Abstract
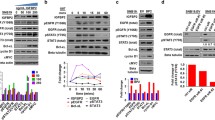
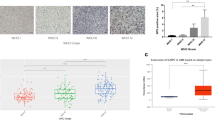
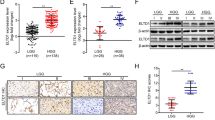
The insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6), as an inhibitor of IGF-II actions, plays an important role in inhibiting survival and migration of tumor cells. In our study, we intended to demonstrate the biological function of IGFBP6 in the development of glioma and its clinical significance. Firstly, Western blot and immunohistochemistry revealed that the expression of IGFBP6 inversely correlated with glioma grade. Secondly, multivariate analysis with the Cox proportional hazards model and Kaplan–Meier analysis indicated that IGFBP6 could be an independent prognostic factor for the survival of glioma patients. In addition, overexpression of IGFBP6 induced glioma cell apoptosis, and depletion of IGFBP6 had the opposite action. Finally, overexpression of IGFBP6 inhibited migration of glioma cells, and depletion of IGFBP6 had the opposite action. Together our findings suggest that IGFBP6 might be an important regulator and prognostic factor for glioma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DC, Rasheed BA, McLendon RE, Bigner DD (2010) Central nervous system. Cancer Biomark 9(1–6):193–210
Bach LA (1999) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6: the “forgotten” binding protein? Horm Metab Res 31:226–234
Bach LA (2005) IGFBP-6 five years on; not so ‘forgotten’? Growth Horm IGF Res 15:185–192
Bach LA (2015) Recent insights into the actions of IGFBP-6. J Cell Commun Signal 9:189–200
Bach LA, Fu P, Yang Z (2013) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-6 and cancer. Clin Sci 124:215–229
Ding Z, Liu Y, Yao L et al (2015) Spy1 induces de-ubiquitinating of RIP1 arrest and confers glioblastoma’s resistance to tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α)-induced apoptosis through suppressing the association of CLIPR-59 and CYLD. Cell Cycle 14(13):2149–2159
Freije WA, Castro-Vargas FE, Fang Z et al (2004) Gene expression profiling of gliomas strongly predicts survival. Cancer Res 64:6503–6510
Fried P, Wolf K (2003) Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 3(5):362–374
Fu P, Thompson JA, Bach LA (2007) Promotion of cancer cell migration: an insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent action of IGF binding protein-6. J Biol Chem 282:22298–22306
Fu P, Liang GJ, Khot SS, Phan R, Bach LA (2010) Cross-talk between MAP kinase pathways is involved in IGF-independent, IGFBP-6-induced Rh30 rhabdomyosarcoma cell migration. J Cell Physiol 224:636–643
Jansen M, Yip S, Louis DN (2010) Molecular pathology in adult gliomas: diagnostic, prognostic and predictive markers. Lancet Neurol 9(7):717–726
Kang Y, Massague J (2004) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell 118(3):277–279
Kutsukake M, Ishihara R, Yoshie M, Kogo H, Tamura K (2007) Involvement of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-related protein 1 in decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. Mol Hum Reprod 13(10):737–743
Leng SL, Leeding KS, Whitehead RH, Bach LA (2001) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-6 inhibits IGF-II-induced but not basal proliferation and adhesion of LIM 1215 colon cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 174:121–127
Lin Y, Zhang G, Zhang J et al (2013) A panel of four cytokines predicts the prognosis of patients with malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 114:199–208
Micutkova L, Diener T, Li C et al (2011) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 delays replicative senescence of human fibroblasts. Mech Ageing Dev 132(10):468–479
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE (2004) Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 4:505–518
Rock K, McArdle O, Forde P et al (2012) A clinical review of treatment outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme-the validation in a nontrial population of the results of a randomised phase III clinical trial: has a more radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol 85(1017):e729–e733
Seurin D, Lassarre C, Blenvenu G, Babajko S (2002) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 inhibits neuroblastoma and cell proliferation and tumour development. Eur J Cancer 38:2058–2065
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Tao T, Cheng C, Ji Y et al (2012) Numbl inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by suppressing TRAF5-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Mol Biol Cell 23(14):2635–2644
Vigneswaran K, Neill S, Hadjipanayis CG (2015) Beyond the World Health Organization grading of infiltrating gliomas: advances in the molecular genetics of glioma classification. Ann Transl Med 3(7):95
Wang Y, Liu F, Mao F et al (2013) Interaction with cyclin H/cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CCNH/CDK7) stabilizes C-terminal binding protein 2 (CtBP2) and promotes cancer cell migration. J Biol Chem 288(13):9028–9034
Weller M, Cloughesy T, Perry JR, Wick W (2013) Standards of care for treatment of recurrent glioblastoma-are we there yet? Neuro-Oncology 15:4–27
Yang Z, Bach LA (2015) Differential effects of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 (IGFBP-6) on migration of two ovarian cancer cell lines. Front Endocrinol 5:231
Zeng X, Yang P, Chen B et al (2013) Quantitative secretome analysis reveals the interactions between epithelia and tumor cells by in vitro modulating colon cancer microenvironment. J Proteom 89:51–70
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu province (No. BK20130386), the Chinese Projects for Postdoctoral Science Funds (No. 2015M571792), and the Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (No. 1402200C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Yuanqi Bei, Qingfeng Huang, Bin Ji and Jianguo Chen have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bei, Y., Huang, Q., Shen, J. et al. IGFBP6 Regulates Cell Apoptosis and Migration in Glioma. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37, 889–898 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0426-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0426-4