Abstract
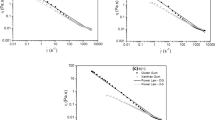
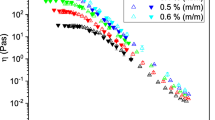
Guar gum (GG) fracturing fluids were studied by incorporating cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) in anhydrous borax crosslinked guar gum gels. To fully understand the impact of CNF on the proppant suspension capability of developed fracturing fluids, their shear rate-dependent viscosity and viscoelasticity were investigated. The shear rate dependencies of fluids was fitted to the Carreau model. The zero shear rate viscosity and elasticity of fracturing fluids increased significantly by incorporating CNF in guar gum gels. On the other hand, the viscosity at high shear rates (>100 s−1) decreased as desired. The proppant settling velocities through fracturing fluids were evaluated by modeling the terminal falling velocity of proppants moving through a Carreau model fluid. The experimental results of the rheological behavior and the modeling results of the proppant settling rate indicated that the fracturing fluids containing CNF had better suspension capabilities. In addition, the lower viscosities of CNF formulated GG gels at higher shear rates will make them more pumpable.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya AR (1986) Particle transport in viscous and viscoelastic fracturing fluids. SPE Prod Eng 1(02):104–110
Acharya A (1987) Viscoelasticity of crosslinked fracturing fluids and proppant transport. In: SPE production operations symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Agoda-Tandjawa G, Durand S, Berot S, Blassel C, Gaillard C, Garnier C, Doublier J-L (2010) Rheological characterization of microfibrillated cellulose suspensions after freezing. Carbohydr Polym 80(3):677–686
Asadi M, Shah SN, Lord DL (1999) Static/dynamic settling of proppant in non-newtonian hydraulic fracturing fluids. In: SPE mid-continent operations symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Asadi M, Conway MW, Barree RD (2002) Zero shear viscosity determination of fracturing fluids: an essential parameter in proppant transport characterizations. In: International symposium and exhibition on formation damage control. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Banerjee C, Ghosh S, Sen G, Mishra S, Shukla P, Bandopadhyay R (2013) Study of algal biomass harvesting using cationic guar gum from the natural plant source as flocculant. Carbohydr Polym 92(1):675–681
Bishop M, Shahid N, Yang J, Barron AR (2004) Determination of the mode and efficacy of the cross-linking of guar by borate using MAS 11B NMR of borate cross-linked guar in combination with solution 11B NMR of model systems. Dalton Trans 17:2621–2634
Bocchinfuso G, Mazzuca C, Sandolo C, Margheritelli S, Alhaique F, Coviello T, Palleschi A (2010) Guar gum and scleroglucan interactions with borax: experimental and theoretical studies of an unexpected similarity. J Phys Chem B 114(41):13059–13068
Bush M, Phan-Thien N (1984) Drag force on a sphere in creeping motion throug a carreau model fluid. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 16(3):303–313
Carreau P, Kee DD, Daroux M (1979) An analysis of the viscous behaviour of polymeric solutions. Can J Chem Eng 57(2):135–140
Chhabra RP (1993) Bubbles, drops, and particles in non-Newtonian fluids. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Elgaddafi R, Ahmed R, George M, Growcock F (2012) Settling behavior of spherical particles in fiber-containing drilling fluids. J Petrol Sci Eng 84:20–28
Gidley JL (1989) Recent advances in hydraulic fracturing. Society of Petroleum Engineers, Richardson, TX
Goel N, Shah SN, Yuan WL, O’Rear EA (2001) Suspension characteristics of borate-crosslinked gels: rheology and atomic force microscopy measurements. J Appl Polym Sci 82(12):2978–2990
Goel N, Shah SN, Grady BP (2002) Correlating viscoelastic measurements of fracturing fluid to particles suspension and solids transport. J Petrol Sci Eng 35(1):59–81
Guenet J-M (2000) Structure versus rheological properties in fibrillar thermoreversible gels from polymers and biopolymers. J Rheol (1978–present) 44(4):947–960
Harris PC, Morgan RG, Heath SJ (2005) Measurement of proppant transport of frac fluids. In: SPE annual technical conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Hu YT, Chung H, Maxey JE (2015a) What is more important for proppant transport, viscosity or elasticity? In: SPE hydraulic fracturing technology conference. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Hu YT, Kishore T, Maxey J, Loveless D (2015b) Effects of crosslinking chemistry on proppant suspension in guar networks. In: SPE international symposium on oilfield chemistry. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Jafry HR, Pasquali M, Barron AR (2011) Effect of functionalized nanomaterials on the rheology of borate cross-linked guar gum. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(6):3259–3264
Jin L, Penny GS (1995) Dimensionless methods for the study of particle settling in non-Newtonian fluids. J Petrol Technol 47(03):223–228
Jones J, Marques C (1990) Rigid polymer network models. Journal de Physique 51(11):1113–1127
Kesavan S, Prud’Homme RK (1992) Rheology of guar and (hydroxypropyl) guar crosslinked by borate. Macromolecules 25(7):2026–2032
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorris A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(24):5438–5466
Lasseuguette E, Roux D, Nishiyama Y (2008) Rheological properties of microfibrillar suspension of TEMPO-oxidized pulp. Cellulose 15(3):425–433
Legemah M, Guerin M, Sun H, Qu Q (2014) Novel high-efficiency boron crosslinkers for low-polymer-loading fracturing fluids. SPE J 19(04):737–743
Lei C, Clark PE (2004) Crosslinking of guar and guar derivatives. In: SPE annual technical conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Machač I, Šiška B, Machačová L (2000) Terminal falling velocity of spherical particles moving through a Carreau model fluid. Chem Eng Process 39(4):365–369
Pääkkö M, Ankerfors M, Kosonen H, Nykänen A, Ahola S, Österberg M, Ruokolainen J, Laine J, Larsson PT, Ikkala O (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis combined with mechanical shearing and high-pressure homogenization for nanoscale cellulose fibrils and strong gels. Biomacromolecules 8(6):1934–1941
Pérez R, Siquier S, Ramίrez N, Müller A, Sáez A (2004) Non-Newtonian annular vertical flow of sand suspensions in aqueous solutions of guar gum. J Petrol Sci Eng 44(3):317–331
Pezron E, Leibler L, Ricard A, Audebert R (1988a) Reversible gel formation induced by ion complexation. 2. Phase diagrams. Macromolecules 21(4):1126–1131
Pezron E, Ricard A, Lafuma F, Audebert R (1988b) Reversible gel formation induced by ion complexation. 1. Borax-galactomannan interactions. Macromolecules 21(4):1121–1125
Pezron E, Ricard A, Leibler L (1990) Rheology of galactomannan-borax gels. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 28(13):2445–2461
Power D, Larson I, Hartley P, Dunstan D, Boger D (1998) Atomic force microscopy studies on hydroxypropylguar gels formed under shear. Macromolecules 31(25):8744–8748
Power DJ, Paterson L, Boger DV (2001) Advanced rheological techniques for optimizing borate-crosslinked fracturing fluid selection and performance. SPE Drill Complet 16(04):239–242
Risica D, Barbetta A, Vischetti L, Cametti C, Dentini M (2010) Rheological properties of guar and its methyl, hydroxypropyl and hydroxypropyl-methyl derivatives in semidilute and concentrated aqueous solutions. Polymer 51(9):1972–1982
Roodhart L (1985) Proppant settling in non-Newtonian fracturing fluids. In: SPE/DOE low permeability gas reservoirs symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Siró I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17(3):459–494
Tayal A, Pai VB, Khan SA (1999) Rheology and microstructural changes during enzymatic degradation of a guar-borax hydrogel. Macromolecules 32(17):5567–5574
Wang S, Zhang Y, Guo J, Lai J, Wang D, He L, Qin Y (2014) A study of relation between suspension behavior and microstructure and viscoelastic property of guar gum fracturing fluid. J Petrol Sci Eng 124:432–435
Wientjes RH, Duits MH, Jongschaap RJ, Mellema J (2000) Linear rheology of guar gum solutions. Macromolecules 33(26):9594–9605
Zasadzinski JA, Chu A, Prud’Homme RK (1986) Transmission electron microscopy of gel network morphology: relating network microstructure to mechanical properties. Macromolecules 19(12):2960–2964
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Alberta Innovates Bio Solutions and NSERC Bioconversion Network. We thank the National Institute for Nanotechnology and Alberta Innovates-Technology Futures for providing training and research equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Boluk, Y. Rheological behavior and particle suspension capability of guar gum: sodium tetraborate decahydrate gels containing cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 23, 3013–3022 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1015-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1015-x