Abstract
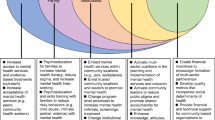
Upon immigration to the rural areas in the US, Latino families may experience cultural, geographic, linguistic and social isolation, which can detrimentally affect their wellbeing by acting as chronic stressors. Using a community engagement approach, this is a pilot mixed-method study with an embedded design using concurrent qualitative and quantitative data. The purpose of this study is to evaluate family and social environments in terms of protective factors and modifiable risks associated with mental well-being in Latino immigrants living in rural areas of Florida. Latino immigrant mother and adolescent dyads were interviewed by using in-depth ethnographic semistructured interviews and subsequent quantitative assessments, including a demographic questionnaire and three structured instruments: the Family Environment Scale Real Form, the SF-12v2™ Health Survey and the short version (eight items) of PROMIS Health Organization Social Isolation. This mixed-method pilot study highlighted how family, rural, and social environments can protect or impair wellbeing in rural Latino immigrant mother and adolescent dyads.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayón, C., & Naddy, M. B. G. (2013). Latino immigrant families’ scocial support networks:strengths and limitations during a time of stringent immigration legistation and economic insecurity. Journal of Community Psychology, 41(3), 359–377. doi:10.1002/jcop.21542.
Bathum, M. E., & Baumann, L. C. (2007). A sense of community among immigrant Latinas. Fam Community Health, 30(3), 167–177. doi:10.1097/01.FCH.0000277760.24290.de.
Carlisle, C. E., Mamdani, M., Schachar, R., & To, T. (2012). Predictors of psychiatric aftercare among formerly hospitalized adolescents. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 57(11), 666–676.
Chang, E. C., Sanna, L. J., & Hirsch, J. K. (2010). Loneliness and negative life events as predictors of hopelessness and suicidal behaviors in Hispanics: Evidence for a diathesis-stress model. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 66(12), 1242–1253. doi:10.1002/jclp.20721.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. P. (2011). Designing and conducting mixed-methods research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Dinwiddie, G. Y., Gaskin, D. J., Chan, K. S., Norrington, J., & McCleary, R. (2013). Residential segregation, geographic proximity and type of services used: Evidence for racial/ethnic disparities in mental health. Social Science and Medicine, 80, 67–75. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.11.024.
Finch, B., Kolody, B., & Vega, W. (2000). Perceived discrimination and depression among Mexican origin adults in California. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 41, 295–313.
Gonzales, N. A., Coxe, S., Roosa, M. W., White, R. M. B., Knight, G. P., Zeiders, K. H., et al. (2011). Economic hardship, neighborhood context and parenting: Prospective effects on Mexican-American adolescent’s mental health. American Journal of Community Psychology, 47, 98–113.
Gonzales, N. A., Deardoff, J., Formoso, D., Barr, A., & Barrera, M, Jr. (2006). Family mediators of the relation between acculturation and adolescent mental health. Family Relations, 55, 318–330.
Grzywacz, J. G., Quandt, S. A., Early, J., Tapia, J., Graham, C. N., & Arcury, T. A. (2006). Leaving family for work: Ambivalence and mental health among Mexican migrant farmworker men. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 8(1), 85–97.
Heilemann, M. S., Coffey-Love, M., & Frutos, L. (2004). Perceived reasons for depression among low income women of Mexican descent. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, XVIII(5), 185–192.
Hiott, A. E., Grzywacz, J., Arcury, T., & Quandt, S. (2006). Gender differences in anxiety and depression among immigrant Latinos. Family System Health, 24(2), 137–146.
Hiott, A. E., Grzywacz, J., Davis, S., Quandt, S., & Arcury, T. (2008). Migrant farmworker stress: Mental health implications. Journal of Rural Health, 24(1), 32-39.
Jesse, D. E., & Swanson, M. S. (2007). Risks and resources associated with antepartum risk for depression among rural southern women. Nursing Research, 56(6), 378–386.
Ko, L. K., & Perreira, K. M. (2010). “It turned my world upside down”: Latino youths’ perspectives on immigration. Journal of Adolescent Research, 25(3), 465–493.
Leidy, M. S., Guerra, N. G., & Toro, R. I. (2012). Positive parenting, family cohesion and child social competence among immigrant Latino families. Journal of Latina/o Psychology, 1(S), 3–13. doi:10.1037/2168-1678.1.S.3.
Loury, S., Jesse, E., & Wu, Q. (2011). Binge drinking among male Mexican immigrants in Rural North Carolina. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 13(4), 664–670. doi:10.1007/s10903-010-9402-0.
Miles, M., & Huberman, M. (Eds.). (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Mora, D. C., Grzywacz, J. G., Anderson, A. M., Chen, H., Arcury, T. A., Marin, A. J., et al. (2013). Social isolation among Latino workers in rural North Carolina: Exposure and health implications. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health,. doi:10.1007/s10903-013-9784-x.
Nair, R. L., White, R. M. B., Rosa, M. W., & Zeiders, K. H. (2013). Cultural stressors and mental health symptoms among Mexican Americans: A prospective study examining the impact of the family and neighborhood context. Journal of Youth Adolescence, 42, 1611–1623.
Ornelas, I. J., Perreira, K. M., Beeber, L., & Maxwell, L. (2009). Challenges and strategies to maintaining emotional health: Qualitative perspectives of Mexican immigrant mothers. Journal of Family Issues, 30(11), 1556–1575.
Peña, J. B., Kuhlberg, J. A., Zayas, L. H., Baumann, A. A., Gulbas, L., Hausmann-Stabile, C., et al. (2011). Familism, family environment, and suicide attempts among Latina youth. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 41(3), 330–341. doi:10.1111/j.1943-278X.2011.00032.x.
Potochnick, S. R., & Perreira, K. M. (2010). Depression and anxiety among first-generation immigrant Latino youth: Key correlates and implications for future research. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 198(7), 470–477. doi:10.1097/NMD.0b013e3181e4ce24.
Raffaelli, M., Tran, S. P., Wiley, A. R., Galarza-Heras, M., & Lazarevic, V. (2012). Risk and resilience in rural communities: The experiences of immigrant Latina mothers. Family Relations, 61, 559–570. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3729.2012.00717.x.
Ryan, G. W., & Bernard, R. H. (2003). Techniques to identify themes. Field. Methods, 15(85), 85–109. doi:10.1177/1525822X02239569.
Sandelowski, M. (2000). Focus on research methods combining qualitative and quantitative sampling, data collection, and analysis techniques in mixed-method studies. Research in Nursing & Health, 23, 246–255.
Sano, Y., Garasky, S., Greder, K. A., Cook, C. C., & Browder, D. E. (2011). Understanding food insecurity among Latino immigrant families in rural America. Journal of Family and Economic Issues, 32, 111–123. doi:10.1007/s10834-010-9219-y.
Schmitz, M. (2006). Influence of social and family contexts on self-esteem of Latino youth. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 28(4), 516–530. doi:10.1177/0739986306293999.
Scott, A. J., & Wilson, R. F. (2011). Social determinants of health among African Americans in a rural community in the deep South: An ecological exploration. Rural and Remote Health, 11(1634).
Sharkey, J. R., Johnson, C. M., & Dean, W. R. (2011). Relationship of household food insecurity to health-related quality of life in a large sample of rural and urban women. Women and Health, 51(5), 442–460. doi:10.1080/03630242.2011.584367.
Shattell, M. M., Smith, K. M., Quinlan-Colwell, A., & Villalba, J. A. (2008). Factors contributing to depression in latinas of mexican origin residing in the United States: Implications for nurses. Journal of the American Psychiatric Nurses Association, 14(3), 193–204. doi:10.1177/1078390308319034.
Smokowski, P. R., & Bacallao, M. L. (2007). Acculturation, internalizing mental health symptoms, and self-esteem: Cultural experiences of Latino adolescents in North Carolina. Child Psychiatry Human Development, 37(3), 273–292. doi:10.1007/s10578-006-0035-4.
Smith-Morris, C., Morales-Campos, D., Castañeda Alvarez, E. A., & Turner, M. (2013). An anthropology of Familismo: On narratives and description of Mexican/Immigrants. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 35(1), 35–60. doi:10.1177/0739986312459508.
Stacciarini, J. M. R., Smith, R. F., Wiens, B., Pérez, A., Locke, B., & Laflam, M. (2014). I didn’t ask to come to this country…I was a child: The mental health implications of growing up undocumented. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health. doi:10.1007/s10903-014-0063-2.
Stacciarini, J. M. R., Wiens, B., Coady, M., Schwait, A. B., Pérez, A., Locke, B., et al. (2011). CBPR: Building partnerships with Latinos in rural area for a wellness approach to mental health. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 32, 486–492. doi:10.3109/01612840.2011.576326.
Sweat, M. D., & Denison, J. A. (1995). Reducing HIV incidence in developing countries with structural and environmental interventions. AIDS, 9(Suppl A), S251–S257.
Terrazas, A. (Producer). (2010, July 9, 2014). Mexicans immigrants in the United States. Migration Information Source. Retrieved from http://www.migrationpolicy.org/article/mexican-immigrants-united-states-0#5.
Tomaka, J., Thompson, S., & Palacios, R. (2006). The relation of social Isolation, loneliness, and social support to disease outcomes among the elderly. Journal of Aging Health, 18, 359–384. doi:10.1177/0898264305280993.
Valdez, C. R., Padilla, B., & Valentine, J. L. (2013). Consequences of Arizona’s Immigration Policy on Social Capital Among Mexican Mothers With Unauthorized Immigration Status. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stacciarini, JM.R., Smith, R., Garvan, C.W. et al. Rural Latinos’ Mental Wellbeing: A Mixed-Methods Pilot Study of Family, Environment and Social Isolation Factors. Community Ment Health J 51, 404–413 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-014-9774-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-014-9774-z