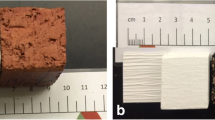
Results from studies of the removal from storage and solidification of low- and intermediate-level liquid radioactive waste in inorganic binders (cementation) are presented. Cavitation technology for recycling radiochemical wastes from nuclear power plant decommissioning increases the extraction throughput and strength of the cement compound.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety [Russian translation], TsNIIATOMINFORM, Moscow (2002).
Publication 103, International Commission on Radiation Safety (ICRS) [Russian translation], Izd. PKF Alana, Moscow (2009).
A. A. Klyuchnikov, E. M. Pazukhin, Yu. M. Shigera, and V. Yu. Shigera, NPP Radioactive Wastes and Methods for Managing Them, Inst. Probl. Bezopasn. AES NAN Ukrainy, Kiev (2005).
V. M. Kuznetsov, Principal Problems and Current Status of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facilities of the Russian Federation, RDP Yabloko, Moscow (2002).
V. M. Lebedev, Nuclear Fuel Cycle, Energoatomizdat, Moscow (2005).
V. G. Volkov and A. S. Chesnokov, Prom. Ved., No. 11–12, 7 (2011).
V. M. Ivchenko, V. A. Kulagin, and A. F. Nemchin, Cavitation Technology, G. V. Logvinovich (ed.), Izd. KGU, Krasnoyarsk (1990).
V. A. Kulagin, Methods and Means for Processing Multicomponent Media Using Cavitation Effects: Dissert. Doct. Techn. Sci., Krasnoyarsk (2004).
T. A. Kulagina, O. A. Kozin, and A. I. Matyushenko, Ecological Safety of Technical Sector Facilities, Izd. Grotesk, Krasnoyarsk (2015).
T. A. Kulagina, V. A. Popkov, and N. A. Naumenko, “Calculated heat and mass exchange during long-term storage of radioactive wastes,” Zh. Sverdl. Fed. Univ. Tekh. Tekhnol., 7, No. 3, 340–359 (2014).
O. A. Kozin, Methods and Means for Improving the Ecological Safety of Nuclear-Energy Cycle Waste Management: Auth Abstr. Dissert. Cand. Techn. Sci., Krasnoyarsk (2011).
T. A. Kulagina, V. A. Kulagin, V. V. Moskvichev, and V. A. Popkov, “Use of cavitation technology in spent nuclear-fuel management,” Ekol. Prom. Rossii, 20, No. 10, 4–10 (2016).
The work was supported financially by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, the Krasnoyarsk Krai Administration, and the Krasnoyarsk Krai Foundation for Support of Scientific and Scientific-Technical Activity in the framework of Scientific Project No. 16-41-242156 r_ofi_m.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskoe i Neftegazovoe Mashinostroenie, No. 11, pp. 37–41, November, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulagina, T.A., Kulagin, V.A. & Popkov, V.A. Environmental Effects of Cavitation Technology for Radioactive Waste Management. Chem Petrol Eng 53, 738–744 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-018-0414-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-018-0414-2