Abstract
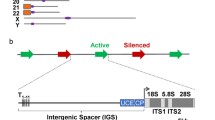
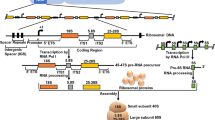
In eukaryotes the ribosomal gene population shows two different states in terms of chromatin structure. One subset is organized as nucleosomes (silent copies) while the other has a non-nucleosomal configuration (active copies). Insect cells are not the exception and this bimodal distribution of ribosomal chromatin also occurs in salivary gland cells, and cells of other larval tissues, of the midge Chironomus thummi. In run-on experiments on salivary glands cells we confirmed that transcribed rRNA genes show a non-nucleosomal configuration. The proportion of rRNA genes adopting an open, non-nucleosomal configuration was found to be tissue-dependent, suggesting that the population of unfolded ribosomal chromatin in C. thummi was established during cell differentiation. We propose that cell differentiation determines the fraction of non-nucleosomal rRNA gene copies and thus defines the range of possible rRNA synthesis rates in a particular cell type. In the salivary gland the fraction of unfolded chromatin was not significantly affected when transcription was repressed. However, transcription activation by pilocarpine led to a moderate increase in this fraction. These findings indicate that, in addition to a possible increase in the number of RNA-polymerases per transcribing rDNA unit, the proportion of transcribed ribosomal genes in differentiated cells can be modulated in response to an exceptional rRNA synthesis requirement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aprikian P, Moorefield B, Reeder RH (2001) New model for the yeast RNA polymerase I transcription cycle. Mol Cell Biol 21: 4847-855.
Bandit M, Koller T, Sogo JM (1999) Transcriptional activity and chromatin structure of enhancer-deleted rRNA genes in Sacharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 19: 4953-960.
Barettino D, Morcillo G, Díez JL (1982) Induction of heat-shock Balbiani rings after RNA synthesis inhibition in polytene chromosomes of Chironomus thummi. Chromosoma 87: 507-17.
Bergtrom G, Laufer H, Rogers R (1976) Fat body: a site of hemoglobin synthesis in Chironomus thummi (Diptera). J Cell Biol 69: 264-74.
Conconi A, Widmer RM, Koller T, Sogo JM (1989) Two different chromatin structures coexist in ribosomal RNA genes throughout the cell cycle. Cell 57: 753-61.
Conconi A, Sogo JM, Ryan CA (1992) Ribosomal gene clusters are uniquely proportionated between open and closed chromatin structures in both tomato leaf cells and exponentially growing suspension cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 5256-260.
Dammann R, Lucchini R, Koller T, Sogo JM (1993) Chromatin structures and transcription of rDNA in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 21: 2331-338.
Dammann R, Lucchini R, Koller T, Sogo JM (1995) Transcription in the yeast rRNA gene locus: distribution of the active gene copies and chromatin structure of their flanking regulatory. Mol Cell Biol 15: 5294-303.
De Bernardin W, Koller T, Sogo JM (1986) Structure of in-vivo transcribing chromatin as studied in simian virus 40 minichromosomes. J Mol Biol 191: 469-82.
Díez JL, Santa-Cruz MC, Aller P (1977) Effect of cycloheximide on RNA synthesis in Chironomus polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma 61: 369-79.
Fahy D, Conconi A, Smerdon MJ (2005) Rapid changes in transcription and chromatin structure of ribosomal genes in yeast during growth phase transitions. Exp Cell Res 305: 365-73.
French SL, Osheim YN, Cioci F, Nomura M, Beyer AL (2003) In exponentially growing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, rRNA synthesis is determined by the summed RNA polymerase I loading rate rather than by the number of active genes. Mol Cell Biol 23: 1558-568.
Gorab E, de Lacoba MG, Botella L (1995) Structural constraints in expansion segments from a midge 26S rDNA. J Mol Evol 41: 1016-021.
Haaf T, Hayman DL, Schmid M (1991) Quantitative determination of rDNA transcription units in vertebrate cells. Exp Cell Res 193: 78-6.
Hadjiolov AA (1985) The nucleolus and ribosome biogenesis. In: Alfert M, Beermann W, Goldstein L, Porter KR, Sitte P eds., Cell Biology Monographs, vol. 12. Vienna: Springer Verlag.
Hägele K (1975) Chironomus. In: King RC, ed., Handbook of Genetics. Northwestern University, pp. 269-78.
Lucchini R, Sogo JM (1992) Different chromatin structures along the spacers flanking active and inactive Xenopus rRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol 12: 4288-296.
Lucchini R, Sogo JM (1995) Replication of transcriptionally active chromatin. Nature 374: 276-80.
Lucchini R, Sogo JM (1998) The dynamic structure of ribosomal RNA gene chromatin. In: Paule MR, ed., Transcription of Ribosomal RNA Genes by Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase I. Austin, TX: Landes Bioscience, pp. 255–276.
Mähr R, Meyer B, Daneholt B, Eppenberger HM (1980) Activation of Balbiani ring genes in Chironomus tentans after a pilocarpine-induced depletion of the secretory products from the salivary gland lumen. Dev Biol 80: 409-18.
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Meyer B, Mahr R, Eppenberger HM, Lezzi M (1983) The activity of Balbiani rings 1 and 2 in salivary glands of Chironomus tentans larvae under different modes of development and after pilocarpine treatment. Dev Biol 98: 265-77.
Paule MR (1998) Regulation of ribosomal RNA expression. In: Paule MR, ed., Transcription of Ribosomal RNA Genes by Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase I. Austin, TX: Landes Bioscience, pp. 195–200.
Percipalle P, Östlund Farrants A-K (2006) Chromatin remodelling and transcription: be-WICHed by nuclear myosin 1. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18: 267-74.
Reeder RH (1989) Regulatory elements of the generic ribosomal gene. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1: 447-66.
Sandmeier JJ, French S, Osheim Y et al. (2002) RPD3 is required for the inactivation of yeast ribosomal DNA genes in stationary phase. EMBO J 21: 4959-968.
Santoro R, Grummt I (2005) Epigenetic mechanism of rRNA gene silencing: temporal order of NoRC-mediated histone modification, chromatin remodeling, and DNA methylation. Mol Cell Biol 25: 2539-546.
Sass H (1980) Features of in-vitro puffing and RNA synthesis in polytene chromosomes of Chironomus. Chromosoma 78: 33-8.
Schmidt ER, Godwin EA, Keyl HG, Israelewski N. (1982) Cloning and analysis of ribosomal DNA of Chironomus thummi piger and Chironomus thummi thummi. The nontranscribed spacer of C. thummi contains a highly repetitive DNA sequence. Chromosoma 87: 389-07.
Stancheva I, Lucchini R, Koller T, Sogo JM (1997) Chromatin structure and methylation of rat rRNA genes studied by formaldehyde fixation and psoralen cross-linking. Nucleic Acids Res 25: 1727-735.
Stefanovsky V, Moss T (2006) Regulation of rRNA synthesis in human and mouse cells is not determined by changes in active gene count. Cell Cycle 5: 735-39.
Stefanovsky V, Langlois F, Gagnon-Kugler T, Rothblum LI, Moss T (2006) Growth factor signaling regulates elongation of RNA polymerase I transcription in mammals via UBF phosphorylation and r-chromatin remodeling. Mol Cell 21: 629-39.
Widmer RM, Lucchini R, Lezzi M et al. (1984) Chromatin structure of a hyperactive secretory protein gene (in Balbiani ring 2) of Chironomus. EMBO J 3: 1635-641.
Wiesendanger B (1994) The proportion of non-nucleosomal, transcribable and nucleosomal, non transcribable ribosomal RNA gene copies is cell type specific. Ph.D. thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology of Zürich: No. 10801.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Cristina Sanz and Eduardo Gorab contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanz, C., Gorab, E., Ruiz, M.F. et al. Chromatin structure of ribosomal genes in Chironomus thummi (Diptera: Chironomidae): tissue specificity and behaviour under drug treatment. Chromosome Res 15, 429–438 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-007-1134-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-007-1134-1