Abstract
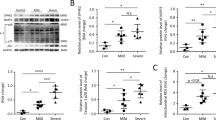
Pulmonary surfactant is a lipoprotein complex on the alveolar surface. It reduces the surface tension at the air–water interface and stabilizes the alveoli during expiration. Surfactant deficiency or dysfunction is associated with occurrence and development of many pulmonary diseases. Family members of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase are rate-limiting enzymes for surfactant phospholipid synthesis. We had reported recently that the expression of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase alpha (CCT-α) was inhibited during N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA)-induced lung injury. But the molecular mechanism underlining remains elusive. In this work, we reported that NMDA induced nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activation and nuclear factor–kB (NF–κB) subunit p65 nuclear translocation in A549 cells, which were responsible for decreased (CCT-α) expression. Furthermore, NOS activation and elevated NO production are upstream regulators for p65 nuclear translocation and (CCT-α) expression inhibition. Our results provided important clues for further elucidating the mechanisms underlying glutamate-induced lung injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakovic M, Waite KA, Vance DE. Functional significance of Sp1, Sp2, and Sp3 transcription factors in regulation of the murine CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase alpha promoter. J Lipid Res. 2000;41:583–94.
Brindicci C, Ito K, Barnes PJ, Kharitonov SA. Effect of an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on differential flow-exhaled nitric oxide in asthmatic patients and healthy volunteers. Chest. 2007;132:581–8.
Campbell KJ, Rocha S, Perkins ND. Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by RelA(p65) NF-kappa B. Mol Cell. 2004;13:853–65.
Chen JH, Lin HH, Chiang TA, Hsu JD, Ho HH, Lee YC, et al. Gaseous nitrogen oxide promotes human lung cancer cell line A549 migration, invasion, and metastasis via iNOS-mediated MMP-2 production. Toxicol Sci. 2008;106:364–75.
Griscavage JM, Wilk S, Ignarro LJ. Inhibitors of the proteasome pathway interfere with induction of nitric oxide synthase in macrophages by blocking activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:3308–12.
Hoffmann A, Baltimore D. Circuitry of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Immunol Rev. 2006;210:171–86.
Jiang MH, Kaku T, Hada J, Hayashi Y. Different effects of eNOS and nNOS inhibition on transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res. 2002;946:139–47.
Jiang X, Zhu D, Okagaki P, Lipsky R, Wu X, Banaudha K, et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate and TrkB receptor activation in cerebellar granule cells: an in vitro model of preconditioning to stimulate intrinsic survival pathways in neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;993:134–45. discussion 159-160.
Kent C. CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1348:79–90.
Kourembanas S, McQuillan LP, Leung GK, Faller DV. Nitric oxide regulates the expression of vasoconstrictors and growth factors by vascular endothelium under both normoxia and hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:99–104.
Kowara R, Moraleja KL, Chakravarthy B. Involvement of nitric oxide synthase and ROS-mediated activation of L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in NMDA-induced DPYSL3 degradation. Brain Res. 2006;1119:40–9.
Munhoz CD, Lepsch LB, Kawamoto EM, Malta MB, Lima Lde S, Avellar MC, et al. Chronic unpredictable stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via glucocorticoid secretion. J Neurosci. 2006;26:3813–20.
Polak MJ, Xiao S, Ashton CA, Baylis C. Nmda alters the development of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and nitric oxide synthetase activity in the isolated perfused rat lung. Exp Lung Res. 2002;28:251–63.
Prasad R, Giri S, Nath N, Singh I, Singh AK. GSNO attenuates EAE disease by S-nitrosylation-mediated modulation of endothelial-monocyte interactions. Glia. 2007;55:65–77.
Rocha S, Campbell KJ, Perkins ND. p53- and Mdm2-independent repression of NF-kappa B transactivation by the ARF tumor suppressor. Mol Cell. 2003;12:15–25.
Said SI. Glutamate receptors and asthmatic airway disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999;20:132–4.
Said SI, Berisha HI, Pakbaz H. Excitotoxicity in the lung: N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced, nitric oxide-dependent, pulmonary edema is attenuated by vasoactive intestinal peptide and by inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:4688–92.
Shen L, Li L, She H, Yue S, Li C, Luo Z. Inhibition of Pulmonary Surfactants Synthesis during N-Methyl-d-Aspartate-Induced Lung Injury. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010 Apr 9. [Epub ahead of print]
Shen L, Han JZ, Li C, Yue SJ, Liu Y, Qin XQ, et al. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on glutamate-induced lung injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28:392–7.
Skerry TM, Genever PG. Glutamate signalling in non-neuronal tissues. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:174–81.
Stepulak A, Sifringer M, Rzeski W, Endesfelder S, Gratopp A, Pohl EE, et al. NMDA antagonist inhibits the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway and suppresses cancer growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15605–10.
Tang F, Yue S, Luo Z, Feng D, Wang M, Qian C, et al. Role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005;40:437–44.
Taylor CT. Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation. J Physiol. 2008;586:4055–9.
von Knethen A, Callsen D, Brune B. NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation by nitric oxide attenuated apoptotic cell death in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10:361–72.
Wang S, Kotamraju S, Konorev E, Kalivendi S, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB during doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells and myocytes is pro-apoptotic: the role of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J. 2002;367:729–40.
Wang M, Luo Z, Liu S, Li L, Deng X, Huang F, et al. Glutamate mediates hyperoxia-induced newborn rat lung injury through N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009;40:260–7.
Wright JR. Pulmonary surfactant: a front line of lung host defense. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:1453–5.
Zerbini LF, Wang Y, Czibere A, Correa RG, Cho JY, Ijiri K, et al. NF-kappa B-mediated repression of growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins 45alpha and gamma is essential for cancer cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:13618–23.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ms. Huijun Liu for technical assistance and Dr. Suzanne Jackowski for CCT-α antibody. This work was supported by grants (Nos. 30370531, 30471835) from National Natural Science Foundation of China (to Z.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lian Li and Li Shen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Shen, L., She, H. et al. Nitric oxide-induced activation of NF–κB-mediated NMDA-induced CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase alpha expression inhibition in A549 cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 27, 41–47 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-010-9168-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-010-9168-0