Abstract
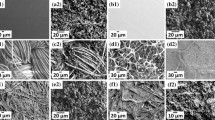
Superhydrophobic surfaces have attracted great attention due to their interesting properties. The ever-increasing environmental concern accelerated the development of bio-based superhydrophobic coating materials. As a high-yield agricultural waste, bagasse is cheap, ready available, renewable and biodegradable. It would be an ideal raw material for the preparation of bio-based superhydrophobic coatings to further improve its application value. Although the hydrophobization of bagasse have been reported, the according works mainly focus on the reaction mechanism and/or their oil-absorption properties. As far as we know, the design of bagasse-based superhydrophobic coatings has been uncovered. Herein, mechanically pretreated bagasse was esterified with stearoyl chloride. Spray-coating the suspension of as-synthesized bagasse esters onto various substrates (glass slide, aluminum flake and filter paper), superhydrophobic surfaces were generated. SEM images in combination with the high-resolution C1s XPS deconvolution spectra implied that nano-structured bagasse esters were deposited on the synthesized micro-scaled esters, which was necessary for their superhydrophobicity. The as-prepared superhydrophobic surfaces exhibited good anti-fouling, oil absorption performance and high time/temperature/pH stability. This research would provide a novel perspective for the design of other bio-based superhydrophobic coatings.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelwahab NA, Shukry N, El-kalyoubi SF (2017) Preparation and characterization of polymer coated partially esterified sugarcane bagasse for separation of oil from seawater. Environ Technol 38:1905–1914. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1240243
Aloui H, Khwaldia K (2017) Effect of coating weight and nanoclay content on functional and physical properties of bionanocomposite-coated paper. Cellulose 24:4493–4507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1436-1
Antunes FAF, Santos JC, Chandel AK, Carrier DJ, Peres GFD, Milessi TSS, da Silva SS (2019) Repeated batches as a feasible industrial process for hemicellulosic ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse by using immobilized yeast cells. Cellulose 26:3787–3800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02341-z
Baidya A, Ganayee MA, Ravindran SJ, Tam KC, Das SK, Ras RHA, Pradeep T (2017) Organic sovent-free fabrication of durable and multifuctional superhydrophobic paper from waterborne fluorinated cellulose nanofiber building blocks. ACS Nano 11:11091–11099. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b05170
Cai Y, Chen D, Li N, Xu Q, Li H, He J, Lu J (2019) Superhydrophobic metal-organic framework membrane with self-repairing for high-efficiency oil/water emulsion separation. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:2709–2717. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05793
Chen M, Chen C, Liu C, Sun R (2013) Homogeneous modification of sugarcane bagasse with maleic anhydride in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride without any catalysts. Ind Crop Prod 46:380–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.02.023
Chen M, Zhang X, Zhang A, Liu C, Sun R (2016) Direct preparation of green and renewable aerogel materials from crude bagasse. Cellulose 23:1325–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0814-9
Cheng QY, An XP, Li YD, Huang CL, Zeng JB (2017) Sustainable and biodegradable superhydrophobic coating from epoxidized soybean oil and ZnO nanoparticles on cellulosic substrates for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 5:11440–11450. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02549
Cheng QY, Zhao XL, Weng YX, Li YD, Zeng JB (2019) Fully sustainable, nanoparticle-free, fluorine-free, and robust superhydrophobic cotton fabric fabricated via an eco-friendly method for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:15696–15705. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b03852
Ferreira BCS, Teodoro FS, Mageste AB, Gil LF, de Freitas RP, Gurgel LVA (2015) Application of a new carboxylate-functionalized sugarcane bagasse for adsorptive removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Ind Crop Prod 65:521–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.10.020
Gan T, Zhang Y, Su Y, Hu H, Huang A, Huang Z, Chen D, Yang M, Wu J (2017) Esterification of bagasse cellulose with metal salts as efficient catalyst in mechanical activation-assisted solid phase reaction system. Cellulose 24:5371–5387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1524-2
Gao H, Du J, Liao Y (2019) Removal of chromium (VI) and orange II from aqueous solution using magnetic polyetherimide/sugarcane bagasse. Cellulose 26:3285–3297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02301-7
Halysh V, Sevastyanova O, Pikus S, Dobele G, Pasalskiy B, Gun’ko VM, Kartel M (2020) Sugarcane bagasse and straw as low-cost lignocellulosic sorbents for the removal of dyes and metal ions from water. Cellulose 27:8181–8197
Huang J, Wang S, Lyu S, Fu F (2018) Preparation of a robust cellulose nanocrystal superhydrophobic coating for self-cleaning and oil-water separation only by spraying. Ind Crop Prod 122:438–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.06.015
Khanjani P, King AWT, Partl GJ, Johansson LS, Kostiainen MA, Ras RHA (2018) Superhydrophobic paper from nanostuctured fluorinated cellulose esters. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:11280–11288. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b19310
Li W, Sun N, Stoner B, Jiang X, Lu X, Rogers RD (2011) Rapid dissolution of lignocelulosic biomass in ionic liquids using temperatures above the glass transition of lignin. Green Chem 13:2038–2047. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1gc15522a
Liu CF, Sun RC, Qin MH, Zhang AP, Ren JL, Xu F, Ye J, Wu SB (2007) Chemical modification of ultrasound-pretreated sugarcane bagasse with maleic anhydride. Ind Crop Prod 26:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2007.03.007
Liu H, Huang J, Chen Z, Chen G, Zhang KQ, Al-Deyab SS, Lai Y (2017) Robust translucent superhydrophobic PDMS/PMMA film by facile one-step spray for self-cleaning and efficient emulsion separation. Chem Eng J 330:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.114
Lu Y, Song J, Liu X, Xu W, Xing Y, Wei Z (2013) Preparation of superoleophobic and superhydrophobic titanium surfaces via an environmentally friendly electrochemical etching method. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 1:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc3000527
Moze M, Senegacnik M, Gregorčič P, Hocevar M, Zupancic M, Golobič I (2020) Laser-engineered microcavity surfaces with a nanoscale superhydrophobic coating for extreme boiling performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:24419–24431. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c01594
Niu X, Liu Y, Fang G, Huang C, Rojas OJ, Pan H (2018) Highly transparent, strong, and flexible films with modified cellulose nanofiber bearing UV shielding property. Biomacromol 19:4565–4575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.8b01252
Pereira PHF, Voorwald HJC, Cioffi MOH, Da Silva MLCP, Rego AMB, Ferraria AM, De Pinho MN (2014) Sugarcane bagasse cellulose fibres and their hydrous nibium phosphate composites: synthesis and characterization by XPS, XRD and SEM. Cellulose 21:641–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0113-2
Qiu S, Li Y, Li G, Zhang Z, Li Y, Wu T (2019) Robust superhydrophobic sepiolite-coated polyurethane sponge for highly efficient and recyclable oil absorption. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:5560–5567. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00098
Razavi SMR, Oh J, Sett S, Feng L, Yan X, Hoque MJ, Liu A, Haasch RT, Masoomi M, Bagheri R, Miljkovic N (2017) Superhydrophobic surfaces made from naturally derived hydrophobic materials. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 5:11362–11370. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02424
Razavi SMR, Oh J, Haasch RT, Kim K, Masoomi M, Bagheri R, Slauch JM, Miljkovic N (2019) Environment-friendly antibiofouling superhydrophobic coatings. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:14509–14520. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02025
Roosendaal SJ, Giebels IAME, Vredenberg AM, Habraken FHPM (1998) Determination of photoelectron attenuation lengths in thin oxide films on iron surfaces using quantitative XPS and elastic recoil detection. Surf Interface Anal 26:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9918(199809)26:103.0.CO;2-B
Said AEAA, Ludwick AG, Aglan HA (2009) Usefulness of raw bagasse for oil absorption: a comparison of raw and acylated bagasse and their components. Bioresource Technol 100:2219–2222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.09.060
Seta FT, An X, Liu L, Zhang H, Yang J, Zhang W, Nie S, Yao S, Gao H, Xu Q, Bu Y, Liu H (2020) Preparation and characterization of high yield cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) derived from ball mill pretreatment and maleic acid hydrolysis. Carbohyd Polym 234:115942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115942
Subramanian S, Pande G, Weireld GD, Giraudon JM, Lamonier JF, Batra VS (2013) Sugarcane bagasse fly ash as an attractive agro-industry source for VOC removal on porous carbon. Ind Crop Prod 49:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.014
Sun JX, Sun XF, Sun RC, Fowler P, Baird MS (2003) Inhomogeneities in the chemical structure of sugarcane bagasse lignin. J Agric Food Chem 51:6719–6725. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf034633j
Sun XF, Sun RC, Sun JX (2004) Acetylation of sugarcane bagasse using NBS as a catalyst under mild reaction conditions for the production of oil sorption-active materials. Bioresource Technol 95:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.02.025
Thai QB, Nguyen ST, Ho DK, Tran TD, Huynh DM, Do NHN, Luu TP, Le PK, Le DK, Phan-Thien N, Duong HM (2020) Cellulose-based aerogels from sugarcane bagasse for oil spill-cleaning and heat insulation applications. Carbohyd Polym 228:115365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115365
Wang J, Geng G, Wang A, Liu X, Du J, Zou Z, Zhang S, Han F (2015) Double biomimetic fabrication of robustly superhydrophobic cotton fiber and its application in oil spill cleanup. Ind Crop Prod 77:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.08.044
Wang S, Sha J, Wang W, Qin C, Li W, Qin C (2018) Superhydrophobic surfaces generated by one-pot spray-coating of chitosan-based nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 195:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.068
Wang Y, Zhang D, Deng J, Zhou F, Duan Z, Su Q, Pang S (2019) Mosquito’s compound eyes as inspiration for fabrication of conductive superhydrophobic nanocarbon materials from waste wheat straw. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:3883–3894. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04906
Wei J, Zhang G, Dong J, Wang H, Guo Y, Zhuo X, Li C, Liang H, Gu S, Li C, Dong X, Li Y (2018) Facile, scalable spray-coating of stable emulsion for transparent self-cleaning surface of cellulose-based materials. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6:11335–11344. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00962
Xiang T, Han Y, Guo Z, Wang R, Zheng S, Li S, Li C, Dai X (2018) Fabrication of inherent anticorrosion superhydrophobic surfaces on metals. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 6:5598–5606. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00639
Yang Y, Deng Y, Tong Z, Wang C (2014) Renewable lignin-based xerogels with self-cleaning properties and superhydrophobicity. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 2:1729–1733. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500250b
Yang S, He WT, Fu Y, Zhang Y, Yuan TQ, Sun RC (2017) A bio-based coating onto the surface Populus fiber for oil spillage cleanup applications. Ind Crop Prod 98:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.01.031
Zang J, Yu S, Zhu G, Zhou X (2019) Fabrication of superhydrophobic surface on aluminum alloy 6061 by a facile and effective anodic oxidation method. Surf Coat Tech 380:125078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.125078
Zhang S, Li W, Wang W, Wang S, Qin C (2019) Reactive superhydrophobic paper from one-step spray-coating of cellulose-based derivative. Appl Surf Sci 497:143816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143816
Zhao Y, Liu Y, Xu Q, Barahman M, Lyons AM (2015) Catalytic, self-cleaning surface with stable superhydrophobic properties: printed polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) arrays embedded with TiO2 nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:2632–2640. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5076315
Zhou S, Liu P, Wang M, Zhao H, Yang J, Xu F (2016) Sustainable, reusable and superhydrophobic aerogels from microfibrillated cellulose for highly effective oil/water separation. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 4:6409–6416. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01075
Zulfiqar U, Thomas AG, Yearsley K, Bolton LW, Matthews A, Lewis DJ (2019) Renewable adsorbent for the separation of surfactant-stabilized oil in water emulsions based on nanostructured sawdust. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 7:18935–18942. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04294
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2018GXNSFBA138027); Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University (XGZ170232); the Dean Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp and Papermaking and Pollution Control (ZR201804-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, C., Wang, W., Li, W. et al. Developing bagasse towards superhydrophobic coatings. Cellulose 28, 3617–3630 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03743-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03743-8