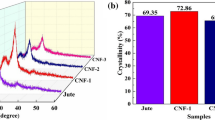
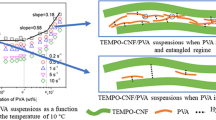
Abstract
The effects of pH, inorganic ion concentration, and dephosphorylation by hydrolysis on the transparency and viscosity of phosphorylated cellulose nanofibers (P-CNF) with different phosphate group contents and degrees of fibrillation were studied in order to boost its use as a rheology modifier. From the neutralization titration curve of P-CNF dispersions, acidity values of pKa1 = 3.1 and pKa2 = 8.3 were determined. These values were almost constant regardless of the amount of phosphate groups. The P-CNF dispersion maintained high transparency and viscosity in the pH range of 3–11 owing to a wide range of acidity values and the buffer capacity of the phosphate group. The viscosity of P-CNF dispersions was influenced by the amount of phosphate groups and the degree of fibrillation, which also affected the viscosity behavior of the dispersion when inorganic salts were added. The long-term storage stability of phosphate groups introduced on P-CNF was also examined by accelerated (heating) test. The hydrolysis reaction of P-CNFs took several days to reduce the phosphorous content to one-tenth of the initial content at 80 °C. Kinetic analysis showed that dephosphorylation proceeded as a first order reaction, as found for other phosphorylated esters. As dephosphorylation proceeded, the transparency and viscosity of the P-CNF dispersion decreased because P-CNFs tended to aggregate through hydrogen bonding, which also seemed to suppress dephosphorylation. Furthermore, the activation energy of deesterification obtained was 130.0 kJ/mol. The decrease in the ratio of phosphate groups was highest when the degree of anion neutralization of the phosphate groups was 50%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bunton CA, Llewellyn DR, Oldham KG, Vernon CA (1958a) The reactions of organic phosphates. Part I. The hydrolysis of methyl dihydrogen phosphate. J Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9580003588
Bunton CA, Llewellyn DR, Oldham KG, Vernon CA (1958b) The reactions of organic phosphates. Part II. The hydrolysis of α-d-glucose 1-(dihydrogen phosphate). J Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9580003574
Cori CF, Colowick SP, Cori GT (1937) The isolation and synthesis of glucose-1-phosphoric acid. J Biol Chem 121:465–477
Dong S, Snyder JF, Williams KS, Andzelm JW (2013) Cation-induced hydrogels of cellulose nanofibrils with tunable moduli. Biomacromolecules 14:3338–3345. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400993f
Fall AB, Lindström SB, Sundman O, Ödberg L, Wågberg L (2011) Colloidal stability of aqueous nanofibrillated cellulose dispersions. Langmuir 27:11332–11338. https://doi.org/10.1021/la201947x
Fall AB, Burman A, Wågberg L (2014) Cellulosic nanofibrils from eucalyptus, acacia and pine fibers. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29:176–184. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2014-29-01-p176-184
Fujisawa S, Okita Y, Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Isogai A (2011) Preparation and characterization of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril films with free carboxyl groups. Carbohyd Polym 84:579–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.029
Fukuzumi H, Tanaka R, Saito T, Isogai A (2014) Dispersion stability and aggregation behavior of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils in water as a function of salt addition. Cellulose 21:1553–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0180-z
Ghanadpour M, Carosio F, Larsson PT, Wågberg L (2015) Phosphorylated cellulose nanofibrils: a renewable nanomaterial for the preparation of intrinsically flame-retardant materials. Biomacromol 16:3399–3410. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01117
Goi Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2018) Mechanical properties and preparing processes of the TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers hydrogels. J Fibre Sci Technol 74:24–29. https://doi.org/10.2115/fiberst.2018-0004
Ho T, Zimmermann T, Hauert R, Caseri W (2011) Preparation and characterization of cationic nanofibrillated cellulose from etherification and high-shear disintegration processes. Cellulose 18:1391–1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9591-2
Iwamoto S, Endo T (2015) 3 nm Thick lignocellulose nanofibers obtained from esterified wood with maleic anhydride. ACS Macro Lett 4:80–83. https://doi.org/10.1021/mz500787p
Iwamoto S, Kai W, Isogai A, Iwata T (2009) Elastic modulus of single cellulose microfibrils from tunicate measured by atomic force microscopy. Biomacromolecules 10:2571–2576. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm900520n
Iwamoto S, Saito Y, Yagishita T, Kumagai A, Endo T (2019) Role of moisture in esterification of wood and stability study of ultrathin lignocellulose nanofibers. Cellulose 26:4721–4729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02408-x
Koga H, Tokunga E, Hidaka M, Umemura Y, Saito T, Isogai A, Kitaoka T (2010) Topochemical synthesis and catalysis of metal nanoparticles exposed on crystalline cellulose nanofibers. Chem Commun 46:8567–8569. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02754E
Kubo J, Nakatsubo T, Ito K, Tajima H (2017) Cellulose xanthate nanofibers. WO2017111103A1. 2017-06-29
Kurosaki T, Furugaki H (1990) Hydrolysis of monododecyl phosphate. J Jpn Oil Chem Soc 39:184–190. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos1956.39.3_184
Lin L, Hori M, Maruta A (2018) Sulfuric acid esterification modified cellulose nanofibers and method for producing cellulose nanofibers. WO2018131721A1. 2018-07-19
Naderi A, Lindström T (2014) Carboxymethylated nanofibrillated cellulose: effect of monovalent electrolytes on the rheological properties. Cellulose 21:3507–3514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.026
Naderi A, Lindström T, Sundström J (2014) Carboxymethylated nanofibrillated cellulose: rheological studies. Cellulose 21:1561–1571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0192-8
Naderi A, Lindström T, Weise CF, Flodberg G, Sundström J, Junel K, Erlandsson J, Runebjörk A (2016) Phosphorylated nanofibrillated cellulose: production and properties. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 31:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0394-0
Naderi A, Koschella A, Heinze T, Shih KC, Nieh MP, Pfeifer A, Chang CC, Erlandsson J (2017a) Sulfoethylated nanofibrillated cellulose: production and properties. Carbohyd Polym 169:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1190-4
Naderi A, Larsson PT, Stevanic JS, Lindström T, Erlandsson J (2017b) Effect of the size of the charged group on the properties of alkoxylated NFCs. Cellulose 24:1307–1317. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2016-31-01-p020-029
Noguchi Y, Homma I, Matsubara Y (2017) Complete nanofibrillation of cellulose prepared by phosphorylation. Cellulose 24:1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1191-3
Qi Z, Saito T, Fan Y, Isogai A (2012) Multifunctional coating films by layer-by-layer deposition of cellulose and chitin nanofibrils. Biomacromol 13:553–558. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm201659b
Saito T, Nishiyama Y, Putaux JL, Vignon M, Isogai A (2006) Homogeneous suspensions of individualized microfibrils from TEMPO-catalyzed oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 7:1687–1691. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060154s
Saito T, Kuramae R, Wohlert J, Berglund LA, Isogai A (2013) An ultrastrong nanofibrillar biomaterial: the strength of single cellulose nanofibrils revealed via sonication-induced fragmentation. Biomacromol 14:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm301674e
Sakurada I, Nukushina Y, Ito T (1962) Experimental determination of the elastic modulus of crystalline regions in oriented polymers. J Polym Sci 57:651–660. https://doi.org/10.1295/koron1944.19.285
Šturcová A, Davies GR, Eichhorn SJ (2005) Elastic modulus and stress-transfer properties of tunicate cellulose whiskers. Biomacromolecules 6:1055–1061. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm049291k
Tsutsumi Y, Koga H, Qi ZD, Saito T, Isogai A (2014) Nanofibrillar chitin aerogels as renewable base catalysts. Biomacromol 15:4314–4319. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm501320b
Wohlert J, Bergenstråhle-Wohlert M, Berglund LA (2012) Deformation of cellulose nanocrystals: entropy, internal energy and temperature dependence. Cellulose 19:1821–1836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9774-5
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Akira Isogai for providing insightful comments and Takuya Isogai for performing atomic force microscopy experiments. We thank Simon Partridge, PhD, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, Y., Homma, I. & Watanabe, T. Properties of phosphorylated cellulose nanofiber dispersions under various conditions. Cellulose 27, 2029–2040 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02922-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02922-y