Abstract
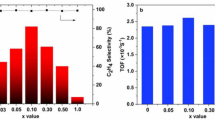
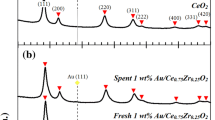
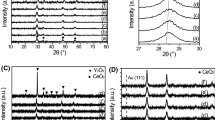
Supported gold catalysts are highly efficient for selective hydrogenation of acetylene. It has been shown that reducible materials such as ceria may influence the catalytic performance due to its unique charge shift between reduced and oxidized state. However, its role in catalytic performance remains fiercely debated. In this paper, differently morphological CeO2 supported Au catalysts were prepared with pretreatment under air and H2 atmospheres respectively, and evaluated for selective hydrogenation of acetylene. No matter with rod (abbreviated as R) or polyhedral (abbreviated as P) shape, the catalysts of Au/CeO2 reduced in air exhibits better catalytic performance than that in H2 atmosphere. The Au/CeO2 (R)-air catalyst shows the best performance. The C2H2 conversion is about three times of that over the catalyst of Au/CeO2 (R)-H2 at 300 °C. The Raman result and XPS analysis clearly showed a dependence of catalytic activity on the oxygen vacancy concentration of catalysts, revealing the correlation between its defect features and pretreatment atmosphere. Our report not only deepens the knowledge of catalytic performance affected by defect features of catalyst but also provides a possibility for the efficient heterogeneous gold/ceria catalysts by controlling the pretreatment atmosphere.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haruta M, Tsubota S, Kobayashi T, Kageyama H, Genet MJ, Delmon BM (1993) Low-temperature oxidation of CO over gold supported on TiO2, Fe2O3 and Co3O4. J Catal 144:175–192
Hutchings GJ (1985) Vapor phase hydrochlorination of acetylene: correlation of catalytic activity of supported metal chloride catalysts. J Catal 96:292–295
Sárkány A (2009) Acetylene hydrogenation on SiO2, supported gold nanoparticles. React Kinet Catal Lett 96:43–54
Jia JF, Haraki K, Kondo JN, Domen K, Tamaru K (2000) Selective hydrogenation of acetylene over Au/Al2O3 catalyst. J Phys Chem B 104:11153–11156
Tabakova T, Idakiev V, Andreeva D, Mitov I (2000) Influence of the microscopic properties of the support on the catalytic activity of Au/ZnO, Au/ZrO2, Au/Fe2O3, Au/Fe2O3-ZnO, Au/Fe2O3-ZrO2, catalysts for the WGS reaction. Appl Catal A 202:91–97
Chang HK, Thompson LT (2005) Deactivation of Au/CeOx, water gas shift catalysts. J Catal 230:66–74
Liu X, Mou CY, Lee S, Li Y, Secrest J (2012) Room temperature O2, plasma treatment of SiO2, supported Au catalysts for selective hydrogenation of acetylene in the presence of large excess of ethylene. J Catal 285:152–159
Yan X, Wheeler J, Jang B, Lin WY, Zhao B (2014) Stable Au catalysts for selective hydrogenation of acetylene in ethylene. Appl Catal A 487:36–44
Choudhary TV, Sivadinarayana C, Datye AK, Kumar D, Goodman DW (2003) Acetylene hydrogenation on Au-based catalysts. Catal Lett 86:1–8
Segura Y, López N, Pérez-Ramírez J (2007) Origin of the superior hydrogenation selectivity of gold nanoparticles in alkyne + alkene mixtures: triple-versus double. J Catal 247:383–386
Azizi Y, Petit C, Pitchon V (2008) Formation of polymer-grade ethylene by selective hydrogenation of acetylene over Au/CeO2, catalyst. J Catal 256:338–344
Wu GS, Xie T, Yuan XY, Cheng BC, Zhang LD (2004) An improved sol-gel template synthetic route to large-scale CeO2, nanowires. Mater Res Bull 39:1023–1028
Zhang C, Michaelides A, King DA, Jenkins SJ (2009) Oxygen vacancy clusters on ceria: decisive role of cerium electrons. Phys Rev B 79:7715–7722
Hong J, Chu W, Chen M, Wang X, Zhang T (2007) Preparation of novel titania supported palladium catalysts for selective hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene. Catal Commun 8:593–597
Menezes WG, Altmann L, Zielasek V, Thiel K, Bäumer M (2013) Bimetallic Co-Pd catalysts: study of preparation methods and their influence on the selective hydrogenation of acetylene. J Catal 300:125–135
Zhang S, Chen CY, Jang WL, Zhu AM (2015) Radio-frequency H2, plasma treatment of AuPd/TiO2, catalyst for selective hydrogenation of acetylene in excess ethylene. Catal Today 256:161–169
Chai M, Liu X, Li L, Pei G, Ren Y, Su Y (2017) SiO2-supported Au-Ni bimetallic catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of acetylene. Chinese J Catal 38:1338–1346
Pei G, Liu X, Wang A, Lee AF, Isaacs MA, Li L (2015) Ag alloyed Pd single-atom catalysts for efficient selective hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene in excess ethylene. ACS Catal 5:150505113815003
Gluhoi AC, Bakker JW, Nieuwenhuys BE (2010) Gold, still a surprising catalyst: selective hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene over Au nanoparticles. Catal Today 154:13–20
Lee JW, Liu X, Mou CY (2013) Selective hydrogenation of acetylene over SBA-15 supported Au-Cu bimetallic catalysts. J Chinese Chem Soc 60:907–914
Jin B, Wei Y, Zhao Z, Liu J, Jiang G, Duan A (2016) Effects of Au-Ce strong interactions on catalytic activity of Au/CeO2/3DOM Al2O3, catalyst for soot combustion under loose contact conditions. Chinese J Catal 37:923–933
Li ZX, Li LL, Yuan Q, Feng W, Xu J, Sun LD (2008) Sustainable and facile route to nearly monodisperse spherical aggregates of CeO2 nanocrystals with ionic liquids and their catalytic activities for CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 112:18405–18411
Mai HX, Sun LD, Zhang YW, Si R, Feng W, Zhang HP (2005) Shape-selective synthesis and oxygen storage behavior of ceria nanopolyhedra, nanorods, and nanocubes. J Phys Chem B 109:24380–24385
Wang YG, Mei D, Glezakou VA, Li J, Rousseau R (2015) Dynamic formation of single-atom catalytic active sites on ceria-supported gold nanoparticles. Nat Commun 6:6511
Liu Y, Liu B, Wang Q, Li C, Hu W, Liu Y (2012) Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Au/CeO2-Co3O4, catalysts with mesoporous walls for enhanced CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich gases. J Catal 296:65–76
Liu X, Guo P, Wang B, Jiang Z, Pei Y, Fan K (2013) A comparative study of the deactivation mechanisms of the Au/CeO2 catalyst for water-gas shift under steady-state and shutdown/start-up conditions in realistic reformate. J Catal 300:152–162
Wang WW, Du PP, Zou SH, He HY, Wang RX, Jin Z (2015) Highly dispersed copper oxide clusters as active species in copper-ceria catalyst for preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide. ACS Catal 5:2088–2099
Zabilskiy M, Djinović P, Tchernychova E, Tkachenko OP, Kustov LM, Pintar A (2015) Nanoshaped CuO/CeO2 materials: effect of the exposed ceria surfaces on catalytic activity in N2O decomposition reaction. ACS Catal 5:5357–5365
Nottbohm CT, Hess C (2012) Investigation of ceria by combined Raman, UV-Vis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Catal Commun 22:39–42
Gurgul J, Rinke MT, Schellenberg I, Pöttgen R (2013) The antimonide oxides RE ZnSbO and RE MnSbO (RE = Ce, Pr)-an XPS study. Solid State Sci 17:122–127
Han J, Kim HJ, Yoon S, Lee H (2011) Shape effect of ceria in Cu/ceria catalysts for preferential CO oxidation. J Mol Catal A 335:82–88
Agarwal S, Zhu X, Hensen EJM, Lefferts L, Mojet BL (2014) Defect chemistry of ceria nanorods. J Phys Chem C 118:4131–4142
Hess C (2013) In situ Raman spectroscopy of catalysts: examples from current research. Top Catal 56:1593–1600
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Plan of Shandong Province (No. 2018CXGC1108) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21603181 and 21773202). We also acknowledge the financial support from the Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Hydrocarbon Transformation and Utilization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S., Sun, X., Sun, L. et al. Selective Hydrogenation of Acetylene Over Gold Nanoparticles Supported on CeO2 Pretreated Under Different Atmospheres. Catal Lett 149, 465–472 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2628-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2628-5