Abstract
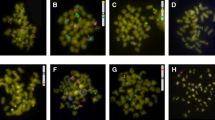
Oreochromis karongae, one of the “chambo” tilapia species from Lake Malawi, has a karyotype of 2n = 38, making it one of the few species investigated to differ from the typical tilapia karyotype (2n = 44). The O. karongae karyotype consists of one large subtelocentric pair of chromosomes, four medium-sized pairs (three subtelocentric and one submetacentric) and 14 small pairs. The five largest pairs could be distinguished from each other on the basis of size, morphology and a series of fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) probes. The largest pair is easily distinguished on the basis of size and a chromosome 1 (linkage group 3) bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) FISH probe from Oreochromis niloticus. BAC clones from O. niloticus chromosome 2 (linkage group 7) hybridised to one of the medium-sized subtelocentric chromosome pairs (no. 5) of O. karongae, distinguishing the ancestral medium-sized pair from the three other medium-sized chromosome pairs (nos. 2, 3 and 4) that appear to have resulted from fusions. SATA repetitive DNA hybridised to the centromeres of all 19 chromosome pairs and also revealed the locations of the relic centromeres in the three fused pairs. Telomeric (TTAGGG)n repeats were identified in the telomeres of all chromosomes, and an interstitial telomeric site (ITS) was identified in three chromosomal pairs (no. 2, 3 and 4). Additionally, two ITS sites were identified in the largest chromosome pair (pair 1), confirming the origin of this chromosome from three ancestral chromosomes. SATA and ITS sites allowed the orientation of the fusions in pairs 2, 3 and 4, which all appear to have been in different orientations (q–q, p–q and p–p, respectively). One of these fusions (O. karongae chromosome pair no. 2) involves a small chromosome (equivalent to linkage group 1), which in O. niloticus carries the main sex-determining gene. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenyloindole staining of the synaptonemal complex in male O. karongae revealed the presumptive positions of the kinetochores, which correspond well to the centromeric positions observed in the mitotic karyotype.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenyloindole
- DIG:
-
Digoxygenin
- DOP-PCR:
-
Degenerate oligonucleotide primed PCR
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation
- FITC:
-
Fluorescin isothiocyanate
- ITS:
-
Interstitial telomeric site
- LE:
-
Lateral element (of an SC bivalent)
- LG:
-
Linkage group
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation–time of flight
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- SATA:
-
Satellite DNA isolated from the tilapia genome by EcoRI digestion and electrophoresis
- SC:
-
Synaptonemal complex
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SSC:
-
Saline-sodium citrate
References
Campos-Ramos R, Harvey SC, Masabanda JS et al (2001) Identification of putative sex chromosomes in the blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus, through synaptonemal complex and FISH analysis. Genetica 111:143–153
Chang X, Kobayashi T, Senthilkumaran B, Kobayashi-Kajura H, Sudhakumari CC, Nagahama Y (2005) Two types of aromatase with different encoding genes, tissue distribution and developmental expression in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 141:101–115
Cnaani A, Lee B-Y, Zilberman N et al (2008) Genetics of sex determination in tilapiine species. Sex Dev 2:43–54
Denton TE (1973) Fish chromosome methodology. CC Thomas, Springfield
Ezaz MT, Harvey SC, Boonphakdee C, Teale AJ, McAndrew BJ, Penman DJ (2004) Isolation and physical mapping of sex-linked AFLP markers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Mar Biotechnol 6:435–445
Ferreira IA, Martins C (2008) Physical chromosome mapping of repetitive DNA sequences in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus: evidences for a differential distribution of repetitive elements in the sex chromosomes. Micron 39:411–418
Ferreira IA, Poletto AB, Mota-Velasco J, Penman DJ, Kocher TD, Martins C (2010) Chromosome evolution in African Cichlid fish: contributions from the physical mapping of repeated DNAs. Cytogenetics and Genome Research (in press)
Foresti F, Oliveira C, Galetti PM, de Almeida-Toledo LF (1993) Synaptonemal complex analysis–analysis in spermatocytes of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces, Cichlidae). Genome 36:1124–1128
Franck JPC, Wright JM, McAndrew BJ (1992) Genetic variability in a family of satellite DNAs from tilapia (Pisces: Cichlidae). Genome 35:719–725
Harvey SC, Powell SF, Kennedy DD, McAndrew BJ, Penman DJ (2002a) Karyotype analysis of Oreochromis mortimeri (Trewavas) and Sarotherodon melanotheron (Rüppell). Aquac Res 33:339–342
Harvey SC, Campos-Ramos R, Kennedy RR et al (2002b) Karyotype evolution in Tilapia: mitotic and meiotic chromosome analysis of Oreochromis karongae and O. niloticus × O. karongae hybrids. Genetica 115:169–177
Harvey SC, Kwon JY, Penman DJ (2003) Physical mapping of the brain and ovarian aromatase genes in the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Anim Genet 34:62–64
Ijdo JW, Wells RA, Baldini A, Reeders ST (1991) Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG)n generated by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 19:4780
Jurinke C, van den Boom D, Cantor CR, Koster H (2002) Automated genotyping using the DNA MassArray technology. Meth Mol Biol 187:179–192
Katagiri T, Kidd C, Tomasino E et al (2005) A BAC-based physical map of the Nile tilapia genome. BMC Genomics 89:1–17
Klinkhardt M, Tesche M, Greven H (1995) Database of fish chromosomes. Westarp Wissenschaften, Magdeburg
Lee BY, Kocher TD (2007) Exclusion of Wilms tumour (WT1b) and ovarian cytochrome P450 aromatase (CYP19A1) as candidates for sex determination genes in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim Genet 38:85–86
Lee BY, Penman DJ, Kocher TD (2003) Identification of a sex-determining region in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) using bulked segregant analysis. Anim Genet 34:379–383
Lee BY, Hulata G, Kocher TD (2004) Two unlinked loci controlling the sex of blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus). Heredity 92:543–549
Lee BY, Lee WJ, Streelman JT et al (2005) A second-generation genetic linkage map of tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Genetics 170:237–244
Majumdar KC, McAndrew BJ (1986) Relative DNA content of somatic nuclei and chromosomal studies in three genera, Tilapia, Sarotherodon, and Oreochromis of the tribe Tilapiini (Pisces, Cichlidae). Genetica 68:175–188
Martins C, Galetti PM Jr (2001) Organization of 5S rDNA in species of the fish Leporinus: two different genomic locations are characterized by distinct non transcribed spacers. Genome 44:903–910
Mitelman F (ed) (1995) An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN). Karger/Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics, Basel
Ocalewicz K, Mota-Velasco JC, Campos-Ramos R, Penman DJ (2009) FISH and DAPI staining of the synaptonemal complex of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) allow orientation of the unpaired region of bivalent 1 observed during early pachytene. Chromosome Res 17:773–782
Oliveira C, Wright JM (1998) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of heterochromatin in the chromosomes of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Teleostei: Cichlidae). Chromosome Res 6:205–211
Oliveira C, Chew JSK, Foresti FP, Dobson M, Wright JM (1999) A LINE2 repetitive DNA sequence from the cichlid fish, Oreochromis niloticus: sequence analysis and chromosomal distribution. Chromosoma 108:457–468
Park EH (1974) A list of the chromosome numbers of fishes. Coll Rev Lib Arts and Sciences Seoul Nat Univ 20:346–372
Phillips RB, Amores A, Morasch MR, Wilson C, Postlethwait JH (2006a) Assignment of zebrafish genetic linkage groups to chromosomes. Cytogenet Genome Res 114:155–162
Phillips RB, Nichols KM, DeKoning JJ et al (2006b) Assignment of rainbow trout linkage groups to specific chromosomes. Genetics 174:1661–1670
Piferrer F, Blázquez M (2005) Aromatase distribution and regulation in fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 31(2–3):215–226
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2934–2938
Post A (1965) Vergleichende Untersuchungen der Chromosomenzahlen bei Susswasser Teleosteem. Z Zoolog Syst Evol Forsch 3:47–93
Shirak A, Seroussi E, Cnaani A et al (2006) Amh and Dmrta2 genes map to Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) linkage group 23 within QTL regions for sex determination. Genetics 174(3):1573–1581
Sodsuk P, McAndrew BJ, Turner GF (1995) Evolutionary relationships of the Lake Malawi Oreochromis species: evidence from allozymes. J Fish Biol 47:321–333
Sullivan BA, Schwartz S (1995) Identification of centromeric antigens in dicentric Robertsonian translocations: CENP-C and CENP-E are necessary components of functional centromeres. Hum Mol Genet 4:2189–2197
Sullivan BA, Willard HF (1998) Stable dicentric X chromosomes with two functional centromeres. Nat Genet 20:227–228
Thompson KW (1981) Karyotypes of six species of African Cichlidae (Pisces: Perciformes). Experientia 37:351–352
Trewavas E (1983) Tilapiine Fishes of the Genera Sarotherodon, Oreochromis and Danakilia. British Museum (Natural History), London
Turner GF, Robinson RL (1991) Ecology, morphology and taxonomy of the Lake Malawi Oreochromis (Nyasalapia) species flock. Ann Mus R Afr Cent Sci Zool 262:23–28
Volff JN, Nanda A, Schmid M, Schartl M (2007) Governing sex determination in fish: regulatory putsches and ephemeral dictators. Sex Dev 1:85–99
Wallace BMN, Wallace H (2003) Synaptonemal complex karyotype of zebrafish. J Hered 90:136–140
Acknowledgements
J.C. Mota-Velasco was supported by a PhD grant from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia (CONACYT), México. I.A. Ferreira and M.B. Cioffi were supported by PhD grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Brazil. K. Ocalewicz and R. Campos-Ramos were supported by a grant from the Research Council of Norway, and C. Martins was supported by FAPESP. A. Shirak and B.-Y. Lee were supported by research grant IS-3995-07 from the United States–Israel Binational Agricultural Research and Development (BARD) Fund. We thank Prof Tom Kocher for assistance in several respects, including provision of DNA clones used as FISH probes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Walther Traut.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
(GIF 56 kb)
High resolution image
(TIFF 431 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
(GIF 121 kb)
High resolution image
(TIFF 571 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
(GIF 258 kb)
High resolution image
(TIFF 998 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mota-Velasco, J.C., Ferreira, I.A., Cioffi, M.B. et al. Characterisation of the chromosome fusions in Oreochromis karongae . Chromosome Res 18, 575–586 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-010-9141-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-010-9141-z