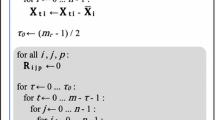An iterative algorithm is described for three-dimensional deconvolution in the Fourier plane using parallel computations on CPU and GPU. The algorithm demonstrates easy scalability and can process any number of input images of any size. It is only limited by the local storage volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Larichev, P. V. Ivanov, N. G. Iroshnikov, V. I. Shmalgauzen, and L. J. Otten, “Adaptive system for eye-fundus imaging,” Quantum Electronics, 32, No. 10, 902–908 (2002). doi:https://doi.org/10.1070/QE2002v032n10ABEH002314.
Q. Wu, F. Merchant, and K. Castleman, Microscope Image Processing, Academic Press (2008).
D. Sage, L. Donati, F. Soulez, D. Fortun, G. Schmit, A. Seitz, R. Guiet, C. Vonesch, and M. Unser, “DeconvolutionLab2: An opensource software for deconvolution microscopy,” Methods of Image Processing for Biologists, 115, 28–41 (2017). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.12.015.
A. Eklund, P. Dufort, D. Forsberg, and S. M. LaConte, “Medical image processing on the GPU – Past, present and future,” Medical Image Analysis, 17, No. 8, 1073–1094 (2013). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2013.05.008.
C. W. Quammen, D. Feng, and R. M. Taylor, Performance of 3D Deconvolution Algorithms on Multi-Core and Many-Core Architectures, Technical Report TR09-001, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Department of Computer Science (2009).
S. Kromwijk, S. Lefkimmiatis, and M. Unser, “High-performance 3D deconvolution of fluorescence micrographs,” in: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conf. on Image Processing (ICIP’14), Paris (2014), pp. 1718–1722. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2014.7025344.
P. Karas, M. Kuderjavý, and D. Svoboda, “Deconvolution of huge 3-D images: parallelization strategies on a multi-GPU system,” in: J. Kołodziej, B. Di Martino, D. Talia, and K. Xiong (editors), Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing. ICA3PP 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, vol. 8285: 279-290. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03859-9_24.
M. A. Bruce and J. B. Manish, .“Real-time GPU-based 3D deconvolution,” .Optics Express, 21, No. 4, 4766–4773 (2013). doi:https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.21.004766.
L. Domanski, T. Bednarz, P. Vallotton, and J. Taylor, “Heterogeneous parallel 3D image deconvolution on a cluster of GPUs and CPUs,” in: 19th International Congr. on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12–16 December 2011 (2011). http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011/A8/domanski.pdf.
L. D’Amore, L. Marcellino, V. Mele, and D. Romano, “Deconvolution of 3D fluorescence microscopy images using graphics processing units,” in: R. Wyrzykowski, J. Dongarra, K. Karczewski, and J. Waśniewski (editors), Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics PPAM 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, vol. 7203, Part 1, pp. 690-699 (2012). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31464-3_70.
L. Cao, P. Juan, and Y. Zhang, “Real-time deconvolution with GPU and Spark for big imaging data analysis,” in: G. Wang, A. Zomaya, G. Martinez, and K. Li (editors), Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, vol. 9530: 240-250 (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27137-8_19.
R. Zanella, G. Zanghirati, R. Cavicchioli, L. Zanni, P. Boccacci, M. Bertero, and G. Vicidomini, Towards Real-Time Image Deconvolution: Application to Confocal and STED Microscopy, Scientific Reports 3, Article number: 2523 (2013). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02523.
A. V. Razgulin, N. G. Iroshnikov, A. V. Larichev, T. E. Romanenko, and A. S. Goncharov, “Fourier domain iterative approach to optical sectioning of 3d translucent objects for ophthalmology purposes,” Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., 42–2(W4): 173-177 (2017). doi:https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-2-W4-173-2017.
A. V. Razgulin, N. G. Iroshnikov, A. V. Larichev, S. D. Pavlov, and T. E. Romanenko, “On a problem of numerical sectioning in ophthalmology,” Computer Optics, 39, No. 5, 777–786 (2015). doi: https://doi.org/10.18287/0134-2452-2015-39-5-777-786.
A. Krylov, A. Nasonov, A. Razgulin, and T. Romanenko, “A post-processing method for 3D fundus image enhancement,” in: 2016 IEEE 13th International Conf. on Signal Processing (ICSP), Chengdu (2016), pp. 49–52. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSP.2016.7877794.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Prikladnaya Matematika i Informatika, No. 58, 2018, pp. 95–110.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanenko, T.E., Razgulin, A.V. A Three-Dimensional Deconvolution Algorithm Using Graphic Processors. Comput Math Model 30, 80–90 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10598-019-09436-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10598-019-09436-z