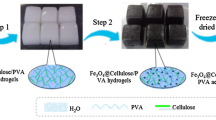
Abstract
It is difficult to recycle photocatalysts for water purification when they are in aqueous suspension. Cellulose aerogels with porous structure and biodegradability are promising carriers for photocatalysts that can be used to solve many environmental problems. In this study, a 3D recyclable g-C3N4@cellulose aerogel for photocatalytic degradation of pollutants was synthesized using a facile chemical cross-linking method. g-C3N4@cellulose aerogel (30% loading) exhibited excellent photocatalytic activity up to 99.0% degradation. In addition, the g-C3N4@cellulose aerogel exhibited high recyclability and structural stability while the photocatalytic efficiency is not significantly reduced in cycling tests. The photocatalyst was optimized using high temperature calcination, resulting in 95.35 m2 g−1 actual surface determined from Brunner–Emmet–Teller measurements. Therefore, aggregation of the photocatalyst can be avoided by the cellulose aerogel support whilst the photocatalytic property remained as efficient as its powder form. Such composites may become attractive material for practical applications.
Graphic abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhameed RM, El-Shahat M, Emam HE (2020) Employable metal (Ag&Pd)@MIL-125-NH2@cellulose acetate film for visible-light driven photocatalysis for reduction of nitro-aromatics. Carbohydr Polym 247:116695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116695
Ahmed HB, Emam HE (2019) Synergistic catalysis of monometallic (Ag, Au, Pd) and bimetallic (Ag–Au, Au–Pd) versus trimetallic (Ag–Au–Pd) nanostructures effloresced via analogical techniques. J Mol Liq 287:110975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.110975
Ahmed HB, Emam HE (2020) Seeded growth core-shell (Ag–Au–Pd) ternary nanostructure at room temperature for potential water treatment. Polym Test 89:106720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106720
Arslan-Alaton I, Gurses F (2004) Photo-Fenton-like and photo-fenton-like oxidation of Procaine Penicillin G formulation effluent. J Photochem Photobiol A 165:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2004.03.016
Berendsen R, Guell C, Henry O, Ferrando M (2014) Premix membrane emulsification to produce oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with various interfacial structures of whey protein and carboxymethyl cellulose. Food Hydrocolloids 38:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.11.005
Cao SW, Low JX, Yu JG, Jaroniec M (2015) Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride. Adv Mater 27:2150–2176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500033
Chen S, Lu W, Han J, Zhong H, Xu T, Wang G, Chen W (2019) Robust three-dimensional g-C3N4@cellulose aerogel enhanced by cross-linked polyester fibers for simultaneous removal of hexavalent chromium and antibiotics. Chem Eng J 359:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.110
Dong S et al (2019) Fabrication of 3D ultra-light graphene aerogel/Bi2WO6 composite with excellent photocatalytic performance: a promising photocatalysts for water purification. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 97:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.02.016
Emam HE, Ahmed HB (2018) Carboxymethyl cellulose macromolecules as generator of anisotropic nanogold for catalytic performance. Int J Biol Macromol 111:999–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.111
Emam HE, Ahmed HB (2019) Comparative study between homo-metallic and hetero-metallic nanostructures based agar in catalytic degradation of dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 138:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.098
Emam HE, Zahran MK, Ahmed HB (2017) Generation of biocompatible nanogold using H2O2-starch and their catalytic/antimicrobial activities. Eur Polym J 90:354–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.03.034
Emam HE, Ahmed HB, Gomaa E, Helal MH, Abdelhameed RM (2019) Doping of silver vanadate and silver tungstate nanoparticles for enhancement the photocatalytic activity of MIL-125-NH2 in dye degradation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 383:111986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111986
Emam HE, Ahmed HB, Gomaa E, Helal MH, Abdelhameed RM (2020a) Recyclable photocatalyst composites based on Ag3VO4 and Ag2WO4@MOF@cotton for effective discoloration of dye in visible light. Cellulose 27:7139–7155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03282-8
Emam HE, Saad NM, Abdallah AEM, Ahmed HB (2020b) Acacia gum versus pectin in fabrication of catalytically active palladium nanoparticles for dye discoloration. Int J Biol Macromol 156:829–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.018
Farooq A et al (2020) Cellulose from sources to nanocellulose and an overview of synthesis and properties of nanocellulose/zinc oxide nanocomposite materials. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1050–1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.163
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
Grishkewich N, Mohammed N, Tang JT, Tam KC (2017) Recent advances in the application of cellulose nanocrystals. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 29:32–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2017.01.005
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110:3479–3500. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900339w
Lan Z-A, Zhang G, Wang X (2016) A facile synthesis of Br-modified g-C3N4 semiconductors for photoredox water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 192:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.062
Li XB, Xiong J, Gao XM, Huang JT, Feng ZJ, Chen Z, Zhu YF (2019) Recent advances in 3D g-C3N4 composite photocatalysts for photocatalytic water splitting, degradation of pollutants and CO2 reduction. J Alloys Compd 802:196–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.06.185
Liu JN, Jia QH, Long JL, Wang XX, Gao ZW, Gu Q (2018) Amorphous NiO as co-catalyst for enhanced visible-light-driven hydrogen generation over g-C3N4 photocatalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 222:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.073
Mao ZP, Xie RY, Fu DW, Zhang LP, Xu H, Zhong Y, Sui XF (2017) PAN supported Ag–AgBr@Bi20TiO32 electrospun fiber mats with efficient visible light photocatalytic activity and antibacterial capability. Separ Purific Technol 176:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.12.027
Niu P, Zhang LL, Liu G, Cheng HM (2012) Graphene-like carbon nitride nanosheets for improved photocatalytic activities. Adv Func Mater 22:4763–4770. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201200922
Park NM, Choi S, Oh JE, Hwang DY (2019) Facile extraction of cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr Polym 223:5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115114
Peng X, Wang SJ, Zhang XM, Shu Y, Su SP, Zhu J (2017) Ag@AgCl embedded on cellulose film: a stable, highly efficient and easily recyclable photocatalyst. Cellulose 24:4683–4689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1438-z
Qi H et al (2019) Bio-templated 3D porous graphitic carbon nitride hybrid aerogel with enhanced charge carrier separation for efficient removal of hazardous organic pollutants. J Colloid Interface Sci 556:366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.08.072
Stackelberg PE, Gibs J, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Zaugg SD, Lippincott RL (2007) Efficiency of conventional drinking-water-treatment processes in removal of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. Sci Total Environ 377:255–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.095
Su XP, Liao Q, Liu L, Meng RJ, Qian ZQ, Gao HY, Yao JM (2017) Cu2O nanoparticle-functionalized cellulose-based aerogel as high-performance visible-light photocatalyst. Cellulose 24:1017–1029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1154-0
Tan L, Yu C, Wang M, Zhang S, Sun J, Dong S, Sun J (2019) Synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis of 3D g-C3N4-agar hybrid aerogels. Appl Surf Sci 467–468:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.067
Tian C, Zhao H, Mei J, Yang S (2019a) Cost-efficient graphitic carbon nitride as an effective photocatalyst for antibiotic degradation: an insight into the effects of different precursors and coexisting ions, and photocatalytic mechanism. Chem Asian J 14:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201801416
Tian C, Zhao H, Mei J, Yang SJ (2019b) Cost-efficient graphitic carbon nitride as an effective photocatalyst for antibiotic degradation: an insight into the effects of different precursors and coexisting ions, and photocatalytic mechanism. Chem Asian J 14:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201801416
Wang YJ et al (2018) Controlled fabrication of TiO2/C3N4 core-shell nanowire arrays: a visible-light-responsive and environmental-friendly electrode for photoelectrocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A. J Mater Sci 53:11015–11026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2368-3
Wang FD, Li J, Su Y, Li Q, Gao BY, Yue QY, Zhou WZ (2019) Adsorption and recycling of Cd(II) from wastewater using straw cellulose hydrogel beads. J Ind Eng Chem 80:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.08.015
Wang Y, Ding K, Xu R, Yu D, Wang W, Gao P, Liu B (2020a) Fabrication of BiVO4/BiPO4/GO composite photocatalytic material for the visible light-driven degradation. J Clean Prod 247:119108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119108
Wang Y et al (2020b) Synthesizing Co3O4-BiVO4/g-C3N4 heterojunction composites for superior photocatalytic redox activity. Separ Purific Technol 239:116562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116562
Weingarten AS et al (2014) Self-assembling hydrogel scaffolds for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nat Chem 6:964–970. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2075
Xia PF, Zhu BC, Yu JG, Cao SW, Jaroniec M (2017) Ultra-thin nanosheet assemblies of graphitic carbon nitride for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction. J Mater Chem A 5:3230–3238. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta08310b
Xu J, Wang ZP, Zhu YF (2017) Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic disinfection performance and organic pollutant degradation activity of porous g-C3N4 nanosheets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:27727–27735. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07657
Xu C, Wang J, Gao B, Dou M, Chen R (2019) Synergistic adsorption and visible-light catalytic degradation of RhB from recyclable 3D mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride/reduced graphene oxide aerogels. J Mater Sci 54:8892–8906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03531-7
Yan SC, Li ZS, Zou ZG (2009) Photodegradation performance of g-C3N4 fabricated by directly heating melamine. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 25:10397–10401. https://doi.org/10.1021/la900923z
Yang R, Zhong S, Zhang L, Liu B (2020) PW12/CN@Bi2WO6 composite photocatalyst prepared based on organic-inorganic hybrid system for removing pollutants in water. Separ Purific Technol 235:116270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116270
Yao CK, Yuan AL, Wang ZS, Lei H, Zhang L, Guo LM, Dong XP (2019) Amphiphilic two-dimensional graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for visible-light-driven phase-boundary photocatalysis. J Mater Chem A 7:13071–13079. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta03253c
Zhang JL, Ma Z (2018) Porous g-C3N4 with enhanced adsorption and visible-light photocatalytic performance for removing aqueous dyes and tetracycline hydrochloride. Chin J Chem Eng 26:753–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.10.010
Zhang G, Zhang J, Zhang M, Wang X (2012) Polycondensation of thiourea into carbon nitride semiconductors as visible light photocatalysts. J Mater Chem 22:8083–8091. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm00097k
Zhang J-Y, Mei J-Y, Yi S-S, Guan X-X (2019) Constructing of Z-scheme 3D g-C3N4-ZnO@graphene aerogel heterojunctions for high-efficient adsorption and photodegradation of organic pollutants. Appl Surf Sci 492:808–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.261
Zhang J-Y, Zhang S-H, Li J, Zheng X-C, Guan X-X (2020) Constructing of 3D graphene aerogel-g-C3N4 metal-free heterojunctions with superior purification efficiency for organic dyes. J Mol Liq 310:113242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113242
Zhang L, Rao L, Wang P, Shi Z, Wang P (2021) Superhydrophobic self-floating TiO2-silicone composite aerogels and their air–liquid–solid triphase photocatalytic system. Appl Surf Sci 536:147726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147726
Zhao H et al (2018) A photochemical synthesis route to typical transition metal sulfides as highly efficient cocatalyst for hydrogen evolution: from the case of NiS/g-C3N4. Appl Catal B Environ 225:284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.083
Zhao H, Sun S, Wu Y, Jiang P, Dong Y, Xu ZJ (2017a) Ternary graphitic carbon nitride/red phosphorus/molybdenum disulfide heterostructure: an efficient and low cost photocatalyst for visible-light-driven H2 evolution from water. Carbon 119:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.03.100
Zhao H, Sun SN, Jiang PP, Xu ZJ (2017b) Graphitic C3N4 modified by Ni2P cocatalyst: an efficient, robust and low cost photocatalyst for visible-light-riven H2 evolution from water. Chem Eng J 315: 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.034
Zhao H, Wang JW, Dong YM, Jiang PP (2017c) Noble-metal-free iron phosphide cocatalyst loaded graphitic carbon nitride as an efficient and robust photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution under visible light irradiation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:8053–8060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01665
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Liu A, Wei Z, Liu S (2017d) Construction of three-dimensional hemin-functionalized graphene hydrogel with high mechanical stability and adsorption capacity for enhancing photodegradation of methylene blue. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:4006–4014. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b10959
Zhao SW, Zheng M, Sun HL, Li SJ, Pan QJ, Guo YR (2020) Construction of heterostructured g-C3N4/ZnO/cellulose and its antibacterial activity: experimental and theoretical investigations. Dalton Trans 49:3723–3734. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9dt03757h
Zheng D, Pang C, Liu Y, Wang X (2015) Shell-engineering of hollow g-C3N4 nanospheres via copolymerization for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem Commun 51:9706–9709. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc03143e
Zhiming P, Yun Z, Fangsong G, Pingping N, Xinchen W (2017) Decorating CoP and Pt nanoparticles on graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets to promote overall water splitting by conjugated polymers. Chemsuschem 10:87–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201600850
Zhou PW et al (2020) A facile method for fabricating color adjustable multifunctional cotton fabrics with solid solution BiOBrxI1−x nanosheets. Cellulose 27:3517–3530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03007-x
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC1801502) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21872025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Zhou, P., Zhang, L. et al. A recyclable 3D g-C3N4 based nanocellulose aerogel composite for photodegradation of organic pollutants. Cellulose 28, 3531–3547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03748-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03748-3