Abstract
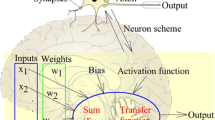
This study pertains to prediction of liquefaction susceptibility of unconsolidated sediments using artificial neural network (ANN) as a prediction model. The backpropagation neural network was trained, tested, and validated with 23 datasets comprising parameters such as cyclic resistance ratio (CRR), cyclic stress ratio (CSR), liquefaction severity index (LSI), and liquefaction sensitivity index (LSeI). The network was also trained to predict the CRR values from LSI, LSeI, and CSR values. The predicted results were comparable with the field data on CRR and liquefaction severity. Thus, this study indicates the potentiality of the ANN technique in mapping the liquefaction susceptibility of the area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krinitzsky, E.L., Hynes, M.E.: The Bhuj, India earthquake: lessons learnt for earthquake safety of dams on alluvium. Eng. Geol. 58, 193–202 (2002)
Ramakrishnan, D., Mohanty, K.K., Nayak, S.R.: Mapping the liquefaction induced soil moisture changes using remote sensing technique: an attempt to map the earth induced liquefaction around Bhuj, Gujarat, India. Geotech. Geolog. Eng. 24, 1581–1602 (2006)
Singh, R., Roy, D., Jain, S.K.: Analysis of earth dams affected by the 2001 Bhuj Earthquake. Eng. Geol. 80, 282–291 (2005)
Malik, J.N., Sohoni, P.S., Karanth, R.V., Merh, S.S.: Modern and historic seismicity of Kachchh Peninsula, Western India. J. Geol. Soc. India 54, 545–550 (1999)
Sitharam, T.G., Govindaraju, L.: Geotechnical aspects and ground response studies in Bhuj earthquake, India. Geotech. Geolog. Eng. 22, 439–455 (2004)
Ramakrishnan, D., Jeyaram, A., Mohanty, K.K., Nayak, S.R.: Mapping the liquefaction susceptible zones in parts of Kachchh region using IRS_WiFS and LISS-III data. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Earth System Process Related to Gujarat Earthquake Using Space Technology, pp. 27–29, 50–51. Department of Civil Engineering, IIT, Kanpur, India (2003)
Khandelwal, M., Roy, M.P., Singh, P.K.: Application of artificial neural network in mining industry. Indian Min. Eng. J. 43(7), 19–23 (2004)
Goh, A.T.C.: Empirical design in geotechnics using neural networks. Geotechnique 45(4), 709–714 (1995)
Goh, A.T.C.: Seismic liquefaction potential assessed by neural networks. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 120(9), 1467–1480 (1995)
Teh, C.L., Wong, K.S., Goh, A.T.C., Jaritngam, S.: Predicting settlement of shallow foundations using neural networks. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 11(2), 129–138 (1997)
Goh, A.T.C.: Neural network modeling of CPT seismic liquefaction data. J Geotech. Eng. 122(1), 70–73 (1996)
Ural, D.N., Saka, H.: Liquefaction assessment by neural networks. Elect. J. Geotech. Eng. http://geotech.civen.okstate.edu/ejge/ppr9803/index.html (1998)
Hanna, M.A., Ural, D., Saygili, G.: Neural network model for liquefaction potential in soil deposits using Turkey and Taiwan earthquake data. Int. J. Soil Dyn. Earthqu. Eng. 27(6), 521–540 (2007)
Ishihara, K.: Liquefaction and flow failure during earthquakes. Geotechnique 43(3), 351–415 (1993)
Chu, B.-L., Hsu, S.-C., Chang, Y.-M.: Ground behavior and liquefaction analyses in central Taiwan-Wufeng. Eng. Geol. 71, 119–139 (2003)
Lee, D.-H., Ku, C.-S., Yuan, H.: A study of the liquefaction risk potential at Yuanlin, Taiwan. Eng. Geol. 71, 97–117 (2003)
Yuan, H., Hiu Yang, S., Andrus, R.D., Hsein Juang, C.: Liquefaction induced ground failure: a study of the Chi-Chi earthquake cases. Eng. Geol. 17, 141–155 (2003)
Seed, H.B., Tokimatsu, K., Harder, L.F., Chung, R.M.: The influence of SPT procedures in soil liquefaction resistance evaluations. J. Geotech. Eng., ASCE. 111(12), 1425–1445 (1985), 16
Youd, T.L., Idriss, I.M., Andrus, R.D., Arango, I., Castro, G., Christian, J.T., Dobry, R., LiamFinn, W.D., Harder, L.F. Jr, Hynes, M.E., Ishihara, K., Koester, J.P., Laio, S.S.C., Marcuson, W.F. III, Martin, G.R., Mitchell, J.K., Moriwaki, Y., Power, M.S., Robertson, P.K., Seed, R.B., Stokoe, K.H. II: Liquefaction resistance of soils: summary report from the 1996 NCEER and 1998 NCEER/NSF workshops on evaluation of liquefaction resistance of soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 127(10), 817–833 (2001)
Seed, H.B., Idriss, I.M.: Simplified procedure for evaluating soil liquefaction potential. J. Soil Mech. Found Div., ASCE 97(SM9), 1249–1273 (1971), 14
Seed, H.B., Idriss, I.M., Arango, I.: Evaluation of liquefaction potential using field performance data. J. Geotech. Eng. 109, 458–482 (1983)
Youd, T.L., Perkins, D.M.: Mapping of liquefaction severity index. J. Geotech. Eng., ASCE. 113(11), 1374–1392 (1987), 17
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning Internal Representation by Error Propagation in Parallel Distributed Processing. Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Cambridge (1986)
Lippmann, R.P.: An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 42, 4–22 (1987)
Flood, I., Kartam, N.: Neural networks in civil engineering. I: Principles and understanding. J. Comput. Civ. Eng., ASCE, 82, 131–148 (1994)
Xia, Y.Y., Xie, Y.M., Zhu, R.G.: An engineering geology evaluation method based on an artificial neural network and its application. Eng. Geol. 47, 149–156 (1997)
Rumelhart, D.E., McClelland, J.L.: Parallel Distributed Processing-Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition 1/2. Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Cambridge (1986)
Widrow, B., Jovitz, M.C., Jacobi, G.T., Goldstein, G.: Generalization and information storage in networks of adaline neurons. In: Yovitz, M.C., Jacobi, G.T., Goldstein, G.D. (eds.) Self Organizing System, pp. 435–461. Spartan Books, Washington D.C. (1962)
Hecht-Neilsen, R.: Counterpropagation networks. Appl. Opt. 26(23), 4979–4984 (1987)
Powell, M.J.D.: Restart procedures for the conjugate gradient method. Math. Program. 12, 241–254 (1977)
Scales, L.E.: Introduction to Non-linear Optimization. Springer, New York (1985)
Gill, P.E., Murray, W., Wright, M.H.: Practical Optimization. Academic, New York (1981)
Battiti, R.: First and second order methods for learning; between steepest descent and Newton’s method. Neural Comput. 4(2), 141–166 (1992)
Singh, T.N., Verma, A.K., Sharma, P.K.: A neuro-genetic approach for prediction of time dependent deformational characteristic of rock and its sensitivity analysis. Geotech. Geolog. Eng. 25, 395–407 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramakrishnan, D., Singh, T.N., Purwar, N. et al. Artificial neural network and liquefaction susceptibility assessment: a case study using the 2001 Bhuj earthquake data, Gujarat, India. Comput Geosci 12, 491–501 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-008-9088-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-008-9088-8