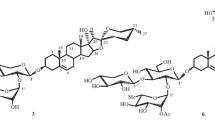
In order to investigate its bioactive compounds, we studied the chemical constituents of the seeds of Allium tuberosum systematically. Our detailed investigation of its seeds has led to the discovery of a new saponin. The new steroidal saponin, named tuberoside B, was isolated from the seeds of Allium tuberosum Rottl. ex Spreng. On the basis of acid hydrolysis, comprehensive spectroscopic analyses and comparison with spectral data of the new compound, its structure was established as (24S,25S)-5β-spirostan-2α,3β,5,24-tetraol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoyl-(1 → 2)-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 → 4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside. The new compound was identified by direct comparison with authentic samples (co-TLC, IR, MS, NMR) and with reported spectral and physical data. This paper deals with the isolation and structural elucidation of the new saponin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Hostettmann and A. Marston, Saponins, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1995, p. 56.
Z. M. Zou, D. Q. Yu, and P. Z. Cong, Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 34, 395 (1999).
Jiangsu New Medicinal College, Dictionary of Chinese Herbal Medicines, Vol. 2, Shanghai People’s Publishing Press, Shanghai, 1979, p. 278.
Jiangsu New Medical College, Dictionary of Chinese Herbal Medicines, Shanghai Science and Technology Publisher, Shanghai, 1986, p. 346.
S. M. Sang, A. N. Lao, H. C. Wang, and Z. L. Chen, Phytochemistry, 52, 1611 (1999).
S. M. Sang, S. L. Mao, A. N. Lao, and Z. L. Chen, Nat. Prod. Res. Dev., 12, 1 (2000).
S. M. Sang, S. L. Mao, A. N. Lao, and Z. L. Chen, Chin. Trad. Herb. Drugs, 31, 244 (2000).
S. M. Sang, Z. H. Xia, S. L. Mao, A. N. Lao, and Z. L. Chen, J. Chin. Mater. Med., 25, 286 (2000).
S. Sang, S. Mao, A. Lao, and Z. L. Chen, J. Agric. Food Chem., 49, 1475 (2001).
S. Sang, S. Mao, A. Lao, and Z. L. Chen, J. Agric. Food Chem., 49, 4780 (2001).
S. Sang, S. Mao, A.Lao, and Z. L. Chen, Food Chem., 83, 499 (2003).
Z. M. Zou, D. Q. Yu, and P. Z. Cong, Phytochemistry, 57, 1219 (2001).
Guohua Hu, Yanhua Lu, and Dongzhi Wei, Biores. Technol., 96 (14), 1630 (2005).
Guohua Hu, Yanhua Lu, and Dongzhi Wei, Chin. Trad. Herb. Drug, 37, 992 (2006).
Guohua Hu, Yanhua Lu, and Dongzhi Wei, Food Chem., 99, 693 (2006).
Guohua Hu, Yanhua Lu, Rengang Mao, Dongzhi Wei, Zhengzhi Ma, and Hua Zhang, J. Ethnopharmacol., 122 (3), 579 (2009).
Guohua Hu, Chun Sheng, Rengang Mao, Zhengzhi Ma, Yanhua Lu, and Dongzhi Wei, Chem. Nat. Compd., 48, 1091 (2013).
P. K. Agrawal, D. C. Jain, R. K. Gupta, and R. S. Thakur, Phytochemistry, 24, 2479 (1985).
S. Seo, Y. Tomita, K. Tori, and Y. Yoshimura, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 100 (11), 3331 (1978).
P. Z. Cong, Application of Mass Spectrometry in Natural Organic Chemistry, Science Publishing Press, Beijing, 1987, p. 786.
Y. Mimaki, T. Nikaido, K. Matsumoto, Y. Sashida, and T. Ohmoto, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 42, 710 (1994).
Acknowledgment
The work are supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31171747), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, Grant No. 2060204.The authors are grateful for the assistance of Wang Xi, Center of Analysis & Research, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, China, and Yu Yinghao, Center of Analysis & Research, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, P. R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 6, November–December, 2013, pp. 930–933.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, G., Lu, Y., Yu, W. et al. A Steroidal Saponin from the Seeds of Allium tuberosum . Chem Nat Compd 49, 1082–1086 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-014-0825-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-014-0825-z