Abstract
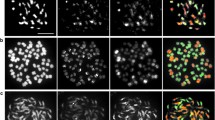
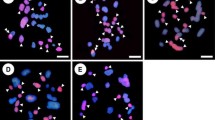
Genomic in-situ hybridization (GISH) was applied to study the behaviour of addition chromosomes in first and second backcross (BC) progenies of hybrids between Brassica napus ssp. napus L. (AACC, 2n = 38) and Sinapis alba L. (SS, 2n = 24) produced by electrofusion. With GISH using genomic DNA of S. alba was used as probe it was possible to clearly distinguish both of the parental genomes and effectively monitor the fate of S. alba chromosomes in the BC1 and BC2 progenies. GISH analysis confirmed the sesquidiploid genome composition (AACCS) of the BC1 progenies, which contained 38 chromosomes from B. napus and 12 chromosomes from S. alba. Genome painting in the pollen mother cells (PMCs) of the BC1 plants revealed intergenomic association between B. napus and S. alba chromosomes, whereby a maximum of 4 trivalents between AC and S chromosomes were identified at metaphase I. In the BC2 progenies, aneuploids with different numbers of additional chromosomes from S. alba, ranging from 1 to 7, were confirmed. Three putative monosomic alien addition lines were characterized, and the results are discussed with respect to the potential for intergenomic chromosome recombination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SNH, Ramanna MS, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (2001) Establishment of a complete series of a monosomic tomato chromosome addition lines in the cultivated potato using RFLP and GISH analyses. Theor Appl Genet 103: 687–695.
Ali HBM, Lysak MA, Schubert I (2005) Chromosomal localization of rDNA in the Brassicaceae. Genome 48: 341–346.
Anamthawat-Jonsson K, Schwarzacher T, Leitch AR, Bennett MD, Heslop-Harrison JS (1990) Discrimination between closely related Triticeae species using genomic DNA as a probe. Theor Appl Genet 79: 721–728.
Benabdelmouna A, Guéritaine G, Abirached-Darmency M, Darmency H (2003) Genome discrimination in progeny of interspecific hybrids between Brassica napus and Raphanus raphanistrum. Genome 46: 469–472.
Bodnaryk RP, Lamb RJ (1991) Mechanisms of resistance to the flea beetle, Phyllotreta cruciferae (Goeze), in yellow mustard seedlings, Sinapis alba L. Can J Plant Sci 71: 13–20.
Brown J, Brown AP, Davis JB, Erickson D (1997) Intergeneric hybridization between Sinapis alba and Brassica napus. Euphytica 93: 163–168.
Brown J, McCaffrey JP, Brown DA, Harmon DA, Harmon BL, Davis JB (2004) Yield reduction in Brassica napus, B. rapa, B. juncea, and Sinapis alba caused by flea beetle (Phyllotreta cruciferae (Goeze) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)) infestation in northern Idaho. J Econ Entomol 97: 1642–1647.
Chevre AM, Eber F, Margale E et al. (1994) Comparison of somatic and sexual Brassica napus–Sinapis alba hybrids and their progeny by cytogenetic studies and molecular characterization. Genome 37: 367–374.
Fahleson J, Lagercrantz U, Mouras A, Glimelius K (1997) Characterization of somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Eruca sativa using species-specific repetitive sequences and genomic in situ hybridization. Plant Sci 123: 133–142.
Fridman E, Carrari F, Liu YS, Fernie AR, Zamir D (2004) Zooming in on a quantitative trait for tomato yield using interspecific introgressions. Science 305: 1786–1789.
Gaikward K, Kirti PB, Sharma A, Prakash S, Chopra VL (1996) Cytogenetical and molecular investigations on somatic hybrids of Sinapis alba and Brassica juncea and their backcross progeny. Plant Breed 115: 480–483.
Hansen LN, Earle ED (1997) Somatic hybrids between Brassica oleracea L. and Sinapis alba L. with resistance to Alternaria brassicae (Berk.) Sacc. Theor Appl Genet 94: 1078–1085.
Jacobsen E, De Jong JH, Kamstra SA, Van den Berg PM, Ramanna MS (1995) Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) and RFLP analysis for the identification of alien chromosomes in the backcross progeny of potato (+) tomato fusion hybrids. Heredity 74: 250–257.
Ji Y, Pertuze R, Chetelat RT (2004) Genome differentiation by GISH in interspeci¢c and intergeneric hybrids of tomato and related nightshades. Chromosom Res 12: 107–116.
Kamstra SA, Ramanna MS, De Jeu MJ, Kuipers GJ, Jacobsen E (1999) Homoeologous chromosome pairing in the distant hybrid Alstroemeria aurea × A. inodora and the genome composition of its backcross derivatives determined by fluorescent in situ hybridization with species-specific probes. Heredity 82: 69–78.
Karlov GI, Khrustaleva LI, Lim KB, Van Tuyl JM (1999) Homoeologous recombination in 2n-gamete producing interspecific hybrids of Lilium (Liliaceae) studied by genomic in situ hybridization (GISH). Genome 42: 681–686.
King IP, Morgan WG, Armstead IP et al. (1998) Introgression mapping in the grasses. I. Introgression of Festuca pratensis chromosomes and chromosome segments into Lolium perenne. Heredity 81: 462–467.
Lelivelt CLC, Leunissen EHM, Frederiks HJ, Helsper JPFG, Krens FA (1993) Transfer of resistance to the beet cyst nematode (Heterodera schachtii Schm.) from Sinapis alba L. (white mustard) to the Brassica napus L. gene pool by sexual and somatic hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 85: 688–696.
Li M, Qian W, Meng J, Li Z (2004) Construction of novel Brassica napus genotypes through chromosomal substitution and elimination using interploid species hybridization. Chromosom Res 12: 417–426.
Lim KB, Chung JD, Kronenburg BCE, Ramanna MS, Jong JH, Tuyl JM (2000) Introgression of Lilium rubellum Baker chromosomes into L. longiflorum Thunb.: a genome painting study of the F1 hybrid, BC1 and BC2 progenies. Chromosom Res 8: 119–125.
Mathias R (1991) Improved embryo rescue technique for intergeneric hybridization between Sinapis species and Brassica napus. Crucif Newsl 14/15: 90–92.
Peterka H, Budahn H, Schrader O, Ahne R, Schütze W (2004) Transfer of resistance against the beet cyst nematode from radish (Raphanus sativus) to rape (Brassica napus) by monosomic chromosome addition. Theor Appl Genet 109: 30–41.
Primard C, Vedel F, Mathieu C, Pelletier G, Chevre AM (1988) Interspecific somatic hybridization between Brassica napus and Brassica hirta (Sinapis alba L.). Theor Appl Genet 75: 546–552.
Raina SN, Rani V (2001) GISH technology in plant genome research. Methods Cell Sci 23: 83–104.
Rakow G, Potts D, Raney P, Katepa-Mupondwa F (2000) Designing oilseed crops for the Canadian dry prairie. In: 3rd Int Crop Sci Congr. Book of Abstracts, p 221, session 4C, poster no. 34. Hamburg, Germany.
Ripley VL, Arnison PG (1990) Hybridization of Sinapis alba L. and Brassica napus L. via embryo rescue. Plant Breed 104: 26–33.
Schrader O, Budahn H, Ahne R (2000) Detection of 5S and 25S rRNA genes in Sinapis alba, Raphanus sativus and Brassica napus by double fluorescence in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 100: 665–669.
Schwarzacher T, Leitch AR, Bennet MD, Heslop-Harrison JS (1989) In situ hybridization of parental genomes in a wide hybrid. Ann Bot 64: 315–324.
Skarzhinskaya M, Landgren M, Glimelius K (1998) Production of intertribal somatic hybrids between Brassica napus L. and Lesquerella fendleri (Gray) Wats. Theor Appl Genet 93: 1242–1250.
Snowdon RJ, Köhler W, Friedt W, Köhler A (1997) Genomic in situ hybridization in Brassica amphidiploids and interspecific hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 95: 1320–1324.
Snowdon RJ, Winter H, Diestel A, Sacristán MD (2000) Development and characterization of Brassica napus–Sinapis arvensis addition lines exhibiting resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans. Theor Appl Genet 101: 1008–1014.
Stevenson M, Armstrong SJ, Ford-Lloyd BV, Jones GH (1998) Comparative analysis of crossover exchanges and chiasmata in Allium cepa × fistulosum after genomic in situ hybridization (GISH). Chromosom Res 6: 567–574.
Takahashi C, Leitch IJ, Ryan A, Bennett MD, Brandham PE (1997) The use of genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) to show transmission of recombinant chromosomes by partially fertile bigeneric hybrid, Gasteria lutzii × Aloe arstata (Aloaceae), to its progeny. Chromosoma 105: 342–348.
Voss A, Snowdon RJ, Lühs W, Friedt W (2000) Intergeneric transfer of nematode resistance from Raphanus sativus into the Brassica napus genome. Acta Hortic 539: 129–134.
Wang YP, Snowdon RJ, Rudloff E, Wehling P, Friedt W, Sonntag K (2004) Cytogenetic characterization and fae1 gene variation in progenies from asymmetric somatic hybrids between Brassica napus and Crambe abyssinica. Genome 47: 724–731.
Wang J, Xiang F, Xia G (2005a) Agropyron elongatum chromatin localization on the wheat chromosomes in an introgression line. Planta 221: 277–286.
Wang YP, Sonntag K, Rudloff E, Chen J (2005b) Intergeneric somatic hybridization between Brassica napus and Sinapis alba. J Integrative Plant Biol 47: 84–91.
Wang YP, Sonntag K, Rudloff E, Wehling P, Snowdon RJ (2006) GISH analysis of disomic Brassica napus–Crambe abyssinica chromosome addition lines produced by microspore culture from monosomic addition lines. Plant Cell Rep (in press). 10.1007/s00299-005-0031-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y.P., Zhao, X.X., Sonntag, K. et al. Behaviour of Sinapis alba chromosomes in a Brassica napus background revealed by genomic in-situ hybridization. Chromosome Res 13, 819–826 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-005-1017-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-005-1017-2