare the use of a platelet derived lysate (Plysate), which is currently under development as a serum substitute, in the culturing of primary human muscle cells to foetal bovine serum (FBS). In cells cultured with Plysate, differentiation into myotubes, glucose-uptake, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity and expression and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 MAPK and PKB/Akt was impaired. Thus for primary human skeletal muscle Plysate is a sub-optimal substitute for FBS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Al-Khalili A.V. Chibalin K. Kannisto B.B. Zhang J. Permert G.D. Holman E. Ehrenborg V.D. Ding J.R. Zierath A. Krook (2003) ArticleTitleInsulin action in cultured human skeletal muscle cells during differentiation: assessment of cell surface GLUT4 and GLUT1 content Cell Mol. Life Sci. 60 991–998 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlt1aitLc%3D Occurrence Handle12827286
L. Al-Khalili D. Krämer P. Wretenberg A. Krook (2004) ArticleTitleHuman skeletal muscle cell differentiation is associated with changes in myogenic markers and enhanced insulin-mediated MAPK and PKB phosphorylation Acta Physiol. Scand. 180 395–403 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-201X.2004.01259.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjt1eks7Y%3D Occurrence Handle15030381
Cha B.S., Ciaraldi T.P., Park K.S., Carter L., Mudaliar S.R. and Henry R.R. 2005. Impaired fatty acid metabolism in type 2 diabetic skeletal muscle is reversed by PPAR{gamma} agonists. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.
S. Donna ParticleDi K. Mamchaoui R.N. Cooper S. Seigneurin-Venin J. Tremblay G.S. Butler-Browne V. Mouly (2003) ArticleTitleTelomerase can extend the proliferative capacity of human myoblasts, but does not lead to their immortalization Mol. Cancer Res. 1 643–653 Occurrence Handle12861050
T. Fiaschi P. Chiarugi F. Buricchi E. Giannoni M.L. Taddei L. Magnelli G. Cozzi G. Raugei G. Ramponi (2003) ArticleTitleDown-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling during myogenesis Cell Mol. Life Sci. 60 2721–2735 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXivFCktbo%3D Occurrence Handle14685695 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00018-003-3293-3
H. Fukamizu F. Grinnell (1990) ArticleTitleSpatial organization of extracellular matrix and fibroblast activity: effects of serumtransforming growth factor betaand fibronectin Exp. Cell Res. 190 276–282 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-4827(90)90197-I Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXmt1yrsLg%3D Occurrence Handle2209728
G. Gstraunthaler (2003) ArticleTitleAlternatives to the use of fetal bovine serum: serum-free cell culture Altex 20 275–281 Occurrence Handle14671707
D.W. Jayme K.E. Blackman (1985) ArticleTitleCulture media for propagation of mammalian cells, viruses, and other biologicals Adv Biotechnol Processes 5 1–30 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28Xht1Grs7k%3D Occurrence Handle2417609
C.E. Jochems J.B. Valk Particleder F.R. Stafleu V. Baumans (2002) ArticleTitleThe use of fetal bovine serum: ethical or scientific problem? Altern. Lab Anim. 30 219–227 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvFehsbo%3D Occurrence Handle11971757
A. Krook H. Wallberg-Henriksson J.R. Zierath (2004) ArticleTitleSending the Signal: Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Glucose Uptake Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 36 1212–1217 Occurrence Handle10.1249/01.MSS.0000132387.25853.3B Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXltlOrtLk%3D Occurrence Handle15235328
Kwon M.S., Dojima T. and Park E.Y. 2004. Use of plant-derived protein hydrolysates for enhancing growth of Bombyx mori insect cells in suspension culture. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem.
J.S. Lebkowski L.R. Schain T.B. Okarma (1995) ArticleTitleSerum-free culture of hematopoietic stem cells: a review Stem Cells 13 607–612 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK287msVChsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8590862 Occurrence Handle10.1002/stem.5530130605
Liselott Johansson J.K., Olov H. and Ohlson S. 2003. Platelet lysate: a replacement for fetal bovine serum in animal cell culture? Cytotechnology 67–74.
J.H. Mumford D.L. Carnes D.L. Cochran T.W. Oates (2001) ArticleTitleThe effects of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on periodontal cells in an in vitro wound model J. Periodontol. 72 331–340 Occurrence Handle10.1902/jop.2001.72.3.331 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkslCls7c%3D Occurrence Handle11327060
Olov H. and Westermark B. 1989. Blood Platelet Lysatemethod of its preparation and a cell culture medium containing blood platelet lysate. European Patent Cooperation 413727.
Olov H. and Westermark B. 2003. Preparation of a blood platelet lysate for use in a cell culture medium for hybridoma cells. Patent USA.
H. Peng J. Huard (2004) ArticleTitleMuscle-derived stem cells for musculoskeletal tissue regeneration and repair Transpl. Immunol. 12 311–319 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXkt1Sntro%3D Occurrence Handle15157924
N. Perez-Reyes C.L. Halbert P.P. Smith E.P. Benditt J.K. McDougall (1992) ArticleTitleImmortalization of primary human smooth muscle cells PNAS 89 1224–1228 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XitFSls7Y%3D Occurrence Handle1311088
R. Ross D.F. Bowen-Pope E.W. Raines (1990) ArticleTitlePlatelet-derived growth factor and its role in health and disease Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 327 155–169 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtlKju7o%3D Occurrence Handle1969656
M.B. Sporn A.B. Roberts (1989) ArticleTitleTransforming growth factor-beta. Multiple actions and potential clinical applications JAMA 262 938–941 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.262.7.938 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXlt1Oisbw%3D Occurrence Handle2666683
M. Tallquist A. Kazlauskas (2004) ArticleTitlePDGF signaling in cells and mice Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15 205–213 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.03.003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXltVKht7k%3D Occurrence Handle15207812
J. Valk Particlevan der D. Mellor R. Brands R. Fischer F. Gruber G. Gstraunthaler L. Hellebrekers J. Hyllner F.H. Jonker P. Prieto M. Thalen V. Baumans (2004) ArticleTitleThe humane collection of fetal bovine serum and possibilities for serum-free cell and tissue culture Toxicol. In Vitro 18 1–12 Occurrence Handle14630056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krämer, D.K., Bouzakri, K., Holmqvist, O. et al. Effect of Serum Replacement with Plysate on Cell Growth and Metabolismin Primary Cultures of Human Skeletal Muscle. Cytotechnology 48, 89–95 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-005-4074-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-005-4074-7