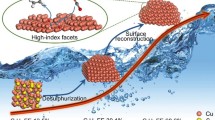
Abstract
Cu2O/CuO/CuS electrocatalyst was prepared by thermal oxidation of cleaned copper mesh in the air into Cu2O/CuO and CuS was deposited on oxide surface using facile successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method. The successive fabrication of the electrocatalyst was confirmed using XRD, SEM, Raman and XPS. The catalytic enhancement is believed to be associated with the reduction of copper sulfide. Together with copper oxides, they offer favorable adsorption sites for electrochemical CO2 reduction. The synthesized catalyst offered significantly enhanced activity and selectivity performance for CO2 reduction at lower overpotential. Remarkably, the faradaic efficiency for formate generation reaches 84% at the potential of − 0.7 V versus RHE. It has also provided a high partial current density of − 20 mA cm− 2.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao S, Lin Y, Jiao X, Sun Y, Luo Q, Zhang W, Li D, Yang J, Xie Y (2016) Partially oxidized atomic cobalt layers for carbon dioxide electroreduction to liquid fuel. Nature 529:68
Inoue T, Fujishima A, Konishi S, Honda K (1979) Photoelectrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in aqueous suspensions of semiconductor powders. Nature 277:637
Dong ZD, Long LJ, Zhang QS (2016) Recent advances in inorganic heterogeneous electrocatalysts for reduction of carbon dioxide. Adv Mater (Weinheim Ger) 28:3423–3452
Qiao J, Liu Y, Hong F, Zhang J (2014) A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem Soc Rev 43:631–675
Kuhl KP, Cave ER, Abram DN, Jaramillo TF (2012) New insights into the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide on metallic copper surfaces. Energy Environ Sci 5:7050–7059
Reske R, Mistry H, Behafarid F, Roldan Cuenya B, Strasser P (2014) Particle size effects in the catalytic electroreduction of CO2 on Cu nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 136:6978–6986
Wang Z, Yang G, Zhang Z, Jin M, Yin Y (2016) Selectivity on etching: creation of high-energy facets on copper nanocrystals for CO2 electrochemical reduction. ACS Nano 10:4559–4564
Raciti D, Livi KJ, Wang C (2015) Highly dense Cu nanowires for low-overpotential CO2 reduction. Nano Lett 15:6829–6835
Ming M, Kristina D, Smith WA (2016) S.W. A., Controllable hydrocarbon formation from the electrochemical reduction of CO2 over Cu nanowire arrays. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:6680–6684
Cao L, Raciti D, Li C, Livi KJT, Rottmann PF, Hemker KJ, Mueller T, Wang C (2017) Mechanistic insights for low-overpotential electroreduction of CO2 to CO on copper nanowires. ACS Catal 7:8578–8587
Christophe J, Doneux T, Buess-Herman C (2012) Electroreduction of carbon dioxide on copper-based electrodes: activity of copper single crystals and copper–gold alloys. Electrocatalysis 3:139–146
Kim D, Resasco J, Yu Y, Asiri AM, Yang P (2014) Synergistic geometric and electronic effects for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using gold–copper bimetallic nanoparticles. Nat Commun 5:4948
Clark EL, Hahn C, Jaramillo TF, Bell AT (2017) Electrochemical CO2 reduction over compressively strained CuAg surface alloys with enhanced multi-carbon oxygenate selectivity. J Am Chem Soc 139:15848–15857
Ma S, Sadakiyo M, Heima M, Luo R, Haasch RT, Gold JI, Yamauchi M, Kenis PJA (2017) Electroreduction of carbon dioxide to hydrocarbons using bimetallic Cu–Pd catalysts with different mixing patterns. J Am Chem Soc 139:47–50
Varela AS, Schlaup C, Jovanov ZP, Malacrida P, Horch S, Stephens IEL, Chorkendorff I (2013) CO2 electroreduction on well-defined bimetallic surfaces: Cu overlayers on Pt(111) and Pt(211). J Phys Chem C 117:20500–20508
Sarfraz S, Garcia-Esparza AT, Jedidi A, Cavallo L, Takanabe K (2016) Cu–Sn bimetallic catalyst for selective aqueous electroreduction of CO2 to CO. ACS Catal 6:2842–2851
Larrazábal GO, Martín AJ, Mitchell S, Hauert R, Pérez-Ramírez J (2016) Enhanced reduction of CO2 to CO over Cu–In electrocatalysts: catalyst evolution is the key. ACS Catal 6:6265–6274
Li CW, Kanan MW (2012) CO2 reduction at low overpotential on Cu electrodes resulting from the reduction of thick Cu2O films. J Am Chem Soc 134:7231–7234
Chen Y, Kanan MW (2012) Tin oxide dependence of the CO2 reduction efficiency on tin electrodes and enhanced activity for Tin/Tin oxide thin-film catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 134:1986–1989
Chen Y, Li CW, Kanan MW (2012) Aqueous CO2 reduction at very low overpotential on oxide-derived Au nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 134:19969–19972
Kas R, Kortlever R, Milbrat A, Koper MTM, Mul G, Baltrusaitis J (2014) Electrochemical CO2 reduction on Cu2O-derived copper nanoparticles: controlling the catalytic selectivity of hydrocarbons. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:12194–12201
Ma M, Djanashvili K, Smith WA (2015) Selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO on CuO-derived Cu nanowires. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:20861–20867
Raciti D, Cao L, Livi KJT, Rottmann PF, Tang X, Li C, Hicks Z, Bowen KH, Hemker KJ, Mueller T, Wang C (2017) Low-overpotential electroreduction of carbon monoxide using copper nanowires. ACS Catal 7:4467–4472
Mistry H, Varela AS, Bonifacio CS, Zegkinoglou I, Sinev I, Choi Y-W, Kisslinger K, Stach EA, Yang JC, Strasser P, Cuenya BR (2016) Highly selective plasma-activated copper catalysts for carbon dioxide reduction to ethylene. Nat Commun 7:12123
Lee S, Kim D, Lee J (2015) Electrocatalytic production of C3-C4 compounds by conversion of CO2 on a chloride-induced bi-phasic Cu2O-Cu catalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:14701–14705
Loiudice A, Lobaccaro P, Kamali EA, Thao T, Huang BH, Ager JW, Buonsanti R (2016) Tailoring copper nanocrystals towards C2 products in electrochemical CO2 reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:5789–5792
Gao D, Zegkinoglou I, Divins NJ, Scholten F, Sinev I, Grosse P Roldan Cuenya B (2017) Plasma-activated copper nanocube catalysts for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction to hydrocarbons and alcohols. ACS Nano 11:4825–4831
Chen CS, Handoko AD, Wan JH, Ma L, Ren D, Yeo BS (2015) Stable and selective electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to ethylene on copper mesocrystals. Catal Sci Technol 5:161–168
Handoko AD, Ong CW, Huang Y, Lee ZG, Lin L, Panetti GB, Yeo BS (2016) Mechanistic insights into the selective electroreduction of carbon dioxide to ethylene on Cu2O-derived copper catalysts. J Phys Chem C 120:20058–20067
Feng X, Jiang K, Fan S, Kanan MW (2015) Grain-boundary-dependent CO2 electroreduction activity. J Am Chem Soc 137:4606–4609
Verdaguer-Casadevall A, Li CW, Johansson TP, Scott SB, McKeown JT, Kumar M, Stephens IEL, Kanan MW, Chorkendorff I (2015) Probing the active surface sites for CO reduction on oxide-derived copper electrocatalysts. J Am Chem Soc 137:9808–9811
Eilert A, Cavalca F, Roberts FS, Osterwalder J, Liu C, Favaro M, Crumlin EJ, Ogasawara H, Friebel D, Pettersson LGM, Nilsson A (2017) Subsurface oxygen in oxide-derived copper electrocatalysts for carbon dioxide reduction. J Phys Chem Lett 8:285–290
Eilert A, Roberts FS, Friebel D, Nilsson A (2016) Formation of copper catalysts for CO2 reduction with high ethylene/methane product ratio investigated with in situ x-ray absorption spectroscopy. J Phys Chem Lett 7:1466–1470
De Luna P, Quintero-Bermudez R, Dinh C-T, Ross MB, Bushuyev OS, Todorović P, Regier T, Kelley SO, Yang P, Sargent EH (2018) Catalyst electro-redeposition controls morphology and oxidation state for selective carbon dioxide reduction. Nat Catal 1:103–110
Yu Z, Qian Z, Jixin Z, Qingyu Y, Xue DS, Wenping S (2017) Nanostructured metal chalcogenides for energy storage and electrocatalysis. Adv Funct Mater 27:1702317
Zhao Z, Peng X, Liu X, Sun X, Shi J, Han L, Li G, Luo J (2017) Efficient and stable electroreduction of CO2 to CH4 on CuS nanosheet arrays. J Mater Chem A 5:20239–20243
Jiaqi X, Xiaodong L, Wei L, Yongfu S, Zhengyu J, Tao Y, Chengming W, Huanxin J, Junfa Z, Shiqiang W, Yi X (2017) Carbon dioxide electroreduction into syngas boosted by a partially delocalized charge in molybdenum sulfide selenide alloy monolayers. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:9121–9125
Zheng X, De Luna P, García de Arquer FP, Zhang B, Becknell N, Ross MB, Li Y, Banis MN, Li Y, Liu M, Voznyy O, Dinh CT, Zhuang T, Stadler P, Cui Y, Du X, Yang P, Sargent EH (2017) Sulfur-modulated tin sites enable highly selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate. Joule 1:794–805
Shinagawa T, Larrazábal GO, Martín AJ, Krumeich F, Pérez-Ramírez J (2018) Sulfur-modified copper catalysts for the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. ACS Catal 8:837–844
Dubale AA, Tamirat AG, Chen H-M, Berhe TA, Pan C-J, Su W-N, Hwang B-J (2016) A highly stable CuS and CuS-Pt modified Cu2O/CuO heterostructure as an efficient photocathode for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 4:2205–2216
Ye M, Wen X, Zhang N, Guo W, Liu X, Lin C (2015) In situ growth of CuS and Cu1.8S nanosheet arrays as efficient counter electrodes for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem A 3:9595–9600
Huang Y, Deng Y, Handoko AD, Goh GKL, Yeo BS (2018) Rational design of sulfur-doped copper catalysts for the selective electroreduction of carbon dioxide to formate. ChemSusChem 11:320–326
Zhang S, Kang P, Meyer TJ (2014) Nanostructured tin catalysts for selective electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. J Am Chem Soc 136:1734–1737
Li F, Chen L, Xue M, Williams T, Zhang Y, MacFarlane DR, Zhang J (2017) Towards a better Sn: efficient electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to formate by Sn/SnS2 derived from SnS2 nanosheets. Nano Energy 31:270–277
Min X, Kanan MW (2015) Pd-catalyzed electrohydrogenation of carbon dioxide to formate: high mass activity at low overpotential and identification of the deactivation pathway. J Am Chem Soc 137:4701–4708
Choi SY, Jeong SK, Kim HJ, Baek I-H, Park KT (2016) Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate on Tin–lead alloys. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:1311–1318
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) (105-3113-E-011-001-, 104-2911-I-011-505-MY2, 103-2923-E-011-004-MY3), the Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA) (101-EC-17-A-08-S1-183) the Top University Projects of Ministry of Education (MOE) (100H451401), and Taiwan’s Deep Decarbonization Pathways toward a Sustainable Society Project (106-0210-02-11-03). Research facilities were provided by the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (NSRRC) and the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology (NTUST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors are exhaustively discussed the results and involved to the final manuscript of this research. Amaha woldu Kahsay: Developed the methodology, performed experiments, investigated the process, processed the experimental data, characterized and analyzed the results, and draft the manuscript. Kassa Belay Ibrahim: Helped to perform XRD measurements and coordinate in research activities. Meng-Che Tsai: Contributed to the analysis of the results and coordinate in the research activities. Mulatu Kassie Birhanu: Worked out in technical activities such as sample preparation and activity measurements. Soressa Abera Chala: Contributed to the analysis of the results, discussion and helped graphic preparations. Wei-Nien Su: Helped in discussing the results, designed the figures, worked on the draft and revision of this manuscript, and supervised this work. Bing-Joe Hwang: Devised and conceived the original ideas of this research, provide study materials, instruments, reagents and other tools for analysis, analyzed and discussed the results, critical revision and supervised this work.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kahsay, A.W., Ibrahim, K.B., Tsai, MC. et al. Selective and Low Overpotential Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Formate on CuS Decorated CuO Heterostructure. Catal Lett 149, 860–869 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02657-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02657-2