Abstract
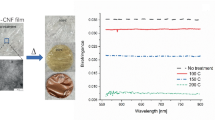
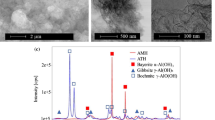
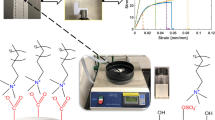
Transparent films of cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) with high moduli and low thermal expansion coefficients have attracted significant attention for use as packaging films or as substrates for flexible electronics. In the present study, the thermal and electrical properties of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl radical-oxidized CNF (T-CNF) films with quaternary alkyl ammonium (QAs) carboxylates were characterized. As the alkyl chain length of the QAs was increased, the thermal decomposition temperature and thermal conductivity of the T-CNF films decreased. The surface resistivities of T-CNF films with tetrapropylammonium and tetrabutylammonium carboxylates were increased up to 1.2 × 109 and 1.5 × 1010 Ω sq−1, respectively. These results indicate that the mobility of the QAs was increased with an increase in their alkyl chain length. The distances between the T-CNFs inside the films, evaluated using small-angle X-ray scattering, increased as the alkyl chain length of the QAs was increased. Solid-state 13C cross-polarization/magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance analyses of the T-CNF films showed that the strength of the ionic bonds between the carboxylates and the QAs decreased with increasing QA alkyl chain lengths. The relaxation times of the carbons of the methyl and methylene groups of the QAs increased as the alkyl chain length of the QAs was increased. This study shows that the thermal, electrical, and structural properties of the T-CNF films can be controlled by the interfibrillar structures of the T-CNFs using a carboxylate ion-exchange process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulin C, Gällstedt M, Lindström T (2010) Oxygen and oil barrier properties of microfibrillated cellulose films and coatings. Cellulose 17:559–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9393-y
Carpenter AW, Lannoy C-F, Wiesner MR (2015) Cellulose nanomaterials in water treatment technologies. Environ Sci Technol 49:5277–5287. https://doi.org/10.1021/es506351r
de Britto D, Assis OBG (2009) Thermal degradation of carboxymethylcellulose in different salty forms. Thermochim Acta 494(1–2):115–122
Diaz JA, Ye Z, Wu X, Moore AL, Moon RJ, Martini A, Boday DJ, Youngblood JP (2014) Thermal conductivity in nanostructured films: from single cellulose nanocrystals to bulk films. Biomacromolecules 15:4096–4101. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm501131a
Eichhorn SJ, Dufresne A, Aranguren M, Marcovich NE, Capadona JR, Rowan SJ, Weder C, Thielemans W, Roman M, Renneckar S, Gindl W, Veigel S, Keckes J, Yano H, Abe K, Nogi M, Nakagaito AN, Mangalam A, Simonsen J, Benight AS, Bismarck A, Berglund LA, Peijs T (2010) Review: current international research into cellulose nanofibers and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 45:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3874-0
Feng Y, Zhang X, Shen Y, Yoshino K, Feng W (2012) A mechanically strong, flexible and conductive film based on bacterial cellulose/graphene nanocomposite. Carbohydr Polym 87:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.08.039
Fornes TD, Hunter DL, Paul DR (2004) Nylon-6 nanocomposites from alkylammonium-modified clay: the role of alkyl tails on exfoliation. Macromolecules 37:1793–1798. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma0305481
Fujisawa S, Okita Y, Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Isogai A (2010) Preparation and characterization of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril films with free carboxyl groups. Carbohydr Polym 84:579–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.029
Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Iwata T, Kumamoto Y, Isogai A (2009) Transparent and high gas barrier films of cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Biomacromolecules 10:162–165. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm801065u
Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Okita Y, Isogai A (2010) Thermal stabilization of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1502–1508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.06.015
Glatter O, Kratky O (1982) Small-angle X-ray scattering. Academic Press, London
Henriksson M, Berglund LA, Isaksson P, Lindström T, Nishino T (2008) Cellulose nanopaper structures of high toughness. Biomacromolecules 9:1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm800038n
Heux L, Dinand E, Vignon MR (1999) Structural aspects in ultrathin cellulose microfibrils followed by 13C CP-MAS NMR. Carbohydr Polym 40(2):115–124
Hoeng F, Denneulin A, Bras J (2016) Use of nanocellulose in printed electronics: a review. Nanoscale 8:13131–13154. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR03054H
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorris A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5438–5466. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201001273
Kobayashi Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2014) Aerogels with 3D ordered nanofiber skeletons of liquid-crystalline nanocellulose derivatives as tough and transparent insulators. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201405123
Koga H, Saito T, Kitaoka T, Nogi M, Suganuma K, Isogai A (2013) Transparent, conductive, and printable composites consisting of TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose and carbon nanotube. Biomacromolecules 14:1160–1165. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400075f
Koga H, Nogi M, Komoda N, Nge TT, Sugahara T, Suganuma K (2014) Uniformly connected conductive networks on cellulose nanofiber paper for transparent paper electronics. NPG Asia Mater 6:e93. https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2014.9
Lavoine N, Bras J, Saito T, Isogai A (2016) Improvement of the thermal stability of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils by heat-induced conversion of ionic bonds to amide bonds. Macromol Rapid Commun 37:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201600186
Osman MA, Ploetze M, Skrabal P (2004) Structure and properties of alkylammonium monolayers self-assembled on montmorillonite platelets. J Phys Chem B 108:2580–2588. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0366769
Richards GN, Zheng G (1991) Influence of metal ions and of salts on products from pyrolysis of wood: applications to thermochemical processing of newsprint and biomass. J Anal Appl Pyrol 21(1–2):133–146
Robinson RA, Stokes RH (1965) Electrolyte solutions 2nd edn revised. Butterworths, London
Sakai K, Kobayashi Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2016) Partitioned airs at microscale and nanoscale: thermal diffusivity in ultrahigh porosity solids of nanocellulose. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20434
Saito T, Nishiyama Y, Putaux J-L, Vignon M, Isogai A (2006) Homogeneous suspensions of individualized microfibrils from TEMPO-catalyzed oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 7:1687–1691. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060154s
Saito T, Hirota M, Tamura N, Kimura S, Fukuzumi H, Heux L, Isogai A (2009) Individualization of nano-sized plant cellulose fibrils by direct surface carboxylation using TEMPO catalyst under neutral conditions. Biomacromolecules 10:1992–1996. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm900414t
Sakamoto I (1987) Studies on ion-solvent interactions IV. Measurements of electrolytic conductivity and ion association equilibria of electrolytes. Shimane Univ Trans 21:101–136
Shimizu M, Saito T, Isogai A (2014a) Bulky quaternary alkylammonium counterions enhance the nanodispersibility of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl-oxidized cellulose in diverse solvents. Biomacromolecules 15:1904–1909. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500384d
Shimizu M, Saito T, Fukuzumi H, Isogai A (2014b) Hydrophobic, ductile, and transparent nanocellulose films with quaternary alkylammonium carboxylates on nanofibril surfaces. Biomacromolecules 15:4320–4325. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm501329v
Shimizu M, Saito T, Isogai A (2016) Water-resistant and high oxygen-barrier nanocellulose films with interfibrillar cross-linkages formed through multivalent metal ions. J Membr Sci 500:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.11.002
Shinohara Y, Kayashima K, Okumura Y, Zhao C, Ito K, Amemiya Y (2006) Small-angle X-ray scattering study of the pulley effect of slide-ring gels. Macromolecules 39:7386–7391. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma061037s
Terenzi C, Prakobna K, Berglund LA, Furó I (2015) Nanostructural effects on polymer and water dynamics in cellulose biocomposites: 2H and 13C NMR relaxometry. Biomacromolecules 16:1506–1515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00330
Turner WR (1971) Normal alkanes. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 10:238–260. https://doi.org/10.1021/i360039a003
Uetani K, Hatori K (2017) Thermal conductivity analysis and applications of nanocellulose. Sci Technol Adv Mater 18:877–892. https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2017.1390692
Uetani K, Okada T, Oyama TH (2015) Crystallite size effect on thermal conductive properties of nonwoven nanocellulose sheets. Biomacromolecules 16:2220–2227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00617
Vietor RJ, Newman RH, Ha M-A, Apperley DC, Jarvis MC (2002) Conformational features of crystal-surface cellulose from higher plants. Plant J 30(6):721–731
Xie W, Gao Z, Pan W-P, Hunter D, Singh A, Vaia R (2001) Thermal degradation chemistry of alkyl quaternary ammonium montmorillonite. Chem Mater 13:2979–2990. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm010305s
Zhao M, Ansari F, Takeuchi M, Shimizu M, Saito T, Berglund LA, Isogai A (2018) Nematic structuring of transparent and multifunctional nanocellulose papers. Nanoscale Horiz 3:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nh00104e
Zhu H, Fang Z, Wang Z, Dai J, Yao Y, Shen F, Preston C, Wu W, Peng P, Jang N, Yu Q, Yu Z, Hu L (2016) Extreme light management in mesoporous wood cellulose paper for optoelectronics. ACS Nano 10:1369–1377. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b06781
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by The Foundation for The Promotion of Ion Engineering, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, M., Kusumi, R., Saito, T. et al. Thermal and electrical properties of nanocellulose films with different interfibrillar structures of alkyl ammonium carboxylates. Cellulose 26, 1657–1665 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2155-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2155-y