Abstract
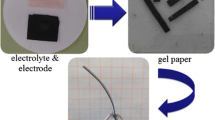
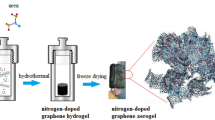
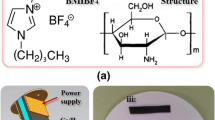
A nanocomposite soft actuator based on porous high-conductivity electrode membrane, which was composed of biopolymer cellulose mixed with chitosan and highly conductive nanoparticles generated by reduced graphene oxide encapsulated multi-walled carbon nanotube, was developed in this paper. No new substance was discovered in the regenerated electrode layer through the scanning analysis from FT-IR and XRD. Actuators exhibited significant enhancement in peak to peak displacement, which was 3.64 times increased than the traditional value at 5 V 0.1 Hz. With the test of solid-state electric double layer capacitor, actuators showed the highest specific capacitance (10.695 F g−1) at the current density of 1 A g−1, the lowest internal resistance (9.2 Ω g−1) in the frequency range of 105–10−2 Hz, and the lowest energy density (901 Wh kg−1) at the current density of 10 A g−1, which demonstrated the absolute advantages in the conductivity and channels for electrons. These findings suggest that research on porous high-conductivity electrode layer holds great promise in the further study of higher performance actuators.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acerce M, Akdoğan EK, Chhowalla M (2017a) Metallic molybdenum disulfide nanosheet-based electrochemical actuators. Nature 549(7672):370
Acerce M, Akdoğan EK, Chhowalla M (2017b) Metallic molybdenum disulfide nanosheet-based electrochemical actuators. Nature 549(7672):370
Acome E, Mitchell SK, Morrissey TG (2018) Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance. Science 359(6371):61–65
Altınkaya E, Seki Y, Yılmaz ÖC (2016) Electromechanical performance of chitosan-based composite electroactive actuators. Compos Sci Technol 129:108–115
Barrios CA (2018) A deflection optical sensor based on a Scotch tape waveguide with an integrated grating coupler. Sens Actuators A Phys 269:500–504
Chen J, Huang X, Zhu Y (2017) Cellulose nanofiber supported 3D interconnected BN nanosheets for epoxy nanocomposites with ultrahigh thermal management capability. Adv Funct Mater 27(5):1604754
Fang X, Li A, Yildiz O (2017) Enhanced anisotropic response of dielectric elastomer actuators with microcombed and etched carbon nanotube sheet electrodes. Carbon 120:366–373
Jang KI, Li K, Chung HU (2017) Self-assembled three dimensional network designs for soft electronics. Nat Commun 8:15894
Kim SS, Jeon JH, Kim HI (2015) High-fidelity bioelectronic muscular actuator based on graphene-mediated and tempo-oxidized bacterial cellulose. Adv Funct Mater 25(23):3560–3570
Kotal M, Kim J, Kim KJ (2016a) Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped graphene electrodes for high-performance ionic artificial muscles. Adv Mater 28(8):1610–1615
Kotal M, Kim J, Kim KJ (2016b) Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped graphene electrodes for high-performance ionic artificial muscles. Adv Mater 28(8):1610–1615
Lasprilla AJR, Martinez GAR, Lunelli BH (2012) Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices-A review. Biotechnol Adv 30(1):321–328
Lu L, Liu J, Hu Y (2012a) Highly stable air working bimorph actuator based on a graphene nanosheet/carbon nanotube hybrid electrode. Adv Mater 24(31):4317–4321
Lu L, Liu J, Hu Y (2012b) Large volume variation of an anisotropic graphene nanosheet electrochemical–mechanical actuator under low voltage stimulation. Chem Commun 48(33):3978–3980
Lu L, Liu J, Hu Y (2013) Graphene-stabilized silver nanoparticle electrochemical electrode for actuator design. Adv Mater 25(9):1270–1274
Muralidharan MN, Shinu KP, Seema A (2016) Optically triggered actuation in chitosan/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 144:115–121
Ozdemir O, Karakuzu R, Sarikanat M (2015) Effects of PEG loading on electromechanical behavior of cellulose-based electroactive composite. Cellulose 22(3):1873–1881
Sun Z, Zhao G, Song W (2017a) A naturally crosslinked chitosan based ionic actuator with cathode deflection phenomenon. Cellulose 24(2):441–445
Sun Z, Song W, Zhao G (2017b) Chitosan-based polymer gel paper actuators coated with multi-wall carbon nanotubes and MnO2 composite electrode. Cellulose 24(10):4383–4392
Terasawa N, Asaka K (2017) High-performance polymer actuators based on an iridium oxide and vapor-grown carbon nanofibers combining electrostatic double-layer and faradaic capacitor mechanisms. Sens Actuators B Chem 240:536–542
Terasawa N, Asaka K (2018) High-performance graphene oxide/vapor-grown carbon fiber composite polymer actuator. Sens Actuators B Chem 255:2829–2837
Wang F, Jeon JH, Park S (2016) A soft biomolecule actuator based on a highly functionalized bacterial cellulose nano-fiber network with carboxylic acid groups. Soft Matter 12(1):246–254
Wang D, Lu C, Zhao J (2017a) High energy conversion efficiency conducting polymer actuators based on PEDOT: PSS/MWCNTs composite electrode. RSC Adv 7(50):31264–31271
Wang Y, Qian J, Zhao N (2017b) Novel hydroxyethyl chitosan/cellulose scaffolds with bubble-like porous structure for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym 167:44–51
Wu G, Hu Y, Liu Y (2015) Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet electrode-based high-performance ionic actuator. Nat Commun 6:7258
Xin Y, Xiong Q, Bai Q (2017) A hierarchically porous cellulose monolith: a template-free fabricated, morphology-tunable, and easily functionalizable platform. Carbohydr Polym 157:429–437
Yuk H, Lin S, Ma C (2017) Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water. Nat Commun 8:14230
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (Grant No. 2018M630330), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. QC2018046), National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31470714), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2572017BB08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Du, S., Li, F. et al. High-performance cellulose based nanocomposite soft actuators with porous high-conductivity electrode doped by graphene-coated carbon nanosheet. Cellulose 25, 5807–5819 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2000-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2000-3