Abstract
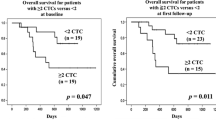
We previously demonstrated that the detection of circulating cancer cells (CCC) expressing survivin mRNA could provide valuable information for predicting recurrence in patients with breast, lung, gastric and colorectal carcinoma. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether the detection of survivin-expressing CCC in the peripheral blood is also useful for predicting recurrence in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Blood samples obtained from 108 ESCC patients and 75 healthy volunteers were quantitatively investigated by a technique that detected reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction products based on a hybridization-enzyme linked immunosorbent essay. Not all of the patients were available for the follow-up study. Only 48 patients who were treated with similar adjuvant therapy regimens were available and followed-up for 33 months after the initial assay test. Survivin-expressing CCC were detected in 51 (47.2%) patients. The presence of survivin-expressing CCC was found to be significantly associated with depth of invasion, vascular invasion, nodal status, and disease stages (P = 0.032, 0.019, 0.018, and 0.001, respectively). During the follow-up period, patients who had positive survivin expressions had a higher relapse rate and a shorter survival time than those who had negative survivin expressions (P = 0.002 and 0.016, respectively). Examination of survivin-expressing CCC could provide valuable information in the prediction of haematogenous recurrence as well as in the prognosis of ESCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel M, Ferry K, Franceschi D et al (2004) Esophageal carcinoma: current controversial topics. Cancer Invest 22:897–912. doi:10.1081/CNV-200039672
Roder JD, Stein HJ, Siewert JR (1995) Oesophageal carcinoma. In: Hermaneck P, Gospodarowicz MK, Henson DE (eds) Prognostic factors in cancer, UICC. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p 37
Lee SJ, Lee KS, Yim YJ et al (2005) Recurrence of squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus after curative surgery: rates and patterns on imaging studies correlated with tumour location and pathological stage. Clin Radiol 60:547–554. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2004.09.002
Huang P, Wang J, Guo Y et al (2003) Molecular detection of disseminated tumor cells in the peripheral blood in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:192–198
Ikoma D, Ichikawa D, Ueda Y et al (2007) Circulating tumor cells and aberrant methylation as tumor markers in patients with esophageal cancer. Anticancer Res 27:535–539
Ito H, Kanda T, Nishimaki T et al (2004) Detection and quantification of circulating tumor cells in patients with esophageal cancer by real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 23:455–464
Kaganoi J, Shimada Y, Kano M et al (2004) Detection of circulating oesophageal squamous cancer cells in peripheral blood and its impact on prognosis. Br J Surg 91:1055–1060. doi:10.1002/bjs.4593
Koike M, Hibi K, Kasai Y et al (2002) Molecular detection of circulating esophageal squamous cell cancer cells in the peripheral blood. Clin Cancer Res 8:2879–2882
Liu Z, Jiang M, Zhao J et al (2007) Circulating tumor cells in preoperative esophageal cancer patients: quantitative assay system and potential clinical utility. Clin Cancer Res 13:2992–2997. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2072
Nakashima S, Natsugoe S, Matsumoto M et al (2003) Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in blood by molecular detection and tumor markers in esophageal cancer. Surgery 133:162–169. doi:10.1067/msy.2003.9
Chiou SK, Jones MK, Tarnawski AS (2003) Survivin–an anti-apoptosis protein: its biological roles and implications for cancer and beyond. Med Sci Monit 9:125–129
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri D (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3:917–921. doi:10.1038/nm0897-917
Grabowski P, Kühnel T, Mühr-Wilkenshoff F et al (2003) Prognostic value of nuclear survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 88:115–119. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600696
Mega S, Miyamoto M, Li L et al (2006) Immunohistochemical analysis of nuclear survivin expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus 19:355–359. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2006.00604.x
Rosato A, Pivetta M, Parenti A et al (2006) Survivin in esophageal cancer: an accurate prognostic marker for squamous cell carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 119:1717–1722. doi:10.1002/ijc.21923
Yie SM, Luo B, Ye NY et al (2006) Detection of Survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in the peripheral blood of breast cancer patients by a RT-PCR ELISA. Clin Exp Metastasis 23:279–289. doi:10.1007/s10585-006-9037-7
Yie SM, Lou B, Ye SR et al (2008) Detection of survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells (CCCs) in peripheral blood of patients with gastric and colorectal cancer reveals high risks of relapse. Ann Surg Oncol 15:3037–3082. doi:10.1245/s10434-008-0069-x
Yie SM, Lou B, Ye SR et al (2009) Clinical significance of detecting survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 63:284–290. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.05.024
Watanable H, Jass JR, Sobin LH (eds) (1990) Histological typing of esophageal and gastric tumors. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Sobin H, Wittekind C (eds) (2002) UICC: TNM classification of malignant tumors, 6th edn. Wiley, New York
Yonenaga Y, Mori A, Onodera H et al (2005) Absence of smooth muscle actin-positive pericyte coverage of tumor vessels correlates with hematogenous metastasis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Oncology 69:159–166
Mino-Miyagawa N, Kimura Y, Hamamoto K (1990) Tumor-antigen 4: its immunohistochemical distribution and tissue and serum concentrations in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and esophagus. Cancer 66:1505–1512. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19901001)66:7<1505::AID-CNCR2820660712>3.0.CO;2-V
Katayama A, Mafune K, Tanaka Y et al (2003) Autopsy findings in patients after curative esophagectomy for esophageal carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 196:866–873. doi:10.1016/S1072-7515(03)00116-9
Jiao X, Krasna MJ (2002) Clinical significance of micrometastasis in lung and esophageal cancer: a new paradigm in thoracic oncology. Ann Thorac Surg 74:278–284. doi:10.1016/S0003-4975(01)03376-8
Mehes G, Witt A, Kubista E et al (2001) Circulating breast cancer cells are frequently apoptotic. Am J Pathol 159:17–20
Brablets T, Jung A, Spaderna S et al (2005) Migrating cancer stem cells-an integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 5:744–749. doi:10.1038/nrc1694
Zhang T, Otevrel T, Gao ZQ et al (2001) Evidence that APC regulates survivin expression: a possible mechanism contributing to the stem cell origin of colon cancer. Cancer Res 61:8664–8667
Moriai R, Asanuma K, Kobayashi D et al (2001) Quantitative analysis of the anti-apoptotic gene survivin expression in malignant haematopoietic cells. Anticancer Res 21:595–600
Torre GC (1998) SCC antigen in malignant and nonmalignant squamous lesions. Tumour Biol 19:517–526. doi:10.1159/000030045
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by grants from the Chengdu Municipal Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. 07GGYB240SF-143), and the Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. 07JY029-091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, M., Yie, SM., Wu, SM. et al. Detection of survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in the peripheral blood of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin Exp Metastasis 26, 751–758 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-009-9274-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-009-9274-7