Abstract
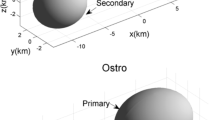
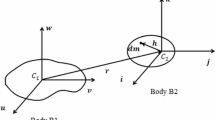
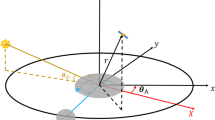
The motion of a massless particle in the gravity of a binary asteroid system, referred as the restricted full three-body problem (RF3BP), is fundamental, not only for the evolution of the binary system, but also for the design of relevant space missions. In this paper, equilibrium points and associated periodic orbit families in the gravity of a binary system are investigated, with the binary (66391) 1999 KW4 as an example. The polyhedron shape model is used to describe irregular shapes and corresponding gravity fields of the primary and secondary of (66391) 1999 KW4, which is more accurate than the ellipsoid shape model in previous studies and provides a high-fidelity representation of the gravitational environment. Both of the synchronous and non-synchronous states of the binary system are considered. For the synchronous binary system, the equilibrium points and their stability are determined, and periodic orbit families emanating from each equilibrium point are generated by using the shooting (multiple shooting) method and the homotopy method, where the homotopy function connects the circular restricted three-body problem and RF3BP. In the non-synchronous binary system, trajectories of equivalent equilibrium points are calculated, and the associated periodic orbits are obtained by using the homotopy method, where the homotopy function connects the synchronous and non-synchronous systems. Although only the binary (66391) 1999 KW4 is considered, our methods will also be well applicable to other binary systems with polyhedron shape data. Our results on equilibrium points and associated periodic orbits provide general insights into the dynamical environment and orbital behaviors in proximity of small binary asteroids and enable the trajectory design and mission operations in future binary system explorations.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellerose, J.: The restricted full three body problem: applications to binary asteroid exploration. PhD thesis, University of Michigan (2008)
Bellerose, J., Scheeres, D.J.: Periodic orbits in the vicinity of the equilateral points of the restricted full three-body problem. In: AAS/AIAA Conference, Lake Tahoe, California, AAS-05-295, vol. 711 (2005)
Bellerose, J., Scheeres, D.: General dynamics in the restricted full three body problem. Acta Astronaut. 62(10), 563–576 (2008a)
Bellerose, J., Scheeres, D.J.: Restricted full three-body problem: application to binary system 1999 KW4. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 31(1), 162–171 (2008b)
Chanut, T., Winter, O., Amarante, A., Araújo, N.: 3d plausible orbital stability close to asteroid (216) Kleopatra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 452(2), 1316–1327 (2015)
Chapman, C., Veverka, J., Thomas, P., Klaasen, K., et al.: Discovery and physical properties of Dactyl, a satellite of asteroid 243 Ida. Nature 374(6525), 783 (1995)
Chappaz, L., Howell, K.: Trajectory exploration within binary systems comprised of small irregular bodies. In: 23rd AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Kauai, Hawaii (2013)
Chappaz, L., Howell, K.C.: Exploration of bounded motion near binary systems comprised of small irregular bodies. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 123(2), 123–149 (2015)
Ćuk, M., Nesvornỳ, D.: Orbital evolution of small binary asteroids. Icarus 207(2), 732–743 (2010)
Dichmann, D., Doedel, E., Paffenroth, R.: The computation of periodic solutions of the 3-body problem using the numerical continuation software auto. Libration Point Orbits and Applications, pp. 429–488 (2003)
Doedel, E., Keller, H.B., Kernevez, J.P.: Numerical analysis and control of bifurcation problems (i): bifurcation in finite dimensions. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1(03), 493–520 (1991)
Doedel, E.J., Romanov, V.A., Paffenroth, R.C., Keller, H.B., Dichmann, D.J., Galán-Vioque, J., et al.: Elemental periodic orbits associated with the libration points in the circular restricted 3-body problem. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 17(08), 2625–2677 (2007)
Fahnestock, E.G.: The full two-body-problem: simulation, analysis, and application to the dynamics, characteristics, and evolution of binary asteroid systems. PhD thesis, University of Michigan (2009)
Fahnestock, E.G., Scheeres, D.J.: Simulation and analysis of the dynamics of binary near-earth asteroid (66391) 1999 KW4. Icarus 194(2), 410–435 (2008)
Gómez, G., Mondelo, J.M.: The dynamics around the collinear equilibrium points of the RTBP. Physica D 157(4), 283–321 (2001)
Hénon, M.: Generating Families in the Restricted Three-Body Problem, vol. 52. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Hou, X., Liu, L.: Bifurcating families around collinear libration points. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 116(3), 241–263 (2013)
Howell, K.C.: Three-dimensional, periodic, ‘halo’ orbits. Celest. Mech. 32(1), 53–71 (1984)
Jacobson, S.A., Scheeres, D.J.: Dynamics of rotationally fissioned asteroids: source of observed small asteroid systems. Icarus 214(1), 161–178 (2011a)
Jacobson, S.A., Scheeres, D.J.: Long-term stable equilibria for synchronous binary asteroids. Astrophys. J. Lett. 736(1), L19 (2011b)
Jacobson, S.A., Scheeres, D.J., McMahon, J.: Formation of the wide asynchronous binary asteroid population. Astrophys. J. 780(1), 60 (2013)
Jiang, Y., Baoyin, H.: Periodic orbit families in the gravitational field of irregular-shaped bodies. Astron. J. 152(5), 137 (2016)
Jiang, Y., Baoyin, H., Li, H.: Periodic motion near the surface of asteroids. Astrophys. Space Sci. 360(2), 63 (2015a)
Jiang, Y., Yu, Y., Baoyin, H.: Topological classifications and bifurcations of periodic orbits in the potential field of highly irregular-shaped celestial bodies. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(1–2), 119–140 (2015b)
Koon, W.S., Lo, M.W., Marsden, J.E., Ross, S.D.: Dynamical Systems, the Three-Body Problem and Space Mission Design. Marsden Books, Wellington (2008)
Kuznetsov, Y.A.: Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory, vol. 112. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Liu, X., Baoyin, H., Ma, X.: Periodic orbits in the gravity field of a fixed homogeneous cube. Astrophys. Space Sci. 334(2), 357–364 (2011)
Margot, J.L., Nolan, M., Benner, L., Ostro, S., Jurgens, R., Giorgini, J., et al.: Binary asteroids in the near-earth object population. Science 296(5572), 1445–1448 (2002)
McMahon, J., Scheeres, D.: Detailed prediction for the BYORP effect on binary near-earth asteroid (66391) 1999 KW4 and implications for the binary population. Icarus 209(2), 494–509 (2010a)
McMahon, J., Scheeres, D.: Secular orbit variation due to solar radiation effects: a detailed model for BYORP. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 106(3), 261–300 (2010b)
Ni, Y., Jiang, Y., Baoyin, H.: Multiple bifurcations in the periodic orbit around Eros. Astrophys. Space Sci. 361(5), 170 (2016)
Ostro, S.J., Margot, J.L., Benner, L.A., Giorgini, J.D., Scheeres, D.J., Fahnestock, E.G., et al.: Radar imaging of binary near-earth asteroid (66391) 1999 KW4. Science 314(5803), 1276–1280 (2006)
Peng, H., Xu, S.: Stability of two groups of multi-revolution elliptic halo orbits in the elliptic restricted three-body problem. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 123(3), 279–303 (2015)
Pravec, P., Harris, A.W.: Binary asteroid population: 1. Angular momentum content. Icarus 190(1), 250–259 (2007)
Scheeres, D.J.: Orbital Motion in Strongly Perturbed Environments: Applications to Asteroid, Comet and Planetary Satellite Orbiters. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Scheeres, D., Williams, B., Miller, J.: Evaluation of the dynamic environment of an asteroid: applications to 433 Eros. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 23(3), 466–475 (2000)
Scheeres, D.J., Fahnestock, E.G., Ostro, S.J., Margot, J.L., Benner, L.A., Broschart, S.B., et al.: Dynamical configuration of binary near-earth asteroid (66391) 1999 KW4. Science 314(5803), 1280–1283 (2006)
Scheeres, D., Van Wal, S., Olikara, Z., Baresi, N.: The dynamical environment for the exploration of Phobos, ists-2017-d-007. International Symposium on Space Technology and Science. Ehime, Japan, pp. 3–9 (2017)
Szebehely, V.: Theory of Orbit: The Restricted Problem of Three Bodies. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2012)
Vaquero, M., Howell, K.C.: Design of transfer trajectories between resonant orbits in the Earth–Moon restricted problem. Acta Astronaut. 94(1), 302–317 (2014)
Werner, R.A., Scheeres, D.J.: Exterior gravitation of a polyhedron derived and compared with harmonic and mascon gravitation representations of asteroid 4769 Castalia. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 65(3), 313–344 (1996)
Woo, P., Misra, A.K.: Equilibrium points in the full three-body problem. Acta Astronaut. 99, 158–165 (2014)
Woo, P., Misra, A.K.: Bounded trajectories of a spacecraft near an equilibrium point of a binary asteroid system. Acta Astronaut. 110, 313–323 (2015)
Yu, Y., Baoyin, H.: Generating families of 3d periodic orbits about asteroids. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 427(1), 872–881 (2012)
Yu, Y., Baoyin, H., Jiang, Y.: Constructing the natural families of periodic orbits near irregular bodies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 453(3), 3269–3277 (2015)
Zamaro, M., Biggs, J.: Natural motion around the Martian moon Phobos: the dynamical substitutes of the libration point orbits in an elliptic three-body problem with gravity harmonics. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 122(3), 263–302 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 11432001 and 11602009, the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by China Association for Science and Technology, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the paper submitted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Wang, Y. & Xu, S. Equilibrium points and associated periodic orbits in the gravity of binary asteroid systems: (66391) 1999 KW4 as an example. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 130, 32 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-018-9827-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-018-9827-7