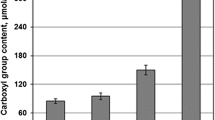
Abstract
Cationized fibers and other kinds of chemically modified fibers impart many advantages in papermaking, but unfeasibly long reaction times are necessary to attain acceptable degrees of substitution, due to the low reactivity of bleached kraft pulps. In this work, different aqueous pretreatments were tested in order to activate cellulose towards a 60 min-long etherification with a quaternary ammonium reagent. Severe decrystallization treatments, namely alkalization with NaOH 20%, NaOH/urea or FeTNa, conducted to the best reactivity results (substitution from 2 to 10%), but the fiber properties were harshly affected. Pretreatments involving H3PO4 at different concentrations were also performed, with distinct results, from unnoticeable effects at 20% to amorphization and excessive depolymerization at 80%. Finally, aqueous ammonium thiocyanate was tested as activator and had little effect on fibers, although the addition of ammonia resulted in high degrees of substitution, while maintaining the pulps’ capability to retain inter-fiber water and cellulose I as the prevalent allomorph.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguado R, Lourenço AF, Ferreira PJ, Moral A, Tijero A (2017) Cationic cellulosic derivatives as flocculants in papermaking. Cellulose 24:3015–3027
Aguado R, Moral A, Tijero A (2018) Cationic fibers from lignocellulosic residues: making waste more appealing for papermaking. J Clean Prod 174:1503–1512
Budtova T, Navard P (2016) Cellulose in NaOH–water based solvents: a review. Cellulose 23:5–55
Eckelt J, Knopf A, Röder T, Weber HK, Sixta H, Wolf BA (2011) Viscosity-molecular weight relationship for cellulose solutions in either NMMO monohydrate or cuen. J Appl Polym Sci 119:670–676
El-Wakil NA, Hassan ML (2008) Structural changes of regenerated cellulose dissolved in FeTNa, NaOH/thiourea, and NMMO systems. J Appl Polym Sci 109:2862–2871
Fischer S (2004) Unconventional dissolution and derivatization of cellulose. Lenzinger Ber 83:71–78
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Ghanadpour M, Carosio F, Larsson PT, Wågberg L (2015) Phosphorylated cellulose nanofibrils: a renewable nanomaterial for the preparation of intrinsically flame-retardant materials. Biomacromolecules 16:3399–3410
Gruber E, Granzow C, Ott T (1996) Neue Wege zur Kationisierung von Cellulose. Das Papier 50:729–734
Harding SE (1997) The intrinsic viscosity of biological macromolecules. Progress in measurement, interpretation and application to structure in dilute solution. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 68:207–262
Hedlund A, Germgård U (2007) Some aspects on the kinetics of etherification in the preparation of CMC. Cellulose 14:161–169
Heinze T (2004) Chemical functionalization of cellulose. In: Dumitriu S (ed) Polysaccharides: structural diversity and functional versatility, 2nd edn. CRC Press, New York, pp 551–5907
Ho TTT, Zimmermann T, Hauert R, Caseri W (2011) Preparation and characterization of cationic nanofibrillated cellulose from etherification and high-shear disintegration processes. Cellulose 18:1391–1406
Hudson SM, Cuculo JA, Wadsworth LC (1983) The solubility of cellulose in liquid ammonia/ammonium thiocyanate solution: the effect of composition and temperature on dissolution and solution properties. Polym Chem 21:651–670
Jin H, Zha C, Gu L (2007) Direct dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea/urea aqueous solution. Carbohydr Res 342:851–858
Littunen K, Snoei de Castro J, Samoylenko A, Xu Q, Quaggin S, Vainio S, Seppälä J (2016) Synthesis of cationized nanofibrillated cellulose and its antimicrobial properties. Eur Polym J 75:116–124
Mahmud-Ali A, Bechtold T (2015) Aqueous thiocyanate–urea solution as a powerful non-alkaline swelling agent for cellulose fibres. Carbohydr Polym 116:124–130
Mayr M, Odabas N, Eckhart R, Henniges U, Bauer W (2017) Cationization of lignocellulose as a means to enhance paper strength properties. BioResources 12:9338–9347
Montplaisir D, Chabot B, Daneault C (2006) Cationisation of thermomechanical pulp fibres. Part 2: influence of strength and retention. Pulp Pap Canada 117:39–42
Nishiyama Y, Langan P, Chanzy H (2002) Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Iβ from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 124:9074–9082
Okano T, Sarco A (1985) Mercerization of cellulose II: alkali-cellulose intermediates and a possible mercerization mechanism. J Appl Polym Sci 30:325–332
Prado HJ, Matulewicz MC (2014) Cationization of polysaccharides: a path to greener derivatives with many industrial applications. Eur Polym J 52:53–75
Sehaqui H, Mautner A, Perez de Larraya U, Pfenninger N, Tingaut P, Zimmermann T (2016) Cationic cellulose nanofibers from waste pulp residues and their nitrate, fluoride, sulphate and phosphate adsorption properties. Carbohydr Polym 135:334–340
Sirviö JA, Anttila AK, Pirttilä AM, Liimatainen H, Kilpeläinen I, Niinimäki J, Hormi O (2014) Cationic wood cellulose films with high strength and bacterial anti-adhesive properties. Cellulose 21:3573–3583
Sood YV, Tyagi R, Tyagi S, Pande PC, Tondon R (2010) Surface charge of different paper making raw materials and its influence on paper properties. J Sci Ind Res 69:300–304
Vinogradov VV, Mizerovskii LN, Akaev OP (2002) Reaction of cellulose with aqueous solutions of orthophosphoric acid. Fibre Chem 34:167–171
Vu Mahn H, Ozturk HB, Bechtold T (2010) Swelling and dissolution mechanism of lyocell fiber in aqueous alkaline solution containing ferric tartaric acid complex. Cellulose 17:521–532
Wan Daud WR, Haafiz MKM, Seeni A (2011) Cellulose phosphate from oil palm biomass as potential biomaterials. BioResources 6:1719–1740
Wei S, Kumar V, Banker GS (1996) Phosphoric acid mediated depolymerization and decrystallization of cellulose: preparation of low crystallinity cellulose a new pharmaceutical excipient. Int J Pharm 142:175–181
Zhang J, Zhang J, Lin L, Chen T, Zhang J, Liu S, Li Z, Ouyang P (2009) Dissolution of microcrystalline cellulose in phosphoric acid—molecular changes and kinetics. Molecules 14:5027–5041
Acknowledgments
Roberto Aguado is thankful to Asociación Universitaria Iberoamericana de Posgrado for the grant to fund an internship in Coimbra. Ana F. Lourenço acknowledges Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia for the Ph.D. Grant SFRH/BDE/108095/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguado, R., Lourenço, A.F., Ferreira, P.J.T. et al. The relevance of the pretreatment on the chemical modification of cellulosic fibers. Cellulose 26, 5925–5936 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02517-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02517-7