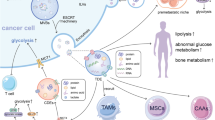
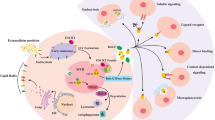
Abstract
The tumor milieu is characteristically acidic as a consequence of the fermentative metabolism of glucose that results in massive accumulation of lactic acid within the cytoplasm. Tumor cells get rid of excessive protons through exchangers that are responsible for the extracellular acidification that selects cellular clones that are more apt at surviving in this challenging and culling environment. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are vesicles with diameters ranging from nm to μm that are released from the cells to deliver nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids to adjacent or distant cells. EVs are involved in a plethora of biological events that promote tumor progression including unrestricted proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, local invasion, preparation of the metastatic niche, metastasis, downregulation or hijacking of the immune system, and drug resistance. There is evidence that the release of specific exosomes is increased many folds in cancer patients, as shown by many techniques aimed at evaluating “liquid biopsies”. The quality of the exosomal contents has been shown to vary at the different moments of tumor life such as local invasion or metastasis. In vitro studies have recently pointed out that cancer acidity is a major determinant in inducing increased exosome release by human cancer cells, by showing that exosomal release was increased as the pH moved from 7.4 pH to the typical pH of cancer that is 6.5. In this review, we emphasize the recent evidence that tumor acidity and exosomes levels are strictly related and strongly contribute to the malignant tumor phenotypes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor, S., Spugnini, E. P., Assaraf, Y. G., Azzarito, T., Rauch, C., & Fais, S. (2015). Microenvironment acidity as a major determinant of tumor chemoresistance: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) as a novel therapeutic approach. Drug Resistance Updates, 23, 69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2015.08.004.
Spugnini, E. P., Sonveaux, P., Stock, C., Perez-Sayans, M., De Milito, A., Avnet, S., … Fais, S. (2015). Proton channels and exchangers in cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1848(10), 2715–2726. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.10.015.
Spugnini, E., & Fais, S. (2017). Proton pump inhibition and cancer therapeutics: A specific tumor targeting or it is a phenomenon secondary to a systemic buffering? Seminars in Cancer Biology, 43, 111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.01.003.
Trédan, O., Galmarini, C. M., Patel, K., & Tannock, I. F. (2007). Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 99(19), 1441–1454. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djm135.
Fais, S., Venturi, G., & Gatenby, B. (2014). Microenvironmental acidosis in carcinogenesis and metastases: New strategies in prevention and therapy. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 33(4), 1095–1108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-014-9531-3.
Gillies, R. J., & Gatenby, R. A. (2015). Metabolism and its sequelae in Cancer evolution and therapy. The Cancer Journal, 21(2), 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1097/PPO.0000000000000102.
Webb, B. A., Chimenti, M., Jacobson, M. P., & Barber, D. L. (2011). Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nature Reviews Cancer, 11(9), 671–677. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3110.
Reshkin, S. J., Cardone, R. A., & Harguindey, S. (2013). Na+-H+ exchanger, pH regulation and cancer. Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery, 8(1), 85–99.
Amith, S. R., & Fliegel, L. (2013). Regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE1) in breast Cancer metastasis. Cancer Research, 73(4), 1259–1264. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4031.
White, K. A., Grillo-Hill, B. K., & Barber, D. L. (2017). Cancer cell behaviors mediated by dysregulated pH dynamics at a glance. Journal of Cell Science, 130(4), 663–669. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.195297.
Vaupel, P., & Multhoff, G. (2017). Accomplices of the hypoxic tumor microenvironment compromising antitumor immunity: Adenosine, lactate, acidosis, vascular endothelial growth factor, potassium ions, and phosphatidylserine. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 1887. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01887.
Multhoff, G., Radons, J., & Vaupel, P. (2014). Critical role of aberrant angiogenesis in the development of tumor hypoxia and associated Radioresistance. Cancers, 6(2), 813–828. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6020813.
Mayer, A., & Vaupel, P. (2013). Hypoxia, lactate accumulation, and acidosis: Siblings or accomplices driving tumor progression and resistance to therapy? In S. Van Huffel, G. Naulaers, A. Caicedo, D. F. Bruley, & D. K. Harrison (Eds.), Oxygen transport to tissue XXXV (Vol. 789, pp. 203–209). New York, NY: Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7411-1_28.
Vaupel, P., & Multhoff, G. (2018). Hypoxia-/HIF-1α-driven factors of the tumor microenvironment impeding antitumor immune responses and promoting malignant progression. In O. Thews, J. C. LaManna, & D. K. Harrison (Eds.), Oxygen transport to tissue XL (Vol. 1072, pp. 171–175). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91287-5_27.
Parks, S. K., & Pouysségur, J. (2017). Targeting pH regulating proteins for cancer therapy–Progress and limitations. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 43, 66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.01.007.
Granja, S., Tavares-Valente, D., Queirós, O., & Baltazar, F. (2017). Value of pH regulators in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 43, 17–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2016.12.003.
Pathria, G., Scott, D. A., Feng, Y., Sang Lee, J., Fujita, Y., Zhang, G., Sahu, A. D., Ruppin, E., Herlyn, M., Osterman, A. L., & Ronai, Z. A. (2018). Targeting the Warburg effect via LDHA inhibition engages ATF4 signaling for cancer cell survival. The EMBO Journal, 37(20), e99735. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899735.
Masson, N., & Ratcliffe, P. J. (2014). Hypoxia signaling pathways in cancer metabolism: The importance of co-selecting interconnected physiological pathways. Cancer & Metabolism, 2(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-3002-2-3.
Tiburcio, P. D., Choi, H., & Huang, L. E. (2014). Complex role of HIF in cancer: The known, the unknown and the unexpected. Hypoxia (Auckland, N.Z.), 2, 59–70. https://doi.org/10.2147/HP.S50651.
Semenza, G. L. (2013). HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 123(9), 3664–3671. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI67230.
Shim, H., Dolde, C., Lewis, B. C., Wu, C. S., Dang, G., Jungmann, R. A., … Dang, C. V. (1997). C-Myc transactivation of LDH-A: Implications for tumor metabolism and growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94(13), 6658–6663.
Stubbs, M., & Griffiths, J. R. (2010). The altered metabolism of tumors: HIF-1 and its role in the Warburg effect. Advances in Enzyme Regulation, 50(1), 44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advenzreg.2009.10.027.
Gillies, R. J., Brown, J. S., Anderson, A. R. A., & Gatenby, R. A. (2018). Eco-evolutionary causes and consequences of temporal changes in intratumoural blood flow. Nature Reviews Cancer, 18(9), 576–585. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0030-7.
Iessi, E., Logozzi, M., Mizzoni, D., Di Raimo, R., Supuran, C., & Fais, S. (2017). Rethinking the combination of proton exchanger inhibitors in Cancer therapy. Metabolites, 8(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010002.
Fais, S. (2016). A nonmainstream approach against cancer. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 31(6), 882–889. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2016.1156105.
Lozupone, F., & Fais, S. (2015). Cancer cell cannibalism: A primeval option to survive. Current Molecular Medicine, 15(9), 836–841.
Fais, S., & Overholtzer, M. (2018). Cell-in-cell phenomena, cannibalism, and autophagy: Is there a relationship? Cell Death & Disease, 9(2), 95. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0111-7.
Fais, S., & Overholtzer, M. (2018). Cell-in-cell phenomena in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 18(12), 758–766. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0073-9.
Zhao, H., Achreja, A., Iessi, E., Logozzi, M., Mizzoni, D., Di Raimo, R., et al. (2018). The key role of extracellular vesicles in the metastatic process. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer, 1869(1), 64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.11.005.
Peinado, H., Alečković, M., Lavotshkin, S., Matei, I., Costa-Silva, B., Moreno-Bueno, G., Hergueta-Redondo, M., Williams, C., García-Santos, G., Ghajar, C. M., Nitadori-Hoshino, A., Hoffman, C., Badal, K., Garcia, B. A., Callahan, M. K., Yuan, J., Martins, V. R., Skog, J., Kaplan, R. N., Brady, M. S., Wolchok, J. D., Chapman, P. B., Kang, Y., Bromberg, J., & Lyden, D. (2012). Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nature Medicine, 18(6), 883–891. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2753.
Nogués, L., Benito-Martin, A., Hergueta-Redondo, M., & Peinado, H. (2018). The influence of tumour-derived extracellular vesicles on local and distal metastatic dissemination. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 60, 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.012.
Peinado, H., Zhang, H., Matei, I. R., Costa-Silva, B., Hoshino, A., Rodrigues, G., Psaila, B., Kaplan, R. N., Bromberg, J. F., Kang, Y., Bissell, M. J., Cox, T. R., Giaccia, A. J., Erler, J. T., Hiratsuka, S., Ghajar, C. M., & Lyden, D. (2017). Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nature Reviews Cancer, 17(5), 302–317. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.6.
Becker, A., Thakur, B. K., Weiss, J. M., Kim, H. S., Peinado, H., & Lyden, D. (2016). Extracellular vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-cell mediators of metastasis. Cancer Cell, 30(6), 836–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.009.
Brinton, L. T., Sloane, H. S., Kester, M., & Kelly, K. A. (2015). Formation and role of exosomes in cancer. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 72(4), 659–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1764-3.
Spugnini, E., Logozzi, M., Di Raimo, R., Mizzoni, D., & Fais, S. (2018). A role of tumor-released exosomes in paracrine dissemination and metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123968.
Logozzi, M., Mizzoni, D., Angelini, D., Di Raimo, R., Falchi, M., Battistini, L., & Fais, S. (2018). Microenvironmental pH and exosome levels interplay in human Cancer cell lines of different Histotypes. Cancers, 10(10), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100370.
Fais, S., Logozzi, M., Lugini, L., Federici, C., Azzarito, T., Zarovni, N., & Chiesi, A. (2013). Exosomes: The ideal nanovectors for biodelivery. Biological Chemistry, 394(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0236.
Yáñez-Mó, M., Siljander, P. R.-M., Andreu, Z., Bedina Zavec, A., Borràs, F. E., Buzas, E. I., et al. (2015). Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 4(1), 27066. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27066.
Luan, X., Sansanaphongpricha, K., Myers, I., Chen, H., Yuan, H., & Sun, D. (2017). Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 38(6), 754–763. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.12.
Ohno, S., Ishikawa, A., & Kuroda, M. (2013). Roles of exosomes and microvesicles in disease pathogenesis. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 65(3), 398–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.019.
Iraci, N., Leonardi, T., Gessler, F., Vega, B., & Pluchino, S. (2016). Focus on extracellular vesicles: Physiological role and Signalling properties of extracellular membrane vesicles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(2), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020171.
Lodillinsky, C., Podsypanina, K., & Chavrier, P. (2016). Social networking in tumor cell communities is associated with increased aggressiveness. IntraVital, 5(1), e1112476. https://doi.org/10.1080/21659087.2015.1112476.
Parolini, I., Federici, C., Raggi, C., Lugini, L., Palleschi, S., De Milito, A., … Fais, S. (2009). Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(49), 34211–34222. doi:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.041152.
Naito, Y., Yoshioka, Y., Yamamoto, Y., & Ochiya, T. (2017). How cancer cells dictate their microenvironment: Present roles of extracellular vesicles. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 74(4), 697–713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2346-3.
Kosaka, N., Iguchi, H., Yoshioka, Y., Takeshita, F., Matsuki, Y., & Ochiya, T. (2010). Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of MicroRNAs in living cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(23), 17442–17452. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.107821.
Cruz, L., Romero, J. A. A., Iglesia, R. P., & Lopes, M. H. (2018). Extracellular vesicles: Decoding a new language for cellular communication in early embryonic development. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 6, 94. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00094.
Gallala, H. D., & Sandhoff, K. (2011). Biological function of the cellular lipid BMP—BMP as a key activator for cholesterol sorting and membrane digestion. Neurochemical Research, 36(9), 1594–1600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0337-6.
Camussi, G., Deregibus, M.-C., Bruno, S., Grange, C., Fonsato, V., & Tetta, C. (2011). Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. American Journal of Cancer Research, 1(1), 98–110.
Antonyak, M. A., & Cerione, R. A. (2014). Microvesicles as mediators of intercellular communication in Cancer. In M. Robles-Flores (Ed.), Cancer Cell Signaling (Vol. 1165, pp. 147–173). New York, NY: Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0856-1_11.
Leal, A. C., Mizurini, D. M., Gomes, T., Rochael, N. C., Saraiva, E. M., Dias, M. S., Werneck, C. C., Sielski, M. S., Vicente, C. P., & Monteiro, R. Q. (2017). Tumor-derived exosomes induce the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps: Implications for the establishment of Cancer-associated thrombosis. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 6438. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06893-7.
Jiménez-Alcázar, M., Kim, N., & Fuchs, T. A. (2017). Circulating extracellular DNA: Cause or consequence of thrombosis? Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 43(6), 553–561. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1597284.
Cui, J., Li, Q., Luo, M., Zhong, Z., Zhou, S., Jiang, L., Shen, N., Geng, Z., Cheng, H., Meng, L., Yi, S., Sun, H., Wu, F., Zhu, Z., Zou, P., You, Y., Guo, A. Y., & Zhu, X. (2018). Leukemia cell-derived microvesicles induce T cell exhaustion via miRNA delivery. Oncoimmunology, 7(7), e1448330. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2018.1448330.
Almiñana, C., Tsikis, G., Labas, V., Uzbekov, R., da Silveira, J. C., Bauersachs, S., & Mermillod, P. (2018). Deciphering the oviductal extracellular vesicles content across the estrous cycle: Implications for the gametes-oviduct interactions and the environment of the potential embryo. BMC Genomics, 19(1), 622. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4982-5.
Felicetti, F., De Feo, A., Coscia, C., Puglisi, R., Pedini, F., Pasquini, L., … Carè, A. (2016). Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-222 is sufficient to increase tumor malignancy in melanoma. Journal of Translational Medicine, 14, 56. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-0811-2.
Valadi, H., Ekström, K., Bossios, A., Sjöstrand, M., Lee, J. J., & Lötvall, J. O. (2007). Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nature Cell Biology, 9(6), 654–659. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1596.
Hannafon, B. N., & Ding, W.-Q. (2013). Intercellular communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(7), 14240–14269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714240.
Zhang, X., Yuan, X., Shi, H., Wu, L., Qian, H., & Xu, W. (2015). Exosomes in cancer: Small particle, big player. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 8, 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-015-0181-x.
Whiteside, T. L. (2016). Tumor-derived exosomes and their role in Cancer progression. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 74, 103–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2015.12.005.
Guo, W., Gao, Y., Li, N., Shao, F., Wang, C., Wang, P., Yang, Z., Li, R., & He, J. (2017). Exosomes: New players in cancer (review). Oncology Reports, 38(2), 665–675. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5714.
Wang, Z., Chen, J.-Q., Liu, J.-L., & Tian, L. (2016). Exosomes in tumor microenvironment: Novel transporters and biomarkers. Journal of Translational Medicine, 14(1), 297. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-1056-9.
Kahlert, C., & Kalluri, R. (2013). Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. Journal of Molecular Medicine (Berlin, Germany), 91(4), 431–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6.
Jiang, X., Hu, S., Liu, Q., Qian, C., Liu, Z., & Luo, D. (2017). Exosomal microRNA remodels the tumor microenvironment. PeerJ, 5, e4196. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4196.
Federici, C., Petrucci, F., Caimi, S., Cesolini, A., Logozzi, M., Borghi, M., D'Ilio, S., Lugini, L., Violante, N., Azzarito, T., Majorani, C., Brambilla, D., & Fais, S. (2014). Exosome release and low pH belong to a framework of resistance of human melanoma cells to cisplatin. PLoS One, 9(2), e88193. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088193.
Luciani, F., Spada, M., De Milito, A., Molinari, A., Rivoltini, L., Montinaro, A., et al. (2004). Effect of proton pump inhibitor pretreatment on resistance of solid tumors to cytotoxic drugs. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 96(22), 1702–1713. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djh305.
De Milito, A., Canese, R., Marino, M. L., Borghi, M., Iero, M., Villa, A., et al. (2010). pH-dependent antitumor activity of proton pump inhibitors against human melanoma is mediated by inhibition of tumor acidity. International Journal of Cancer, 127(1), 207–219. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25009.
Azzarito, T., Venturi, G., Cesolini, A., & Fais, S. (2015). Lansoprazole induces sensitivity to suboptimal doses of paclitaxel in human melanoma. Cancer Letters, 356(2), 697–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.017.
Federici, C., Lugini, L., Marino, M. L., Carta, F., Iessi, E., Azzarito, T., Supuran, C. T., & Fais, S. (2016). Lansoprazole and carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors sinergize against human melanoma cells. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 31(sup1), 119–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2016.1177525.
Canitano, A., Iessi, E., Spugnini, E. P., Federici, C., & Fais, S. (2016). Proton pump inhibitors induce a caspase-independent antitumor effect against human multiple myeloma. Cancer Letters, 376(2), 278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.04.015.
Logozzi, M., Angelini, D. F., Iessi, E., Mizzoni, D., Di Raimo, R., Federici, C., … Fais, S. (2017). Increased PSA expression on prostate cancer exosomes in in vitro condition and in cancer patients. Cancer Letters, 403, 318–329. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.036.
Oosthuyzen, W., Sime, N. E. L., Ivy, J. R., Turtle, E. J., Street, J. M., Pound, J., et al. (2013). Quantification of human urinary exosomes by nanoparticle tracking analysis: Nanoparticle tracking analysis and exosomes. The Journal of Physiology, 591(23), 5833–5842. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2013.264069.
Zhang, W., Peng, P., Kuang, Y., Yang, J., Cao, D., You, Y., & Shen, K. (2016). Characterization of exosomes derived from ovarian cancer cells and normal ovarian epithelial cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis. Tumour Biology: The Journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine, 37(3), 4213–4221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4105-8.
Hisey, C. L., Dorayappan, K. D. P., Cohn, D. E., Selvendiran, K., & Hansford, D. J. (2018). Microfluidic affinity separation chip for selective capture and release of label-free ovarian cancer exosomes. Lab on a Chip, 18(20), 3144–3153. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc00834e.
Ren, J., Ding, L., Zhang, D., Shi, G., Xu, Q., Shen, S., Wang, Y., Wang, T., & Hou, Y. (2018). Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics, 8(14), 3932–3948. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.25541.
Calcinotto, A., Filipazzi, P., Grioni, M., Iero, M., De Milito, A., Ricupito, A., et al. (2012). Modulation of microenvironment acidity reverses Anergy in human and murine tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes. Cancer Research, 72(11), 2746–2756. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1272.
Lugini, L., Valtieri, M., Federici, C., Cecchetti, S., Meschini, S., Condello, M., Signore, M., & Fais, S. (2016). Exosomes from human colorectal cancer induce a tumor-like behavior in colonic mesenchymal stromal cells. Oncotarget, 7(31), 50086–50098. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10574.
Li, X., Seebacher, N. A., Hornicek, F. J., Xiao, T., & Duan, Z. (2018). Application of liquid biopsy in bone and soft tissue sarcomas: Present and future. Cancer Letters, 439, 66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.012.
Miki, Y., Yashiro, M., Okuno, T., Kuroda, K., Togano, S., Hirakawa, K., & Ohira, M. (2018). Clinico-pathological significance of exosome marker CD63 expression on cancer cells and stromal cells in gastric cancer. PLoS One, 13(9), e0202956. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202956.
Kobayashi, M., Sawada, K., Nakamura, K., Yoshimura, A., Miyamoto, M., Shimizu, A., Ishida, K., Nakatsuka, E., Kodama, M., Hashimoto, K., Mabuchi, S., & Kimura, T. (2018). Exosomal miR-1290 is a potential biomarker of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma and can discriminate patients from those with malignancies of other histological types. Journal of Ovarian Research, 11(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-018-0458-0.
Zheng, H., Zhan, Y., Liu, S., Lu, J., Luo, J., Feng, J., & Fan, S. (2018). The roles of tumor-derived exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical implications. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research: CR, 37(1), 226. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0901-5.
Hu, C., Chen, M., Jiang, R., Guo, Y., Wu, M., & Zhang, X. (2018). Exosome-related tumor microenvironment. Journal of Cancer, 9(17), 3084–3092. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.26422.
Wang, J., Zhang, H., Zhou, X., Wang, T., Zhang, J., Zhu, W., Zhu, H., & Cheng, W. (2018). Five serum-based miRNAs were identified as potential diagnostic biomarkers in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biomarkers: Section A of Disease Markers, 23(2), 193–203. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-181258.
Barbagallo, C., Brex, D., Caponnetto, A., Cirnigliaro, M., Scalia, M., Magnano, A., Caltabiano, R., Barbagallo, D., Biondi, A., Cappellani, A., Basile, F., di Pietro, C., Purrello, M., & Ragusa, M. (2018). LncRNA UCA1, upregulated in CRC biopsies and downregulated in serum exosomes, controls mRNA expression by RNA-RNA interactions. Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids, 12, 229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.009.
Xiao, Y., Li, Y., Yuan, Y., Liu, B., Pan, S., Liu, Q., et al. (2018). The potential of exosomes derived from colorectal cancer as a biomarker. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry, 490, 186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.09.007.
Shao, Y., Chen, T., Zheng, X., Yang, S., Xu, K., Chen, X., Xu, F., Wang, L., Shen, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, M., Hu, W., Ye, C., Yu, X. F., Shao, J., & Zheng, S. (2018). Colorectal Cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles establish an inflammatory pre-metastatic niche in liver metastasis. Carcinogenesis, 39, 1368–1379. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgy115.
Xu, Z.-H., Miao, Z.-W., Jiang, Q.-Z., Gan, D.-X., Wei, X.-G., Xue, X.-Z., et al. (2018). Brain microvascular endothelial cell exosome-mediated S100A16 up-regulation confers small-cell lung cancer cell survival in brain. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 5, fj201800428R. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800428R.
Liu, B., & Pilarsky, C. (2018). Analysis of DNA Hypermethylation in pancreatic Cancer using methylation-specific PCR and bisulfite sequencing. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1856, 269–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8751-1_16.
Peng, Z.-Y., Gu, R.-H., & Yan, B. (2018). Downregulation of exosome-encapsulated miR-548c-5p is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120, 1457–1463. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27291.
Jiao, Y.-J., Jin, D.-D., Jiang, F., Liu, J.-X., Qu, L.-S., Ni, W.-K., et al. (2018). Characterization and proteomic profiling of pancreatic cancer-derived serum exosomes. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120, 988–999. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27465.
Logozzi, M., De Milito, A., Lugini, L., Borghi, M., Calabrò, L., Spada, M., … Fais, S. (2009). High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS One, 4(4), e5219. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005219.
Ni, Q., Stevic, I., Pan, C., Müller, V., Oliviera-Ferrer, L., Pantel, K., & Schwarzenbach, H. (2018). Different signatures of miR-16, miR-30b and miR-93 in exosomes from breast cancer and DCIS patients. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 12974. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31108-y.
Boussadia, Z., Lamberti, J., Mattei, F., Pizzi, E., Puglisi, R., Zanetti, C., Pasquini, L., Fratini, F., Fantozzi, L., Felicetti, F., Fecchi, K., Raggi, C., Sanchez, M., D’Atri, S., Carè, A., Sargiacomo, M., & Parolini, I. (2018). Acidic microenvironment plays a key role in human melanoma progression through a sustained exosome mediated transfer of clinically relevant metastatic molecules. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 37(1), 245. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0915-z.
Ban, J.-J., Lee, M., Im, W., & Kim, M. (2015). Low pH increases the yield of exosome isolation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 461(1), 76–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.03.172.
King, H. W., Michael, M. Z., & Gleadle, J. M. (2012). Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer, 12, 421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-421.
Ridge, S. M., Sullivan, F. J., & Glynn, S. A. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cells: Key players in cancer progression. Molecular Cancer, 16(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0597-8.
Andreola, G., Rivoltini, L., Castelli, C., Huber, V., Perego, P., Deho, P., Squarcina, P., Accornero, P., Lozupone, F., Lugini, L., Stringaro, A., Molinari, A., Arancia, G., Gentile, M., Parmiani, G., & Fais, S. (2002). Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 195(10), 1303–1316.
Huber, V., Fais, S., Iero, M., Lugini, L., Canese, P., Squarcina, P., Zaccheddu, A., Colone, M., Arancia, G., Gentile, M., Seregni, E., Valenti, R., Ballabio, G., Belli, F., Leo, E., Parmiani, G., & Rivoltini, L. (2005). Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: Role in immune escape. Gastroenterology, 128(7), 1796–1804.
Iero, M., Valenti, R., Huber, V., Filipazzi, P., Parmiani, G., Fais, S., & Rivoltini, L. (2008). Tumour-released exosomes and their implications in cancer immunity. Cell Death and Differentiation, 15(1), 80–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402237.
Namee, N. M., & O’Driscoll, L. (2018). Extracellular vesicles and anti-cancer drug resistance. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer, 1870(2), 123–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.07.003.
Gurusamy, D., Clever, D., Eil, R., & Restifo, N. P. (2017). Novel “elements” of immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunology Research, 5(6), 426–433. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0117.
Fais, S., O’Driscoll, L., Borras, F. E., Buzas, E., Camussi, G., Cappello, F., Carvalho, J., Cordeiro da Silva, A., del Portillo, H., el Andaloussi, S., Ficko Trček, T., Furlan, R., Hendrix, A., Gursel, I., Kralj-Iglic, V., Kaeffer, B., Kosanovic, M., Lekka, M. E., Lipps, G., Logozzi, M., Marcilla, A., Sammar, M., Llorente, A., Nazarenko, I., Oliveira, C., Pocsfalvi, G., Rajendran, L., Raposo, G., Rohde, E., Siljander, P., van Niel, G., Vasconcelos, M. H., Yáñez-Mó, M., Yliperttula, M. L., Zarovni, N., Zavec, A. B., & Giebel, B. (2016). Evidence-based clinical use of nanoscale extracellular vesicles in nanomedicine. ACS Nano, 10(4), 3886–3899. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b08015.
Letelier, P., Riquelme, I., Hernández, A., Guzmán, N., Farías, J., & Roa, J. (2016). Circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers in biliary tract cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050791.
Yokoyama, S., Takeuchi, A., Yamaguchi, S., Mitani, Y., Watanabe, T., Matsuda, K., Hotta, T., Shively, J. E., & Yamaue, H. (2017). Clinical implications of carcinoembryonic antigen distribution in serum exosomal fraction-measurement by ELISA. PLoS One, 12(8), e0183337. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183337.
Kharaziha, P., Ceder, S., Li, Q., & Panaretakis, T. (2012). Tumor cell-derived exosomes: A message in a bottle. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1826(1), 103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.03.006.
Logozzi, M., Capasso, C., Di Raimo, R., Del Prete, S., Mizzoni, D., Falchi, M., & Fais, S. (2018). Prostate cancer cells and exosomes in acidic condition show increased carbonic anhydrase IX expression and activity. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, in press, 34, 272–278. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2018.1538980.
Cappello, F., Logozzi, M., Campanella, C., Bavisotto, C. C., Marcilla, A., Properzi, F., & Fais, S. (2017). Exosome levels in human body fluids: A tumor marker by themselves? European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 96, 93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2016.09.010.
Properzi, F., Logozzi, M., & Fais, S. (2013). Exosomes: The future of biomarkers in medicine. Biomarkers in Medicine, 7(5), 769–778. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm.13.63.
Properzi, F., Logozzi, M., Abdel-Haq, H., Federici, C., Lugini, L., Azzarito, T., et al. (2015). Detection of exosomal prions in blood by immunochemistry techniques. The Journal of General Virology, 96(Pt 7), 1969–1974. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.000117.
Azzarito, T., Lugini, L., Spugnini, E. P., Canese, R., Gugliotta, A., Fidanza, S., & Fais, S. (2016). Effect of modified alkaline supplementation on Syngenic melanoma growth in CB57/BL mice. PLoS One, 11(7), e0159763. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159763.
Spugnini, E. P., Buglioni, S., Carocci, F., Francesco, M., Vincenzi, B., Fanciulli, M., & Fais, S. (2014). High dose lansoprazole combined with metronomic chemotherapy: A phase I/II study in companion animals with spontaneously occurring tumors. Journal of Translational Medicine, 12, 225. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-014-0225-y.
Iessi, E., Logozzi, M., Lugini, L., Azzarito, T., Federici, C., Spugnini, E. P., Mizzoni, D., di Raimo, R., Angelini, D. F., Battistini, L., Cecchetti, S., & Fais, S. (2017). Acridine Orange/exosomes increase the delivery and the effectiveness of Acridine Orange in human melanoma cells: A new prototype for theranostics of tumors. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 32(1), 648–657. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2017.1292263.
Funding
This work was supported by Regione Lazio FILAS (grant number RU 2014-2041 FascJ9L).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logozzi, M., Spugnini, E., Mizzoni, D. et al. Extracellular acidity and increased exosome release as key phenotypes of malignant tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev 38, 93–101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-019-09783-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-019-09783-8