Abstract
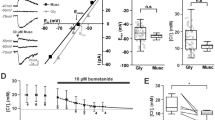
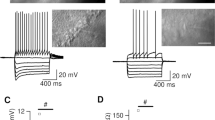
The metabotropic GABAB and adenosine A1 receptors mediate presynaptic inhibition through regulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels, whereas K+ channel regulation is believed to have no role at the CA3-CA1 synapse. We show here that the inhibitory effect of baclofen (20 μM) and adenosine (300 μM) on field EPSPs are differentially sensitive to Cs+ (3.5 mM) and Ba2+ (200 μM), but not 4-aminopyridine (100 μM). Barium had no effect on paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) in itself, but gave significant reduction (14 ± 5%) when applied in the presence of baclofen, but not adenosine, suggesting that the effect is presynaptic and selective on the GABAB receptor-mediated response. The effect of Ba2+ on PPF was not mimicked by tertiapin (30 nM), indicating that the underlying mechanism does not involve GIRK channels. Barium did not affect PPF in slices from young rats (P7–P8), suggesting developmental regulation. The above effects of Ba2+ on adult tissue were reproduced when measuring evoked whole-cell EPSCs from CA1 pyramidal neurons: PPF was reduced by 22 ± 3% in the presence of baclofen and unaltered in adenosine. In contrast, Ba2+ caused no significant change in frequency or amplitude of miniature EPSCs. The Ba2+-induced reduction of PPF was antagonized by LY341495, suggesting metabotropic glutamate receptor involvement. We propose that these novel effects of Ba2+ and Cs+ are exerted through blockade of inwardly rectifying K+ channels in glial cells, which are functionally interacting with the GABAB receptor-dependent glutamate release that generates heterosynaptic depression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson M, Blomstrand F, Hanse E (2007) Astrocytes play a critical role in transient heterosynaptic depression in the rat hippocampal CA1 region. J Physiol 585:843–852
Barish ME, Ichikawa M, Tominaga T, Matsumoto G, Iijima T (1996) Enhanced fast synaptic transmission and a delayed depolarization induced by transient potassium current blockade in rat hippocampal slice as studied by optical recording. J Neurosci 16:5672–5687
Chu Z, Hablitz JJ (2003) GABAB receptor-mediated heterosynaptic depression of excitatory synaptic transmission in rat frontal neocortex. Brain Res 959:39–49
Dallwig R, Vitten H, Dietmer JW (2000) A novel barium-sensitive calcium influx into rat astrocytes at low external potassium. Cell Calcium 28:247–259
Djukic B, Casper KB, Philpot BD, Chin L-S, McCarthy KD (2007) Conditional knock-out of Kir 4.1 leads to glial membrane depolarization, inhibition of potassium uptake, and enhanced short-term synaptic potentiation. J Neurosci 27:11354–11365
Fritschy JM, Meskenaite V, Weinmann O, Honer M, Benke D, Mohler H (1999) GABAB-receptor splice variants GB1a and GB1b in rat brain: developmental regulation, cellular distribution and extrasynaptic localization. Eur J Neurosci 11:761–768
Hartel K, Singaravelu K, Kaiser M, Neusch C, Hulsmann S, Dietmer JW (2007) Calcium influx mediated by the inwardly rectifying K+ channel Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) at low external K+ concentraiton. Cell Calcium 42:271–280
Isaacson JS (1998) GABAB receptor-mediated modulation of presynaptic currents and excitatory transmission at a fast central synapse. J Neurophysiol 80:1571–1576
Jin W, Lu Z (1999) Synthesis of a stable form of tertiapin: a high-affinity inhibitor for inward-rectifier K+ channels. Biochemistry 38:14286–14293
Kofuji P, Newman EA (2004) Potassium buffering in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 129:1045–1056
Koyrakh L, Lujan R, Colon J, Karschin C, Kurachi Y, Karschin A, Wickman K (2005) Molecular and cellular diversity of neuronal G-protein-gated potassium channels. J Neurosci 25:11468–11478
Kumamoto E, Kuba K (1985) Effects of K+-channel blockers on transmitter release in bullfrog sympathetic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:241–247
Ladera C, Godino MC, Cabañero MJ, Torres M, Watanabe M, Luján R, Sánchez-Prieto J (2008) Pre-synaptic GABAB receptors inhibit glutamate release through GIRK channels in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 107:1506–1517
Leaney JL (2003) Contribution of Kir3.1, Kir3.2A and Kir3.2C subunits to native G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18:2110–2118
Lüscher C, Jan LY, Stoffel M, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA (1997) G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs) mediate postsynaptic but not presynaptic transmitter actions in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 19:687–695
Manabe T, Wyllie DJA, Perkel DJ, Nicoll RA (1993) Modulation of synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation: effects on paired pulse facilitation and EPSC variance in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 70:1451–1459
Mark MD, Herlitze S (2000) G-protein mediated gating of inward-rectifier K+ channels. Eur J Biochem 267:5830–5836
Misgeld U, Bijak M, Jarolimek W (1995) A physiological role for GABAB receptors and the effects of baclofen in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 46:423–462
Moldavan MG, Irwin RP, Allen CN (2006) Presynaptic GABA(B) receptors regulate retinohypothalamic tract synaptic transmission by inhibiting voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. J Neurophysiol 95:3727–3741
Nicoll RA, Malenka RC, Kauer JA (1990) Functional comparison of neurotransmitter receptor subtypes in mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev 70:513–565
Qian J, Saggau P (1999) Modulation of transmitter release by action potential duration at the hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapse. J Neurophysiol 81:288–298
Ransom CB, Sontheimer H (1995) Biophysical and pharmacological characterization of inwardly rectifying K+ currents in rat spinal cord astrocytes. J Neurophysiol 73:333–346
Scanziani M, Capogna M, Gahwiler BH, Thompson SM (1992) Presynaptic inhibition of miniature excitatory synaptic currents by baclofen and adenosine in the hippocampus. Neuron 9:919–927
Scholz KP, Miller RJ (1991) GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 444:669–686
Seifert G, Hüttmann K, Binder DK, Hartmann C, Wyczynski A, Neusch C, Steinhäuser C (2009) Analysis of astroglial K+ channel expression in the developing hippocampus reveals a predominant role of the Kir4.1 subunit. J Neurosci 29:7474–7488
Serrano A, Haddjeri N, Lacaille J-C, Robitaille R (2006) GABAergic network activation of glial cells underlies hippocampal heterosynaptic depression. J Neurosci 26:5370–5382
Skov J, Nedergaard S, Andreasen M (2005) New type of synaptically mediated epileptiform activity independent of known glutamate- and GABA-receptors. J Neurophysiol 93:1845–1856
Takahashi T, Kajikawa Y, Tsujimoto T (1998) G-Protein-coupled modulation of presynaptic calcium currents and transmitter release by a GABAB receptor. J Neurosci 18:3138–3146
Takigawa T, Alzheimer C (2002) Phasic and tonic attenuation of EPSPs by inward rectifier K+ channels in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol 539:67–75
Thompson SM, Gahwiler BH (1992) Comparison of the actions of baclofen at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol 451:329–345
Wheeler DB, Randall A, Tsien RW (1996) Changes in action potential duration alter reliance of excitatory synaptic transmission on multiple types of Ca2+ channels in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 16:2226–2237
Wu LG, Saggau P (1995) GABAB receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition in guinea-pig hippocampus is caused by reduction of presynaptic Ca2+ influx. J Physiol 485:649–657
Wu LG, Saggau P (1997) Presynaptic inhibition of elicited neurotransmitter release. Trends Neurosci 20:204–212
Yamada M, Inanobe A, Kurachi Y (1998) G protein regulation of potassium ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 50:723–760
Yoon KW, Rothman SM (1991a) Adenosine inhibits excitatory but not inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 11:1375–1380
Yoon KW, Rothman SM (1991b) The modulation of rat hippocampal synaptic conductances by baclofen and gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Physiol 442:377–390
Zhang JM, Wang HK, Ye CQ, Ge W, Chen Y, Jiang ZL, Wu CP, Poo MM, Duan S (2003) ATP released by astrocytes mediates glutamatergic activity-dependent heterosynaptic suppression. Neuron 40:971–982
Zucker RS, Regehr WG (2002) Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Physiol 64:355–405
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Bertha P. B. Mortensen, Alison Margolis, and Gaston Calfa for invaluable technical assistance and advice. This project was supported by grants from The Lundbeck Foundation, The Brd. Hartmanns Foundation, The Aase og Ejnar Danielsens Foundation, The A.P. Møller Foundation for the Advancement of Medical Science, The Danish Medical Research Council, and by grant no NS22373 (JJH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skov, J., Andreasen, M., Hablitz, J.J. et al. Baclofen and Adenosine Inhibition of Synaptic Transmission at CA3-CA1 Synapses Display Differential Sensitivity to K+ Channel Blockade. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 587–596 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9652-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9652-y