Abstract
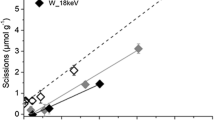
In this study, we investigate the chemical, physical and optical properties of cellulose paper irradiated by an electron beam for disinfection. Cellulose chain scission and oxidation induced by radiation increased considerably at 25 kGy irradiation, whereas folding endurance, morphology, and crystallinity did not undergo significant changes. The cellulose chain scission rate of paper irradiated under air-dried and wet conditions showed no difference; however, cellulose oxidation increased to a higher degree in paper irradiated under wet conditions than under air-dried conditions. Electron beam irradiation did not significantly affect changes in paper color, which is associated with oxidation. However, when irradiated papers were aged, the color difference increased according to the irradiation dose, as the oxidized functional groups of cellulose can act as a trigger for color change. A linear relationship between the cellulose chain scission rate and irradiation dose was found; thus, the cellulose chain scission rate can be predicted for a specific dose. The degree of polymerization was calculated from the predicted cellulose chain scission rate using the Ekenstam equation. According to the prediction, the degree of polymerization decreased to 74% at a dose of 5 kGy, a suitable dose for paper disinfection. In the low-dose range, electron beam irradiation did not adversely affect the physical properties of paper, but significant changes occurred in both the chemical and optical properties of paper. Thus, electron beam irradiation may be of use in disinfecting severely degraded paper due to biological factors; however, the irradiation process diminishes paper permanence.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo M, Brizzi M, Magaudda G, Martinelli G, Plossi-Zappalà RF, Savagnone F (2001) Gamma radiation treatment of paper in different environmental conditions: chemical, physical and microbiological analysis. Restaur 22:107–131. https://doi.org/10.1515/REST.2001.107
Adamo AM, Giovannotti M, Magaudda G, Plossizappala M, Rocchetti F, Rossi G (1998) Effect of gamma rays on pure cellulose paper as a model for the study of a treatment of “biological recovery” of biodeteriorated books. Restaur 19:41–59. https://doi.org/10.1515/rest.1998.19.1.41
Adamo M, Magaudda G, Tata A (2004) Radiation technology for cultural heritage restoration. Restaur 25:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1515/REST.2004.159
Ahn K, Zaccaron S, Zwirchmayr NS, Hettegger H, Hofinger A, Bacher M, Henniges U, Hosoya T, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2019) Yellowing and brightness reversion of celluloses: CO or COOH, who is the culprit? Cellulose 26:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2200-x
Area MC, Calvo AM, Felissia FE, Docters A, Miranda MV (2014) Influence of dose and dose rate on the physical properties of commercial papers commonly used in libraries and archives. RadiatPhysChem 96:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.10.004
Belyakova LA (1960) Gamma-irradiation as a means of disinfecting books against spores of mould fungi. Microbiology 29:762–765
Bouchard J, Méthot M, Jordan B (2006) The effects of ionizing radiation on the cellulose of woodfree paper. Cellulose 13:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-005-9033-0
Bratu E, Moise IV, Cutrubinis M, Negut DC, Virgolici M (2009) Archives decontamination by gamma irradiation. Nukleonika 54:77–84
Calvini P, Santucci L (1978–1979) Alcuni dati sugli effetti dell’irradiazione gamma sulla carta. Bollettino Dell’instituto Centrale per la Patologia del Libro 35:3–10
Chmielewska-Śmietanko D, Gryczka U, Migdal W, Kopeć K (2018) Electron beam for preservation of biodeteriorated cultural heritage paper-based objects. RadiatPhysChem 143:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.07.008
Choi JI, Chung YJ, Kang DI, Lee KS, Lee JW (2012) Effect of radiation on disinfection and mechanical properties of Korean traditional paper, Hanji. RadiatPhysChem 81:1051–1054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2011.11.019
Clough RL (2001) High-energy radiation and polymers: a review of commercial processes and emerging applications. NuclInstrum Method Phys Res B 185:8–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(01)00966-1
D’Almeida MLO, Barbosa PdSM, Fernando M, Boaratti G, Borrely SI (2009) Radiation effects on the integrity of paper. RadiatPhysChem 78:489–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2009.03.032
Drábková K, Ďurovič M, Kučerová I (2018) Influence of gamma radiation on properties of paper and textile fibres during disinfection. RadiatPhysChem 152:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.07.023
Driscoll M, Stipanovic A, Winter W, Cheng K, Manning M, Spiese J, Galloway RA, Cleland MR (2009) Electron beam irradiation of cellulose. RadiatPhysChem 78:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2009.03.080
Emsley AM, Stevens GC (1994) Kinetics and mechanisms of the low-temperature degradation of cellulose. Cellulose 1:26–56
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Hagg WR, Yao CCD (1992) Rate constants for reaction of hydroxyl radicals with several drinking water contaminants. Environ SciTechnol 26:1005–1013. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00029a021
Henniges U, Hasani M, Potthast A, Westman G, Rosenau T (2013) Electron beam irradiation of cellulosic materials-opportunities and limitations. Materials 6:1584–1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6051584
Henniges U, Okubayashi S, Rosenau T, Potthast A (2012) Irradiation of cellulosic pulps: understanding its impact on cellulose oxidation. Biomacromolecules 13:4171–4178. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm3014457
Iller E, Kukielka A, Stupinska H, Mikolajczyk W (2002) Electron-beam stimulation of the reactivity of cellulose pulps for production of derivatives. RadiatPhysChem 63:253–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(01)00646-6
Imamura R, Ueno T, Murakami K (1972) Depolymerization of cellulose by electron beam irradiation. Bull InstChem Rese Kyoto Univ 50:51–63
Jeong M-J, Kang KY, Bacher M, Kim HJ, Jo BM, Potthast A (2014) Deterioration of ancient cellulose paper, Hanji: evaluation of paper permanence. Cellulose 21:4621–4632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0455-4
Jeong M-J, Lee S, Yang BS, Potthast A, Kang KY (2019) Cellulose degradation by calcium thiocyanate. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091494
Ju X, Bowden M, Brown EE, Zhang X (2015) An improved X-ray diffraction method for cellulose crystallinity measurement. CarbohydrPolym 123:476–481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091494
Kang DI (2009) The stability appraisement on cultural property material with the replacing fumigation gas of methyl bromide. J ConservSci 25:283–291
Khan F, Ahmad SR, Kronfli E (2006) γ-Radiation induced changes in the physical and chemical properties of lignocellulose. Biomacromolecules 7:2303–2309. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060168y
Kim JK, Song BS, Kim JH, Park JH, Byun EB, Lee JW (2013) Sterilization characteristics on ionizing irradiation and its industrial application. J Korean Musculoskelet Tissue Transplant Soc 13:49–57
Morin FG, Jordan BD, Marchessault RH (2004) High-energy radiation-induced changes in the crystal morphology of cellulose. Macromolecules 37:2668–2670. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma030528z
Phillips GO, Arthur JC Jr (1985) Effects of high-energy radiation on physical and chemical properties of purified fibrous cellulose. In: Nevell TP, Zeronian SH (eds) Cellulose chemistry and its Applications. Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, pp 290–311
Röhrling J, Potthast A, Rosenau T, Lange T, Borgards A, Sixta H, Kosma P (2002) A novel method for the determination of carbonyl groups in cellulosics by fluorescence labeling. 2. Valid ApplBiomacromol 3:969–975. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm020030p
Sequeira SO, Cabrita EJ, Macedo MF (2014) Fungal biodeterioration of paper: how are paper and book conservators dealing with it? An international survey. Restaur 35:181–199. https://doi.org/10.1515/rest-2014-0005
Sharma G, Wu W, Dalal EN (2005) The CIEDE2000 color-difference formula: implementation notes, supplementary test data, and mathematical observations. Color Res Appl 30:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.20070
Yang G, Zhang Y, Wei M, Shao H, Hu X (2010) Influence of γ-ray radiation on the structure and properties of paper grade bamboo pulp. CarbohydrPolym 81:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.003
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by research funds for newly appointed professors of Jeonbuk National University in 2017; and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A1B03933947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Formal analysis: YH, MJJ, HJP and AP; Investigation: YH and MJJ; Data curation: YH and MJJ; Writing—original draft: YH; Writing—review and editing: MJJ; Supervision: MJJ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, Y., Park, HJ., Potthast, A. et al. Evaluation of cellulose paper degradation irradiated by an electron beam for conservation treatment. Cellulose 28, 1071–1083 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03604-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03604-w