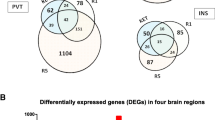
Abstract
Repeated electrical stimulation results in development of seizures and a permanent increase in seizure susceptibility (kindling). The permanence of kindling suggests that chronic changes in gene expression are involved. Kindling at different sites produces specific effects on interictal behaviors such as spatial cognition and anxiety, suggesting that causal changes in gene expression might be restricted to the stimulated site. We employed focused microarray analysis to characterize changes in gene expression associated with amygdaloid and hippocampal kindling. Male Long-Evans rats received 1 s trains of electrical stimulation to either the amygdala or hippocampus once daily until five generalized seizures had been kindled. Yoked control rats carried electrodes but were not stimulated. Rats were euthanized 14 days after the last seizures, both amygdala and hippocampus dissected, and transcriptome profiles compared. Of the 1,200 rat brain-associated genes evaluated, 39 genes exhibited statistically significant expression differences between the kindled and non-kindled amygdala and 106 genes exhibited statistically significant differences between the kindled and non-kindled hippocampus. In the amygdala, subsequent ontological analyses using the GOMiner algorithm demonstrated significant enrichment in categories related to cytoskeletal reorganization and cation transport, as well as in gene families related to synaptic transmission and neurogenesis. In the hippocampus, significant enrichment in gene expression within categories related to cytoskeletal reorganization and cation transport was similarly observed. Furthermore, unique to the hippocampus, enrichment in transcription factor activity and GTPase-mediated signal transduction was identified. Overall, these data identify specific and unique neurochemical pathways chronically altered following kindling in the two sites, and provide a platform for defining the molecular basis for the differential behaviors observed in the interictal period.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K (2001) Modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation by the amygdala: a synaptic mechanism linking emotion and memory. Jpn J Pharmacol 86:18–22
Barton ME, White HS (2004) The effect of CGX-1007 and CI-1041, novel NMDA receptor antagonists, on kindling acquisition and expression. Epilepsy Res 59:1–12
Behr J, Heinemann U, Mody I (2001) Kindling induces transient NMDA receptor-mediated facilitation of high-frequency input in the rat dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol 85:2195–2202
Beldhuis HJ, Everts HG, Van der Zee EA, Luiten PG, Bohus B (1992) Amygdala kindling-induced seizures selectively impair spatial memory. 1. Behavioral characteristics and effects on hippocampal neuronal protein kinase C isoforms. Hippocampus 2:397–409
Bronzino JD, Austin-LaFrance RJ, Morgane PJ, Galler JR (1991a) Effects of prenatal protein malnutrition on kindling-induced alterations in dentate granule cell excitability. I. Synaptic transmission measures. Exp Neurol 112:206–215
Bronzino JD, Austin-LaFrance RJ, Morgane PJ, Galler JR (1991b) Effects of prenatal protein malnutrition on kindling-induced alterations in dentate granule cell excitability. II. Paired-pulse measures. Exp Neurol 112:216–223
Burgdorf J, Zhang XL, Weiss C, Matthews E, Disterhoft JF, Stanton PK, Moskal JR (2009) The N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor modulator GLYX-13 enhances learning and memory, in young adult and learning impaired aging rats. Neurobiol Aging
Canteras NS, Swanson LW (1992) Projections of the ventral subiculum to the amygdala, septum, and hypothalamus: a PHAL anterograde tract-tracing study in the rat. J Comput Neurol 324:180–194
Chen Q, He S, Hu XL, Yu J, Zhou Y, Zheng J, Zhang S, Zhang C, Duan WH, Xiong ZQ (2007) Differential roles of NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in activity-dependent brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene regulation and limbic epileptogenesis. J Neurosci 27:542–552
Colino A, Fernandez de Molina A (1986a) Electrical activity generated in subicular and entorhinal cortices after electrical stimulation of the lateral and basolateral amygdala of the rat. Neuroscience 19:573–580
Colino A, Fernandez de Molina A (1986b) Inhibitory response in entorhinal and subicular cortices after electrical stimulation of the lateral and basolateral amygdala of the rat. Brain Res 378:416–419
Corcoran ME, Moshé SL (eds) (1998) Kindling five. Plenum, New York
Corcoran ME, Moshé SL (eds) (2005) Kindling six. Springer, New York
Corcoran ME, Teskey CG (2009) Characteristics and mechanisms of kindling. In: Schwartzkroin P (ed) Encyclopedia of basic epilepsy research, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 741–746
Ding YX, Zhang Y, He B, Yue WH, Zhang D, Zou LP (2010) A possible association of responsiveness to adrenocorticotropic hormone with specific GRIN1 haplotypes in infantile spasms. Dev Med Child Neurol 52:1028–1032
Endele S, Rosenberger G, Geider K, Popp B, Tamer C, Stefanova I, Milh M, Kortum F, Fritsch A, Pientka FK, Hellenbroich Y, Kalscheuer VM, Kohlhase J, Moog U, Rappold G, Rauch A, Ropers HH, von Spiczak S, Tonnies H, Villeneuve N, Villard L, Zabel B, Zenker M, Laube B, Reis A, Wieczorek D, Van Maldergem L, Kutsche K (2010) Mutations in GRIN2A and GRIN2B encoding regulatory subunits of NMDA receptors cause variable neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Nat Genet 42:1021–1026
Geinisman Y, Morrell F, de Toledo-Morrell L (1988) Remodeling of synaptic architecture during hippocampal “kindling”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:3260–3264
Geula C, Jarvie PA, Logan TC, Slevin JT (1988) Long-term enhancement of K+-evoked release of l-glutamate in entorhinal kindled rats. Brain Res 442:368–372
Goddard GV, Douglas RM (1976) Does the engram of kindling model the engram of normal long term memory? In: Wada JA (ed) Kindling. Raven, New York, p 18
Goddard GV, McIntyre DC, Leech CK (1969) A permanent change in brain function resulting from daily electrical stimulation. Exp Neurol 25:295–330
Gorter JA, van Vliet EA, Aronica E, Breit T, Rauwerda H, Lopes da Silva FH, Wadman WJ (2006) Potential new antiepileptogenic targets indicated by microarray analysis in a rat model for temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 26:11083–11110
Hannesson DK, Corcoran ME (2000) The mnemonic effects of kindling. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:725–751
Hannesson DK, Howland J, Pollock M, Mohapel P, Wallace AE, Corcoran ME (2001) Dorsal hippocampal kindling produces a selective and enduring disruption of hippocampally mediated behavior. J Neurosci 21:4443–4450
Hannesson DK, Howland JG, Pollock M, Mohapel P, Wallace AE, Corcoran ME (2005) Anterior perirhinal cortex kindling produces long-lasting effects on anxiety and object recognition memory. Eur J Neurosci 21:1081–1090
Hannesson DK, Pollock MS, Howland JG, Mohapel P, Wallace AE, Corcoran ME (2008) Amygdaloid kindling is anxiogenic but fails to alter object recognition or spatial working memory in rats. Epilepsy Behav 13:52–61
Heffner TG, Hartman JA, Seiden LS (1980) A rapid method for the regional dissection of the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:453–456
Henry LC, Goertzen CD, Lee A, Teskey GC (2008) Repeated seizures lead to altered skilled behaviour and are associated with more highly efficacious excitatory synapses. Eur J Neurosci 27:2165–2176
Holmes KH, Bilkey DK, Laverty R, Goddard GV (1990) The N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonists aminophosphonovalerate and carboxypiperazinephosphonate retard the development and expression of kindled seizures. Brain Res 506:227–235
Jarvie PA, Logan TC, Geula C, Slevin JT (1990) Entorhinal kindling permanently enhances Ca2(+)-dependent l-glutamate release in regio inferior of rat hippocampus. Brain Res 508:188–193
Kalynchuk LE, Pinel JP, Treit D (1998) Long-term kindling and interictal emotionality in rats: effect of stimulation site. Brain Res 779:149–157
Kamphuis W, Lopes da Silva FH, Wadman WJ (1988) Changes in local evoked potentials in the rat hippocampus (CA1) during kindling epileptogenesis. Brain Res 440:205–215
Kandel ER (2001) The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 294:1030–1038
Krettek JE, Price JL (1974) Projections from the amygdala to the perirhinal and entorhinal cortices and the subiculum. Brain Res 71:150–154
Krettek JE, Price JL (1977) Projections from the amygdaloid complex to the cerebral cortex and thalamus in the rat and cat. J Comput Neurol 172:687–722
Kroes RA, Panksepp J, Burgdorf J, Otto NJ, Moskal JR (2006) Modeling depression: social dominance-submission gene expression patterns in rat neocortex. Neuroscience 137:37–49
Kroes RA, Burgdorf J, Otto NJ, Panksepp J, Moskal JR (2007) Social defeat, a paradigm of depression in rats that elicits 22-kHz vocalizations, preferentially activates the cholinergic signaling pathway in the periaqueductal gray. Behav Brain Res 182:290–300
Lehmann H, Ebert U, Loscher W (1998) Amygdala-kindling induces a lasting reduction of GABA-immunoreactive neurons in a discrete area of the ipsilateral piriform cortex. Synapse 29:299–309
Leung LS, Boon KA, Kaibara T, Innis NK (1990) Radial maze performance following hippocampal kindling. Behav Brain Res 40:119–129
Lieberman DN, Mody I (1998) Substance P enhances NMDA channel function in hippocampal dentate gyrus granule cells. J Neurophysiol 80:113–119
Loscher W, Schwark WS (1987) Further evidence for abnormal GABAergic circuits in amygdala-kindled rats. Brain Res 420:385–390
Lukasiuk K, Kontula L, Pitkanen A (2003) cDNA profiling of epileptogenesis in the rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 17:271–279
Maren S, Fanselow MS (1995) Synaptic plasticity in the basolateral amygdala induced by hippocampal formation stimulation in vivo. J Neurosci 15:7548–7564
Mody I, Heinemann U (1987) NMDA receptors of dentate gyrus granule cells participate in synaptic transmission following kindling. Nature 326:701–704
Perez-Otano I, Ehlers MD (2005) Homeostatic plasticity and NMDA receptor trafficking. Trends Neurosci 28:229–238
Pikkarainen M, Ronkko S, Savander V, Insausti R, Pitkanen A (1999) Projections from the lateral, basal, and accessory basal nuclei of the amygdala to the hippocampal formation in rat. J Comput Neurol 403:229–260
Racine RJ (1972a) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. I. After-discharge threshold. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:269–279
Racine RJ (1972b) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation, II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:281–294
Racine R, Okujava V, Chipashvili S (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. 3. Mechanisms. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:295–299
Racine RJ, Burnham WM, Gilbert M, Kairiss EW (1986) Kindling mechanisms: I. Electrophysiological studies. In: Wada JA (ed) Kindling three. Raven, New York, pp 263–279
Routtenberg A, Rekart JL (2005) Post-translational protein modification as the substrate for long-lasting memory. Trends Neurosci 28:12–19
Schinnick-Gallagher P, Bradley Keele N (1998) Long-lasting changes in the pharmacology and electrophysiology of amino acid receptors in amygdala kindled neurons. In: Corcoran ME, Moshé SL (eds) Kindling five. Plenum, New York, pp 75–87
Shao LR, Dudek FE (2005) Detection of increased local excitatory circuits in the hippocampus during epileptogenesis using focal flash photolysis of caged glutamate. Epilepsia 46(5):100–106
Sloviter RS, Zappone CA, Harvey BD, Frotscher M (2006) Kainic acid-induced recurrent mossy fiber innervation of dentate gyrus inhibitory interneurons: possible anatomical substrate of granule cell hyper-inhibition in chronically epileptic rats. J Comput Neurol 494:944–960
Sutula T, Zhang P, Lynch M, Sayin U, Golarai G, Rod R (1998) Synaptic and axonal remodeling of mossy fibers in the hilus and supragranular region of the dentate gyrus in kainate-treated rats. J Comput Neurol 390:578–594
Teskey GC, Monfils MH, Silasi G, Kolb B (2006) Neocortical kindling is associated with opposing alterations in dendritic morphology in neocortical layer V and striatum from neocortical layer III. Synapse 59:1–9
Tuff LP, Racine RJ, Adamec R (1983a) The effects of kindling on GABA-mediated inhibition in the dentate gyrus of the rat. I. Paired-pulse depression. Brain Res 277:79–90
Tuff LP, Racine RJ, Mishra RK (1983b) The effects of kindling on GABA-mediated inhibition in the dentate gyrus of the rat. II. Receptor binding. Brain Res 277:91–98
von Bohlen und Halbach O, Schulze K, Albrecht D (2004) Amygdala-kindling induces alterations in neuronal density and in density of degenerated fibers. Hippocampus 14:311–318
Wada JA, Sato M, Corcoran ME (1974) Persistent seizure susceptibility and recurrent spontaneous seizures in kindled cats. Epilepsia 15:465–478
Yashiro K, Philpot BD (2008) Regulation of NMDA receptor subunit expression and its implications for LTD, LTP, and metaplasticity. Neuropharmacology 55:1081–1094
Zeeberg BR, Feng W, Wang G, Wang MD, Fojo AT, Sunshine M, Narasimhan S, Kane DW, Reinhold WC, Lababidi S, Bussey KJ, Riss J, Barrett JC, Weinstein JN (2003) GoMiner: a resource for biological interpretation of genomic and proteomic data. Genome Biol 4:R28
Zhang XL, Sullivan JA, Moskal JR, Stanton PK (2008) A NMDA receptor glycine site partial agonist, GLYX-13, simultaneously enhances LTP and reduces LTD at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 55:1238–1250
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (to MEC) and The Falk Foundation, Chicago, IL, (to JRM). We thank Joanne Sitarski, Ken Wolfe, Nigel Otto, and Mary Schmidt for expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corcoran, M.E., Kroes, R.A., Burgdorf, J.S. et al. Regional Changes in Gene Expression after Limbic Kindling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 819–834 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9672-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9672-7